Comparative real-world effectiveness of ustekinumab versus anti-TNF in Crohn's disease: 12-month maintenance phase results from the prospective, observational RUN-CD study using propensity score adjustmentBokemeyer, Plachta-Danielzik, Gilman
et alJ Crohns Colitis (2025)
Abstract: The prospective RUN-CD registry investigates the effectiveness of ustekinumab (UST) and other biologics in Crohn's disease (CD) across Germany. Based on data from the registry, this study presents the maintenance phase results of a 12-month real-world-evidence (RWE) comparison of CD patients initiating new biologic therapies with UST or anti-TNF.After excluding patients using biologics other than UST and anti-TNF and those with missing outcomes, the final sample consisted of 618 CD patients. Clinical remission (CR), defined as a Harvey-Bradshaw Index (HBI) ≤4, was the prespecified endpoint at 12 months. Switching to another biologic therapy was considered an outcome failure. Propensity score (PS) adjustment was used to reduce the effect of confounders.The study included 343 CD patients treated with UST and 264 treated with anti-TNF. Over 12 months, the frequency of therapy switches was significantly higher for infliximab (28%) compared to UST (17%) and adalimumab (17%) (p=0.045). There was no significant difference in CR rates at 12 months between the UST and anti-TNF groups (65.8% vs. 60.0%, p=0.262). However, in week-16 responders, CR rates at 12 months were significantly higher with UST (77.6%) versus anti-TNF (65.4%) (p=0.041). The change in EQ-VAS (QoL) scores between UST and anti-TNF showed a 5.1-point difference favouring UST (p=0.002).In this 12-month RWE comparison, overall CR rates were similar between UST and anti-TNF. However, among week-16 responders, CR rates were significantly higher with UST. Additionally, UST was associated with a significantly greater improvement in QoL compared to anti-TNF.© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Efficacy of High Dose Adalimumab for the Management of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic ReviewJones, Sun, Kennedy
Australas J Dermatol (2025)
Abstract: Adalimumab, a tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in managing hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) at the standard dose of 40 mg weekly; however, many patients do not achieve adequate clinical response with this regimen. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of 80 mg weekly adalimumab in HS management. Four studies, with a total of 67 patients, were reviewed. The studies reported improvements in HS disease severity and quality of life measures with the use of high-dose adalimumab. Adverse events were infrequent and generally mild, with no severe adverse events reported. The findings suggest a favourable response to high-dose adalimumab for patients with severe or refractory HS; however, definitive conclusions are limited by the scarcity and low quality of the available data. Further high-quality research with standardised outcome measures and longer follow-up are needed to validate the role of dose intensification in HS management.© 2025 Australasian College of Dermatologists.
Coexistence of Relapsing Polychondritis, Crohn's Disease, and Pyoderma Gangrenosum Treated Successfully with Adalimumab: A Case Report and Literature ReviewYamazaki, Tominaga, Watanabe
et alIntern Med (2025)
Abstract: Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is a rare, progressive, immune-mediated systemic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology characterized by recurrent inflammation of cartilaginous structures. Approximately 30% of RP cases are associated with autoimmune disease. However, co-occurrence of RP and Crohn's disease (CD) has rarely been reported. We herein report a case of coexisting RP, CD, and pyoderma gangrenosum that was successfully treated with adalimumab in combination with methotrexate. We believe that this case and literature review will facilitate the accurate and prompt diagnosis and treatment of RP combined with CD and various other complications.
Pharmacovigilance study and genetic target prediction analysis of FDA adverse event reports (FAERS) for drug-induced sinusitisWang, Sun, Zhao
et alExpert Opin Drug Saf (2025)
Abstract: Drug-induced sinusitis has been widely reported as an adverse drug reaction in recent years, yet the pharmacogenetic mechanisms and risk factors associated with sinusitis remain elusive.We aimed to identify the major drugs reported in the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) in relation to sinusitis and to analyze their pharmacogenetic mechanisms through drug target analysis.We conducted a review of the publicly available FAERS database from 2004 to the third quarter of 2023. We extracted genetic tools corresponding to each drug, utilized colocalization analysis, Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis, and cross-tissue drug target analysis to predict the impact of drug targets on sinusitis.Following the validation of drug-related risks, a total of 13 medications were ultimately identified, including TNF inhibitors: pomalidomide (ROR: 14.77), certolizumab pegol(ROR: 8.21), etanercept (ROR: 7.961), lenalidomide (ROR: 6.998), adalimumab (ROR: 6.677), infliximab (ROR: 3.939); C4B-targeted drugs: human immunoglobulin G (ROR:3.846) and other risk drugs were commonly reported. Co-localization analysis and MR analysis suggests associations between TNF, C4B, and LTA and sinusitis.We demonstrated the risk of sinusitis associated with 13 drugs, including pomalidomide, and the impact of TNF and C4B drugs on sinusitis, which provides guidance for the use of related drugs and the prevention of sinusitis.

