Siglec-targeted liposomes to identify sialoglycans present on fungal pathogensAmbati, Choudhury, Peter
et alAntimicrob Agents Chemother (2025)
Abstract: The sialic acid Ig-like lectins Siglec-3 and Siglec-15 are pathogen receptors that bind sialic acid-modified glycoproteins, best characterized in metastatic cancers. Because fungi produce sialoglycans and sialo-glycoproteins, we wondered if Siglecs had the potential for targeted delivery of antifungal drugs. We purified the extracellular V-region Ig-like C2 ligand-binding domains and stalk regions of SIG3 and SIG15. We floated the two polypeptides on the surface of liposomes loaded with amphotericin B (AmB) and labeled with rhodamine B to prepare SIG3-Ls and SIG15-Ls. Using these two reagents, we explored the sialoglycans of two evolutionarily distant and deadly human fungal pathogens, the Mucormycete Rhizopus delemar and the Ascomycete Aspergillus fumigatus. We found that SIG3-Ls and SIG15-Ls localized in a continuous layer over the cell wall surface of germ tubes and hyphae of both fungal species and to the conidia of A. fumigatus. Binding was Neu5Ac-specific and appeared confined to N-linked sialoglycans on fungal proteins. SIG3 and SIG15 proteins bound to diverse sialo-glycoproteins extracted from the hyphae of both species. SIG3-Ls and SIG15-Ls delivering sub-micromolar concentrations of AmB were moderately more effective at inhibiting and/or killing both species relative to control liposomes. We discuss the roles that sialo-glycoproteins may play in fungal pathogens.
Immune Cell Interactions and Immune Checkpoints in the Tumor Microenvironment of Gastric CancerCozac-Szőke, Cozac, Negovan
et alInt J Mol Sci (2025) 26 (3)
Abstract: Gastric cancer (GC) ranks as the fifth most prevalent malignant neoplasm globally, with an increased death rate despite recent advancements in research and therapeutic options. Different molecular subtypes of GC have distinct interactions with the immune system, impacting the tumor microenvironment (TME), prognosis, and reaction to immunotherapy. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in the TME are crucial for preventing tumor growth and metastasis, as evidenced by research showing that patients with GC who have a significant density of TILs have better survival rates. But cancer cells have evolved a variety of mechanisms to evade immune surveillance, both sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 15 (Siglec-15) and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) playing a pivotal role in the development of an immunosuppressive TME. They prevent T cell activation and proliferation resulting in a decrease in the immune system's capacity to recognize and eliminate malignant cells. These immune checkpoint molecules function via different but complementary mechanisms, the expression of Siglec-15 being mutually exclusive with PD-L1 and, therefore, providing a different therapeutic approach. The review explores how TILs affect tumor growth and patient outcomes in GC, with particular emphasis on their interactions within the TME and potential targeting of the PD-L1 and Siglec-15 pathways for immunotherapy.
