分子别名(Synonym)
CEDLAP,TGF-beta 1,TGFB1,DPD1,TGF-beta-1,TGFB
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human TGF-Beta 1 Protein, Tag Free (TG1-H4212) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Ala 279 - Ser 390 (Accession # P01137-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Ala 279
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries no "tag".
The protein has a calculated MW of 12.8 kDa (monomer). The protein migrates as 14 kDa (monomer) under reducing (R) condition, and 25 kDa (Dimer) when calibrated against Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker under non-reducing (NR) condition (SDS-PAGE).
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 0.1 EU per μg by the LAL method.
宿主蛋白残留(Host Cell Protein)
<0.5 ng/µg of protein tested by ELISA.
宿主核酸残留(Host Cell DNA)
<0.02 ng/μg of protein tested by qPCR.
无菌(Sterility)
Negative
支原体(Mycoplasma)
Negative.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 0.085% TFA in 30% ACN with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 12 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
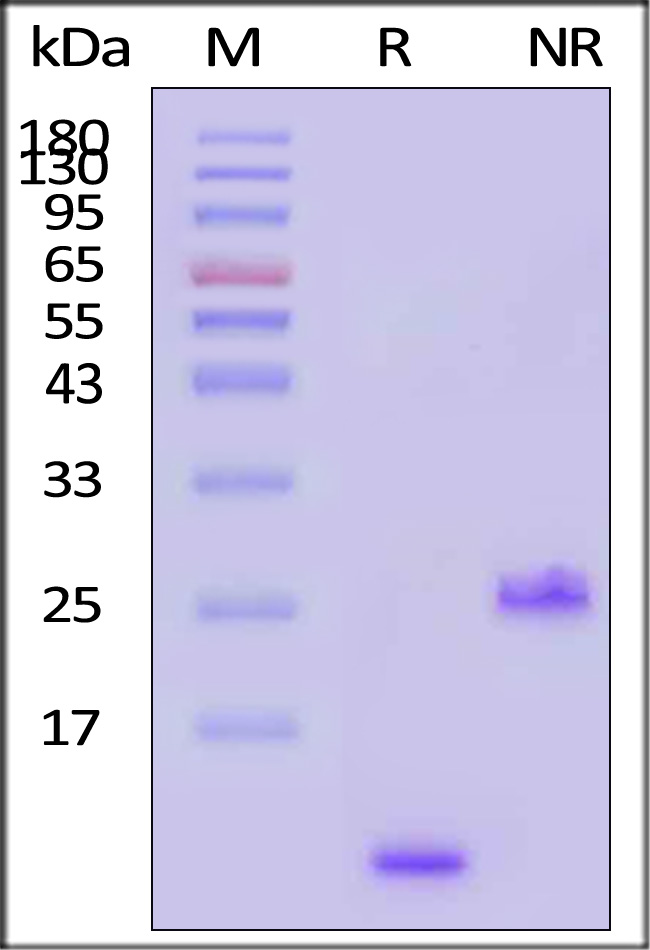
Human TGF-Beta 1 Protein, Tag Free on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95% (With Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker).
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
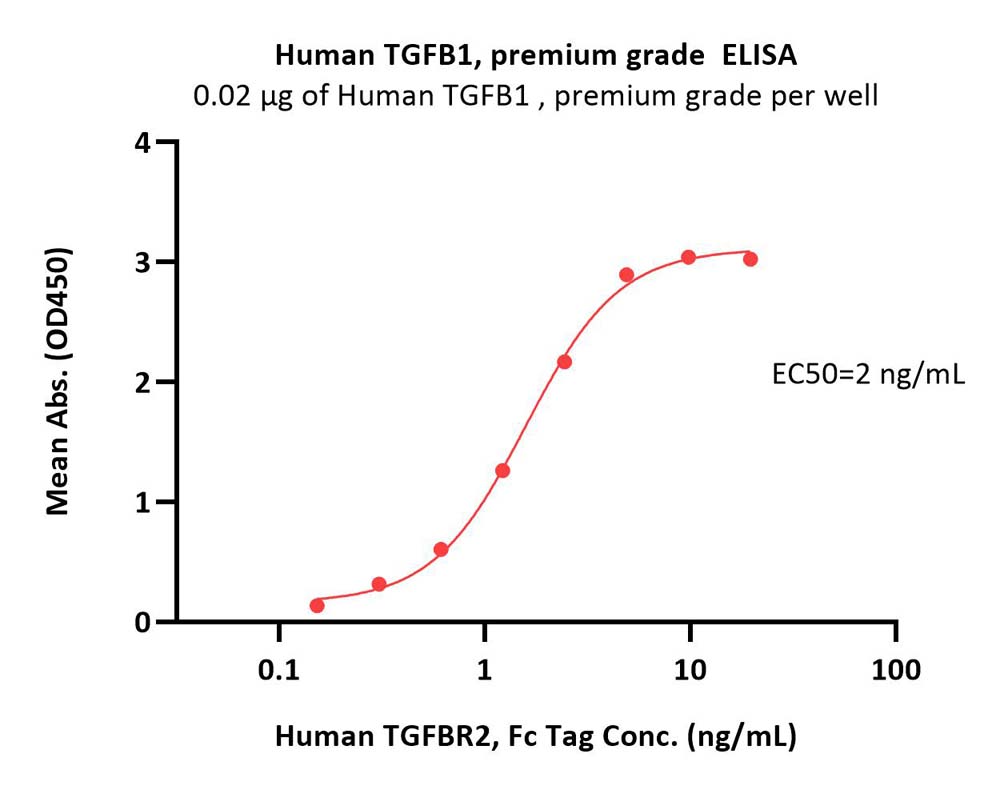
Immobilized Human TGF-Beta 1 Protein, Tag Free (Cat. No. TG1-H4212) at 0.2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human TGFBR2, Fc Tag (Cat. No. TG2-H5252) with a linear range of 0.2-2.5 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-SPR
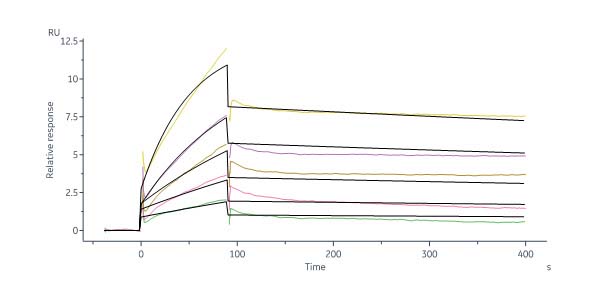
Human TGF-Beta 1 Protein, Tag Free (Cat. No. TG1-H4212) immobilized on CM5 Chip can bind Human TGF-beta RI Protein, Fc Tag (Cat. No. TG1-H5254) with an affinity constant of 99.2 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-CELL BASE