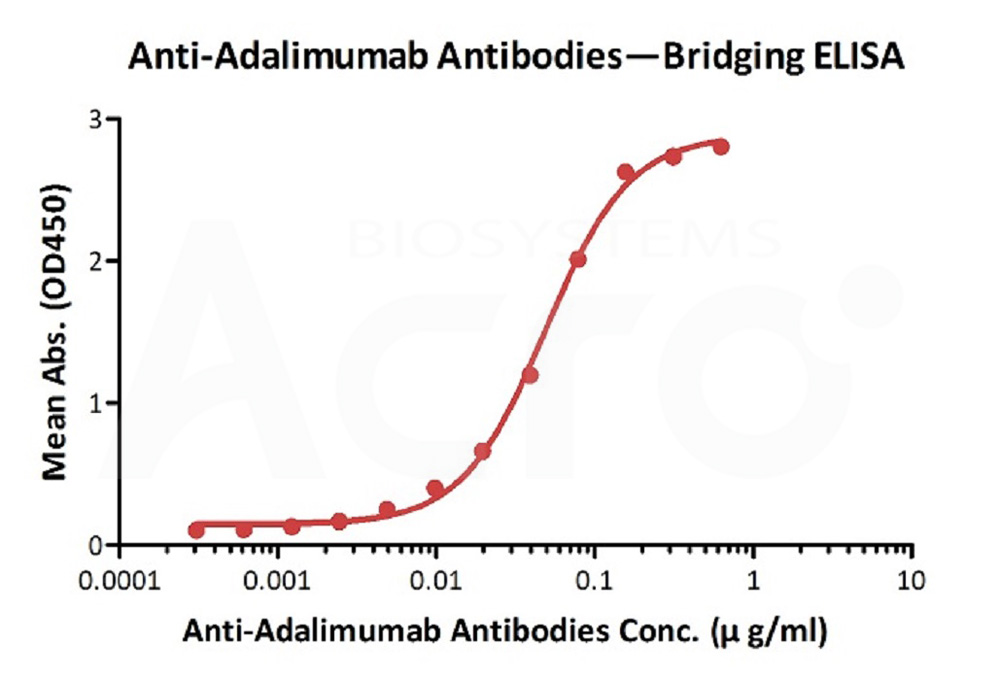
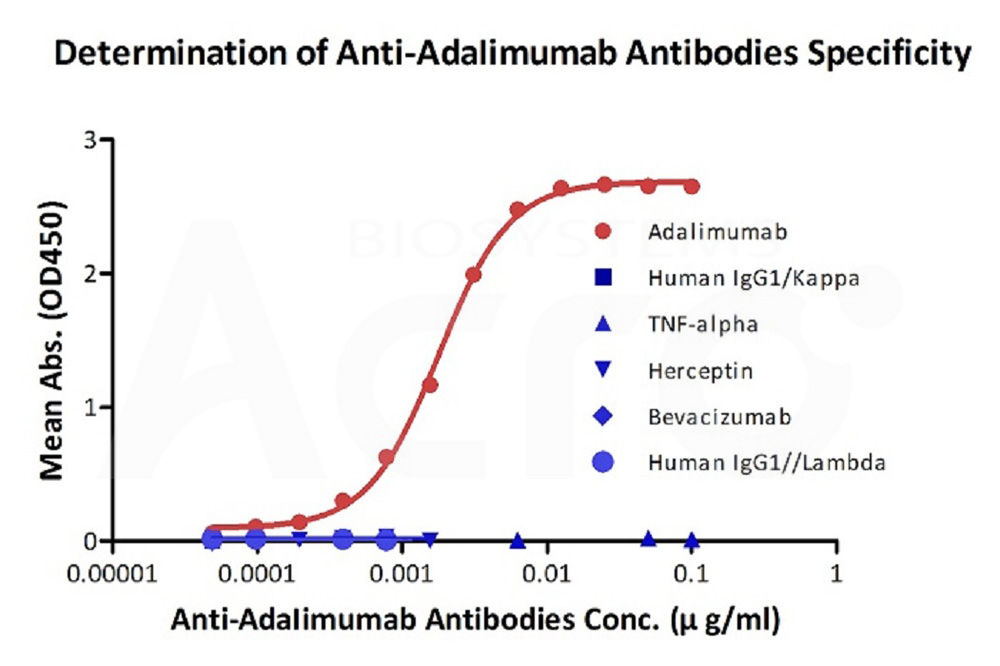
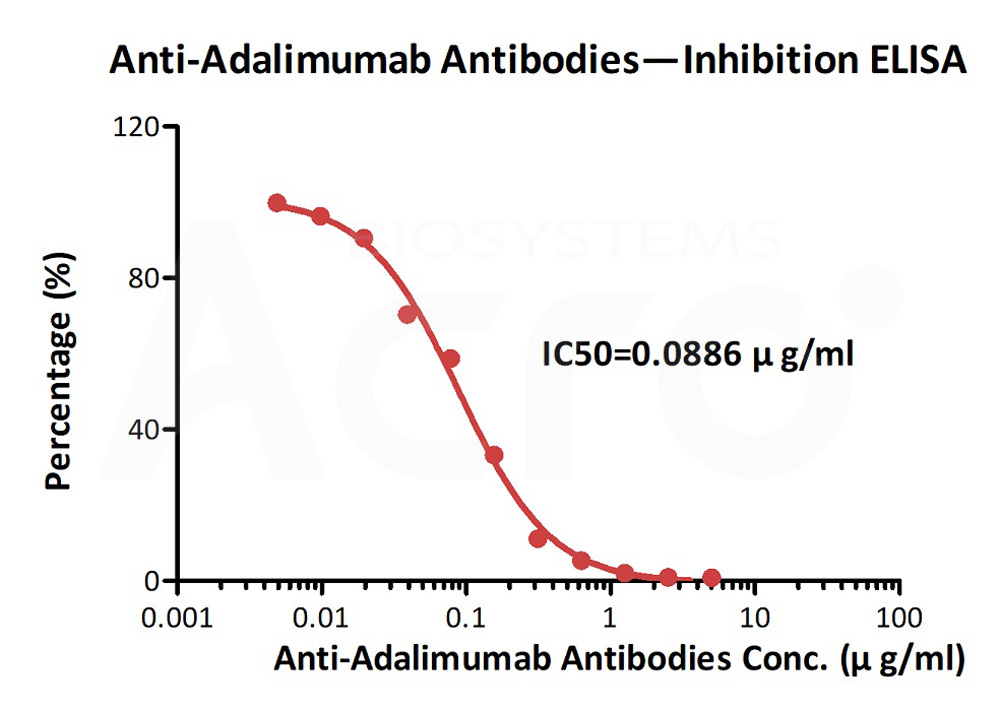
