分子别名(Synonym)
CD47,MER6,IAP,OA3
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag (CD7-C52H1) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Gln 19 - Glu 141 (Accession # F7A802-1). In the region Gln 19 - Glu 141, the AA sequence of Cynomolgus and Rhesus macaque CD47 are homologus.
Predicted N-terminus: Gln 19
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 15.8 kDa. The protein migrates as 30-50 kDa when calibrated against Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)

Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95% (With Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker).
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
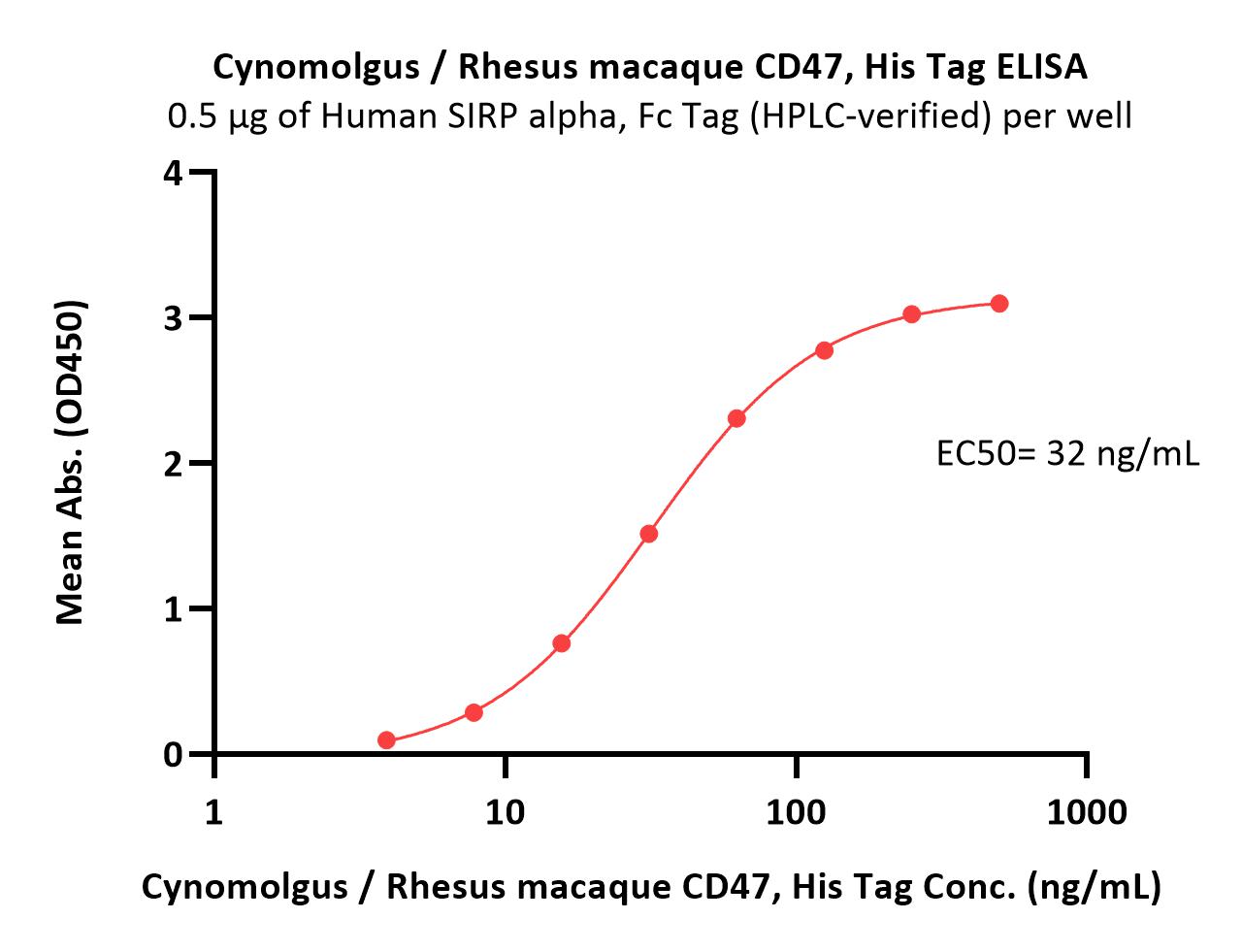
Immobilized Human SIRP alpha, Fc Tag (HPLC-verified) (Cat. No. SIA-H5251) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag (Cat. No. CD7-C52H1) with a linear range of 4-63 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
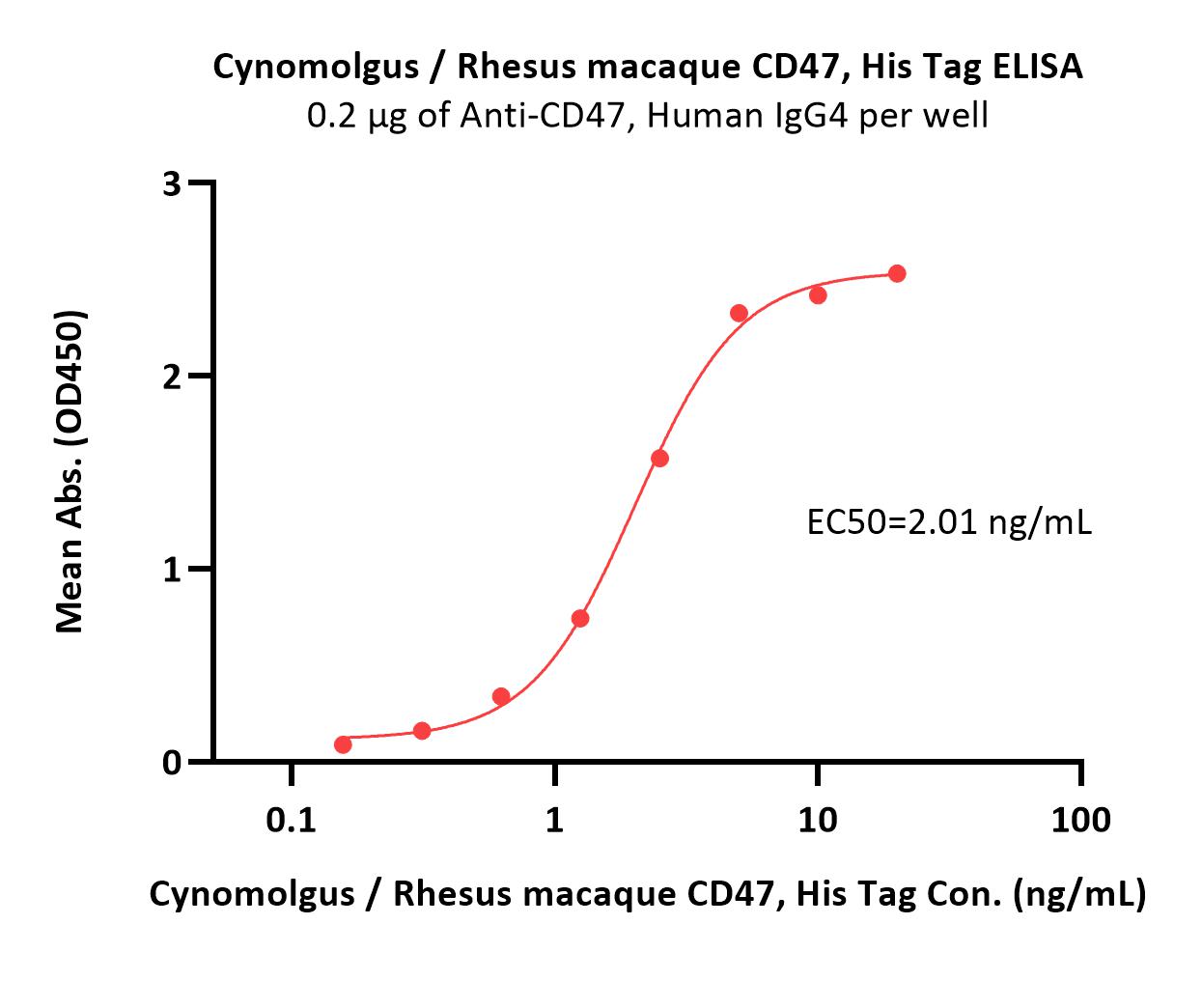