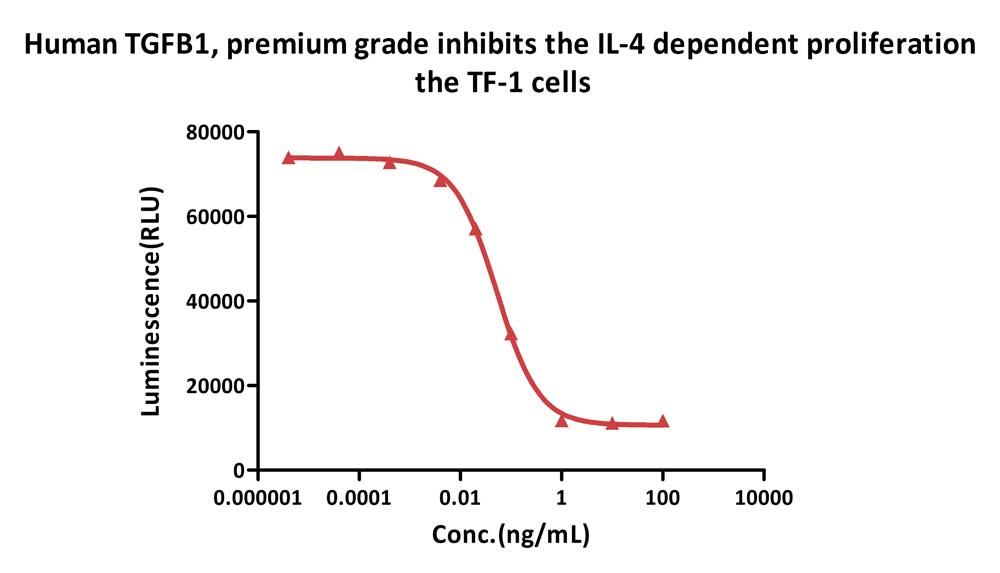
Human TGF-Beta 1 Protein, Tag Free (Cat. No. TG1-H4212) inhibits the Human IL-4, premium grade (Cat. No. IL4-H4218) dependent proliferation the TF-1 cells. The specific activity of Human TGF-Beta 1 Protein, Tag Free is > 8.00ⅹ10^6 IU/mg, which is calibrated against transforming growth factor β1 (NIBSC code: 89/514) (QC tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论背景(Background)
Transforming growth factor beta 1 ( TGFB1) is also known as TGF-β1, CED, DPD1, TGFB. is a polypeptide member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily of cytokines. It is a secreted protein that performs many cellular functions, including the control of cell growth, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and apoptosis. The TGFB1 protein helps control the growth and division (proliferation) of cells, the process by which cells mature to carry out specific functions (differentiation), cell movement (motility), and the self-destruction of cells (apoptosis). The TGFB1 protein is found throughout the body and plays a role in development before birth, the formation of blood vessels, the regulation of muscle tissue and body fat development, wound healing, and immune system function. TGFB1 is particularly abundant in tissues that make up the skeleton, where it helps regulate bone growth, and in the intricate lattice that forms in the spaces between cells (the extracellular matrix). Within cells, this protein is turned off (inactive) until it receives a chemical signal to become active. TGFB1 plays an important role in controlling the immune system, and shows different activities on different types of cell, or cells at different developmental stages. Most immune cells (or leukocytes) secrete TGFB1. TGFB1 has been shown to interact with TGF beta receptor 1, LTBP1, YWHAE, EIF3I and Decorin.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining














