分子别名(Synonym)
CD33 antigen-like 3,SIGLEC-15,CD33L3,sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 15,Siglec15,Siglec-15
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human Siglec-15, His Tag (SG5-H52H3) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Phe 20 - Thr 263 (Accession # Q6ZMC9-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Phe 20
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 28.4 kDa. The protein migrates as 33-40 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 25 mM MES, 150 mM NaCl, pH7.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 24 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 12 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
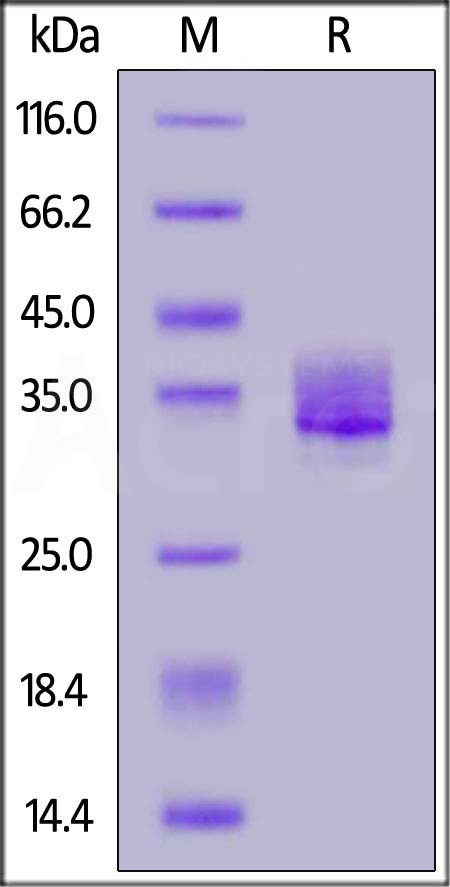
Human Siglec-15, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90%.
SEC-MALS
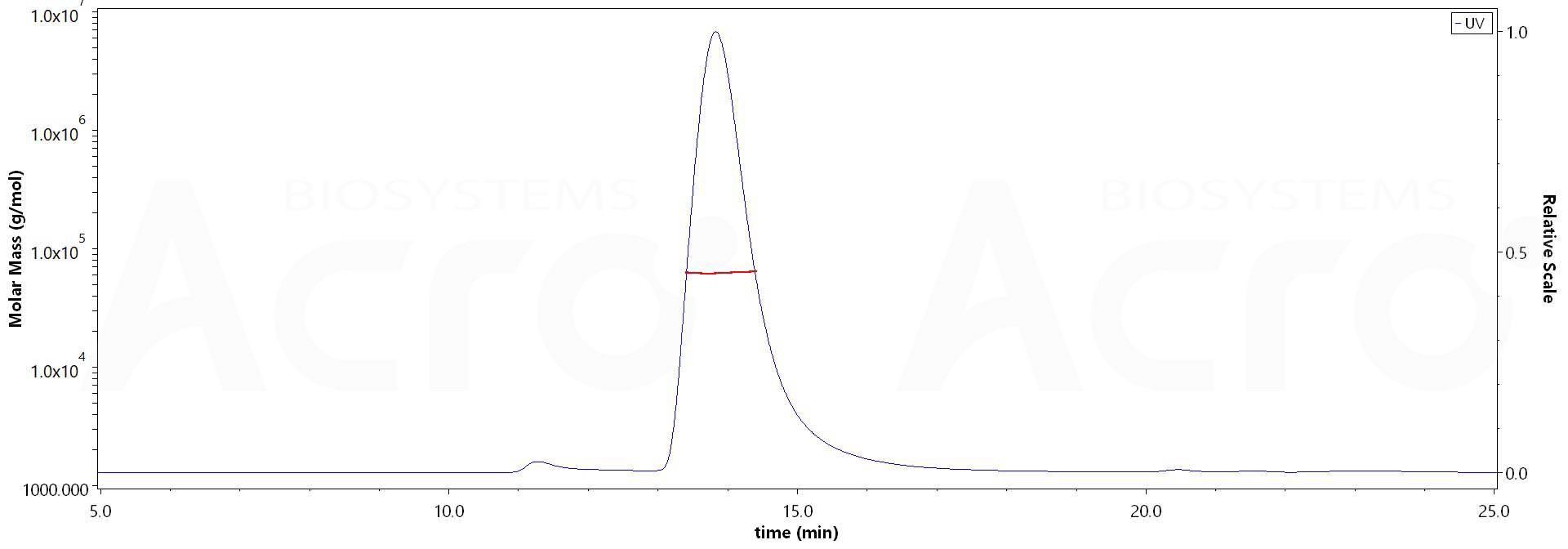