Immobilized Anti-CD47, Human IgG4 at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag (Cat. No. CD7-C52H1) with a linear range of 0.2-5 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-SPR
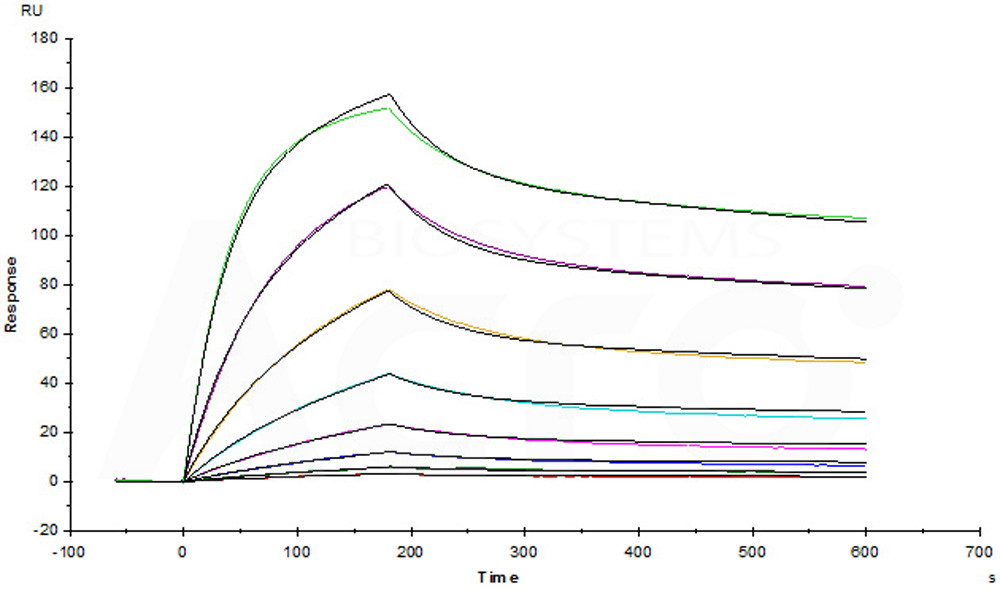
Anti-CD47 Mab (Human IgG4) captured on CM5 chip via anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface, can bind Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag (Cat. No. CD7-C52H1) with an affinity constant of 1.8 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore T200) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-BLI
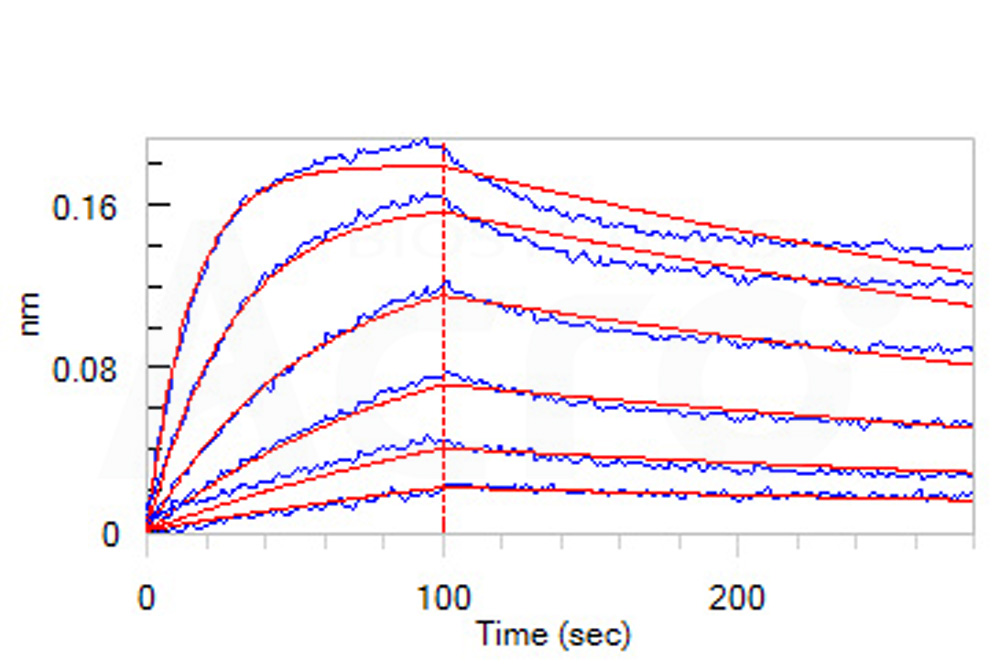
Loaded Anti-Human CD47 MAb (Human IgG4) on AHC Biosensor, can bind Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag (Cat. No. CD7-C52H1) with an affinity constant of 2.93 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论
- 136XXXXXXX0
- 购买该蛋白用于免疫原对小鼠进行免疫,及抗体筛选用。该蛋白活性好,性质稳定,免疫小鼠得到较高的效价,用于抗体结合检测,也得到稳定可靠的结果。多次购买,批间差小,性质稳定。
 >
>- 2023-3-15

- 188XXXXXXX5
- 采购该靶点猴蛋白Cynomolgus / Rhesus macaque CD47, His Tag (CD7-C52H1)是用于杂交瘤抗体药物早期筛选与最终分子的人猴交叉反应验证,目前获得的人猴交叉抗体药物分子已经走到PCC阶段。我这边95%的蛋白是在ACRO采购的,以后也是~
- 2021-7-24
背景(Background)
Leukocyte surface antigen CD47 is also known as Antigenic surface determinant protein OA3, Integrin-associated protein (IAP) and Protein MER6. CD47 contains 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. CD47 is very broadly distributed on normal adult tissues. CD47 has a role in both cell adhesion by acting as an adhesion receptor for THBS1 on platelets, and in the modulation of integrins and plays an important role in memory formation and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus by similarity. CD47 is the receptor for SIRPA, binding to which prevents maturation of immature dendritic cells and inhibits cytokine production by mature dendritic cells. CD47 Interaction with SIRPG mediates cell-cell adhesion, enhances superantigen-dependent T-cell-mediated proliferation and costimulates T-cell activation.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining

















