分子别名(Synonym)
CD22,SIGLEC2,BL-CAM,SIGLEC-2,Siglec2,SIGLEC2FLJ22814
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
FITC-Labeled Human Siglec-2, His Tag (Cat. No. SI2-HF2H6) is expressed from human HEK293 cells. It contains AA Asp 20 - Arg 687 (Accession # P20273-1). It is the FITC labeled form of Human Siglec-2, His Tag (Cat. No. CD2-H52H8).
Predicted N-terminus: Asp 20
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 77.0 kDa. The protein migrates as 100-120 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
偶联(Conjugate)
FITC
Excitation source: 488 nm spectral line, argon-ion laser
Excitation Wavelength: 488 nm
Emission Wavelength: 535 nm
标记(Labeling)
The primary amines in the side chains of lysine residues and the N-terminus of the protein are conjugated with FITC using standard chemical labeling method. The residual FITC is removed by molecular sieve treatment during purification process.
蛋白标记度(Protein Ratio)
The FITC to protein molar ratio is 3-5.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please protect from light and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)

FITC-Labeled Human Siglec-2, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
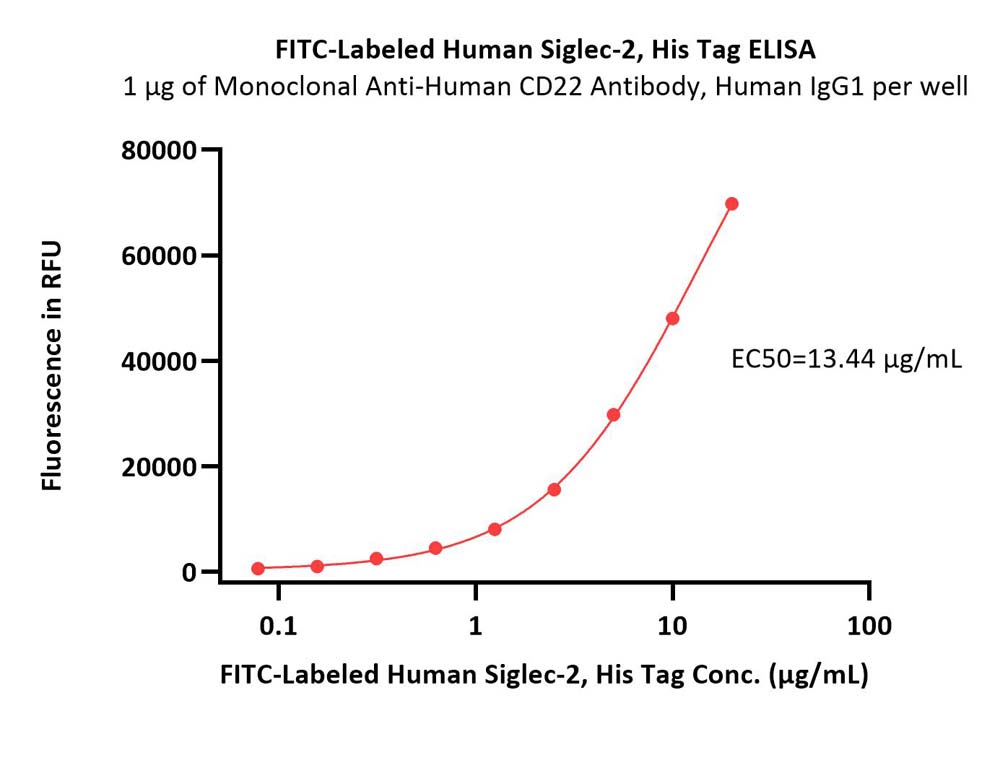
Immobilized Monoclonal Anti-Human CD22 Antibody, Human IgG1 at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind FITC-Labeled Human Siglec-2, His Tag (Cat. No. SI2-HF2H6) with a linear range of 0.078-20 μg/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
CAR阳性表达率检测(Evaluation of CAR expression)
FACS Analysis of Anti-CD22 CAR Expression
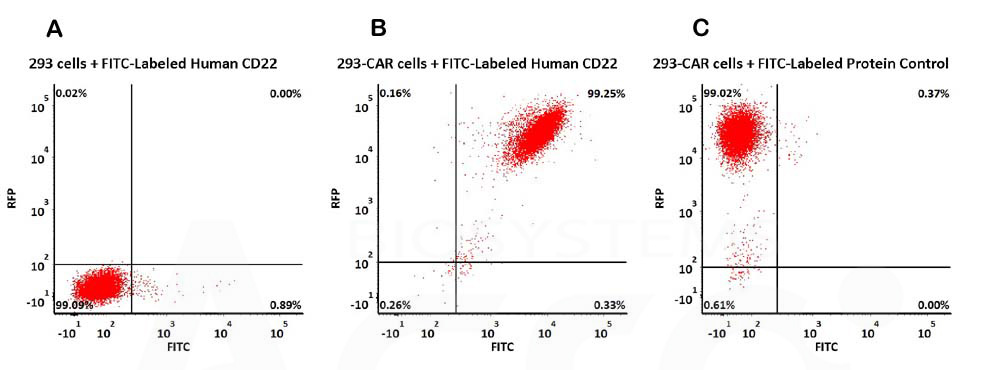
293 cells were transfected with anti-CD22-scFv and RFP tag. 2e5 of the cells were stained with B. FITC-Labeled Human Siglec-2, His Tag (Cat. No. SI2-HF2H6, 10 µg/mL) and C. FITC-labeled Protein Control. A. Non-transfected 293 cells and C. FITC-labeled Protein Control were used as negative control. RFP was used to evaluate CAR (anti-CD22-scFv) expression and FITC was used to evaluate the binding activity of FITC-Labeled Human Siglec-2, His Tag (Cat. No. SI2-HF2H6) (QC tested).
背景(Background)
B-cell receptor CD22 is also known as Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 2 (Siglec-2), B-lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule (BL-CAM), T-cell surface antigen Leu-14, which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and SIGLEC (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin) family. CD22 mediates B-cell B-cell interactions, and may be involved in the localization of B-cells in lymphoid tissues. Siglec-2 / CD22 binds sialylated glycoproteins, one of which is CD45. Siglec2 / CD22 plays a role in positive regulation through interaction with Src family tyrosine kinases and may also act as an inhibitory receptor by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatases via their SH2 domains that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