The purity of Human Siglec-15, His Tag (Cat. No. SG5-H52H3) is more than 85% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 60-70 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
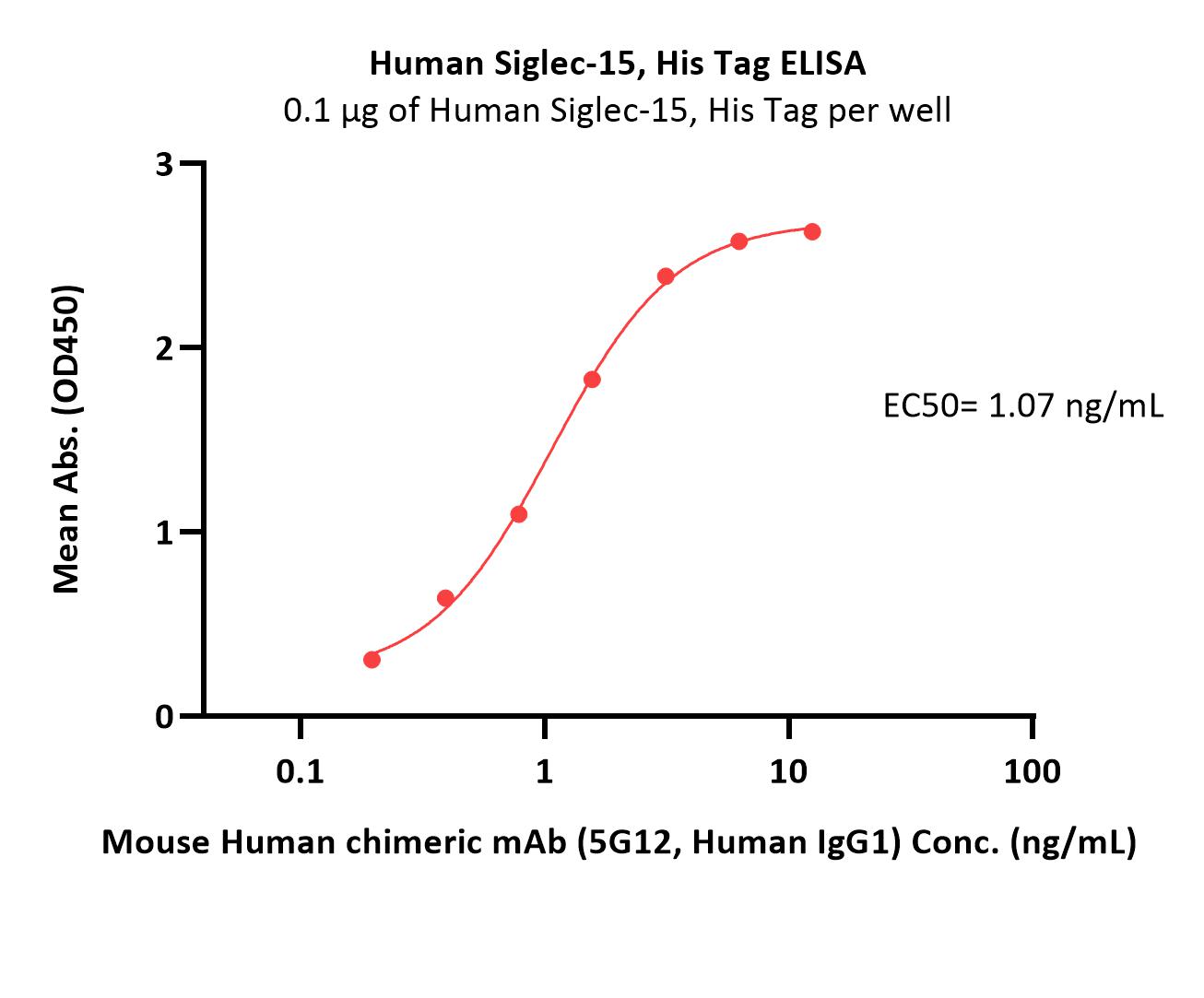
Immobilized Human Siglec-15, His Tag (Cat. No. SG5-H52H3) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse Human chimeric mAb (5G12, Human IgG1) with a linear range of 0.2-2 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
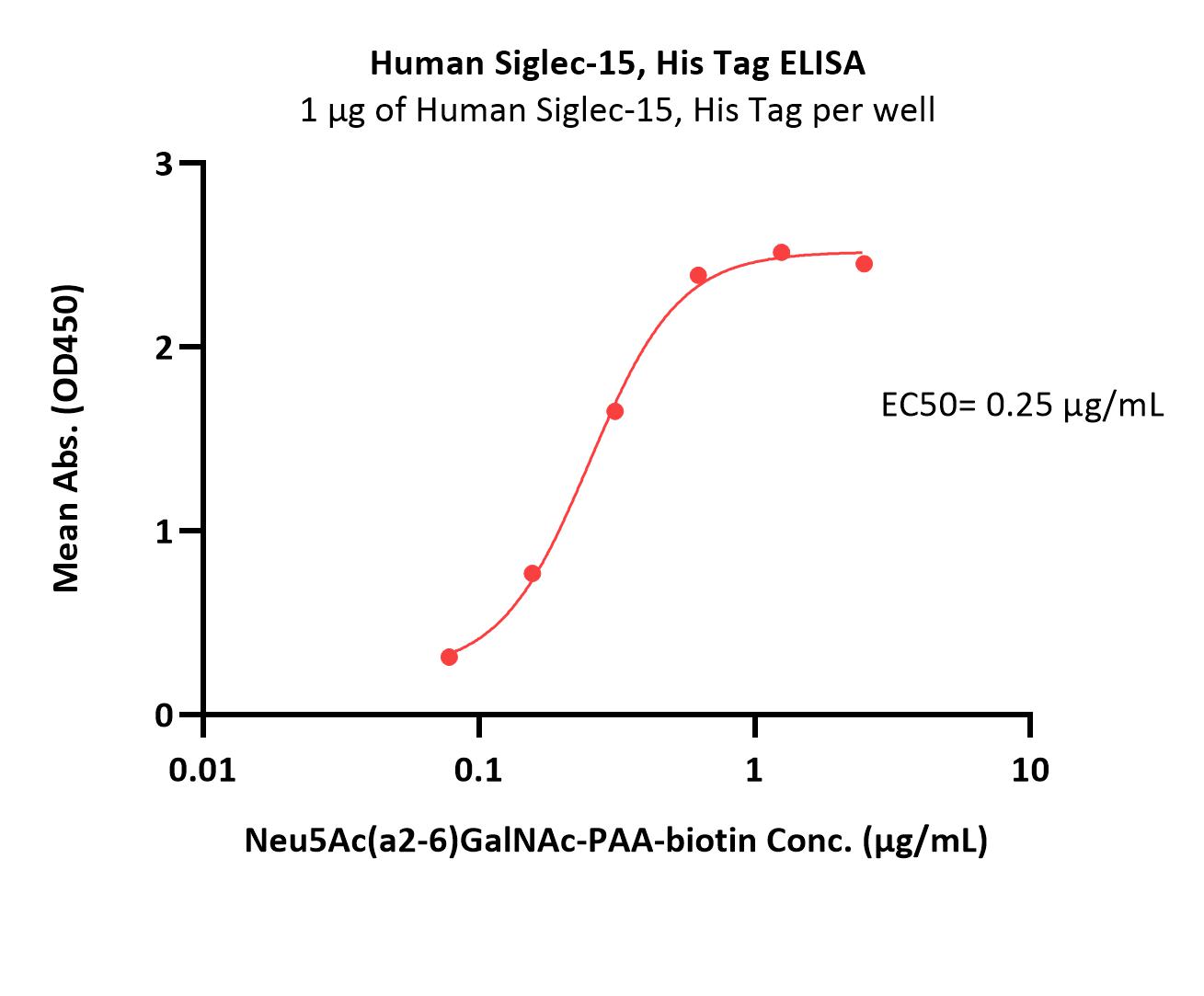
Immobilized Human Siglec-15, His Tag (Cat. No. SG5-H52H3) at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Neu5Ac(a2-6)GalNAc-PAA-biotin with a linear range of 0.078-0.313 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论
- 176XXXXXXX7
- ACRO的IL-2系列的蛋白用了好几种tagd~每种标签都很奈斯,结合活性结果重现性很好,官方的PROTOCOL条件很精准~基本重现没有太多误差。好评
- 2023-2-22

- 153XXXXXXX3
- 我们用此蛋白用于小鼠体内动物实验,探讨重组IL2在小鼠体内实验的最大耐受剂量以及有效性,作为一个对标分子,数据持续更新中,并且结果满足期待,Acro蛋白质量很高,值得信赖,推荐。
- 2023-7-6
背景(Background)
Siglec-15 is a DAP12-associated immunoreceptor, which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and SIGLEC (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin) family. Siglecs are cell surface proteins that bind sialic acid. They are found primarily on the surface of immune cells and are a subset of the I-type lectins. Siglec-15 consisting of immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic tail. Siglec-15 is that recognizes sialylated glycans and regulates osteoclast differentiation. Siglec-15 is a potential therapeutic target for osteoporosis and plays a conserved regulatory role in the immune system of vertebrates.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining


