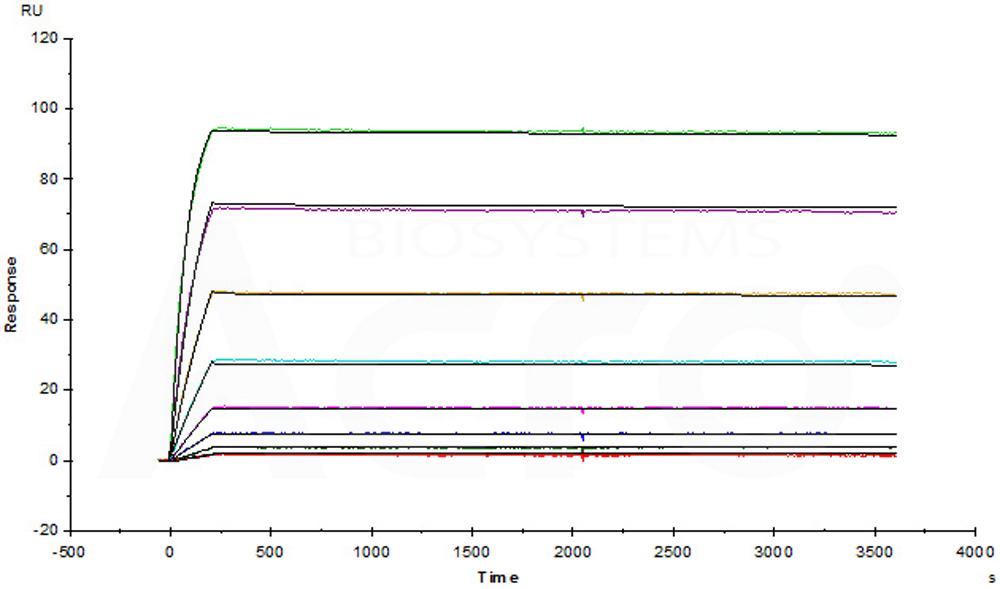























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