Screening and preparation of nanobodies for SIGLEC-15 detectionZhao, Li, Lan
et alProtein Expr Purif (2025) 229, 106679
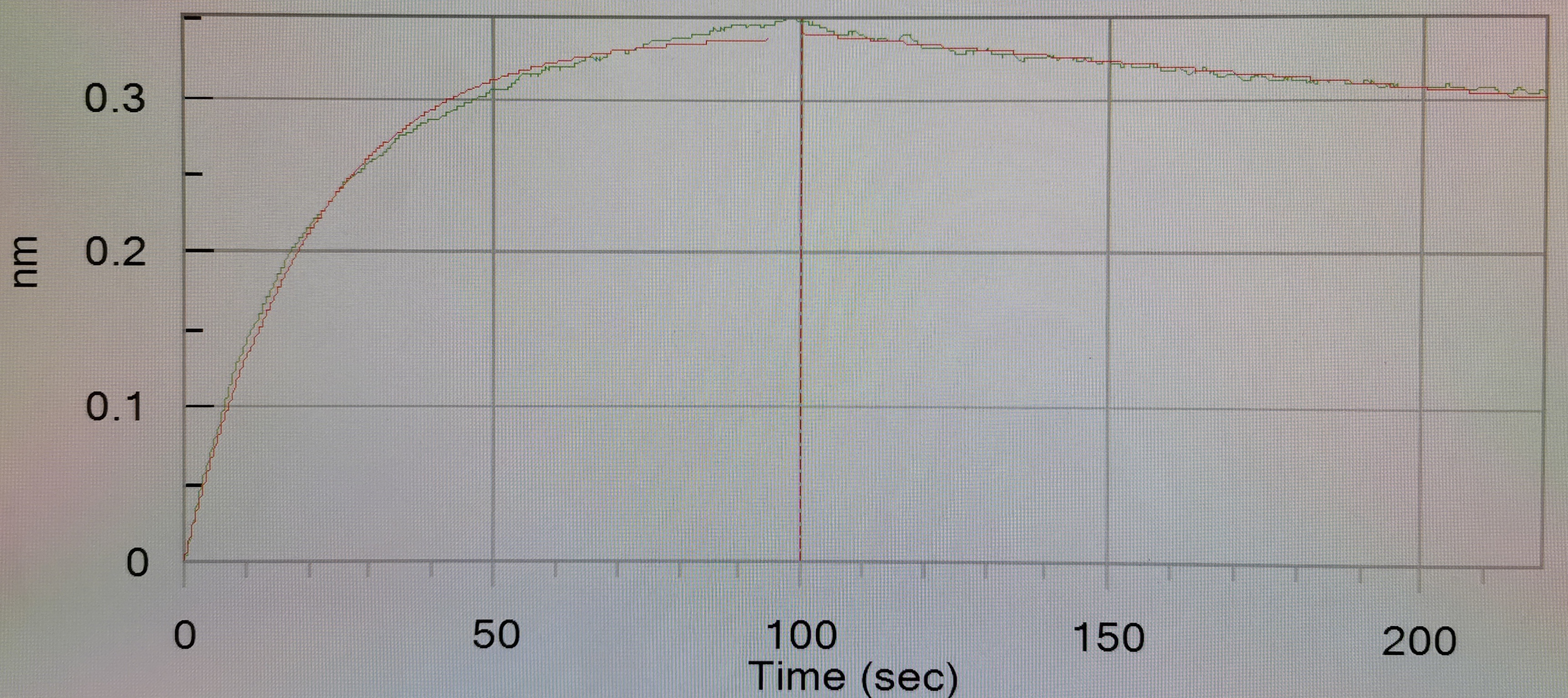
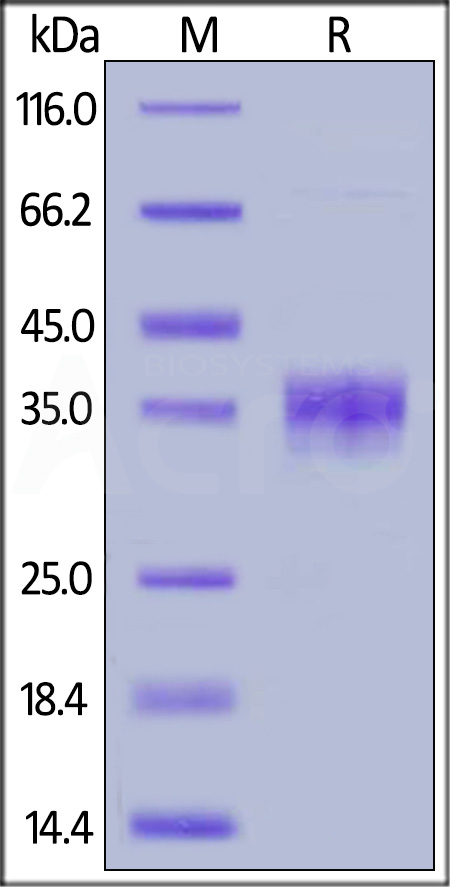
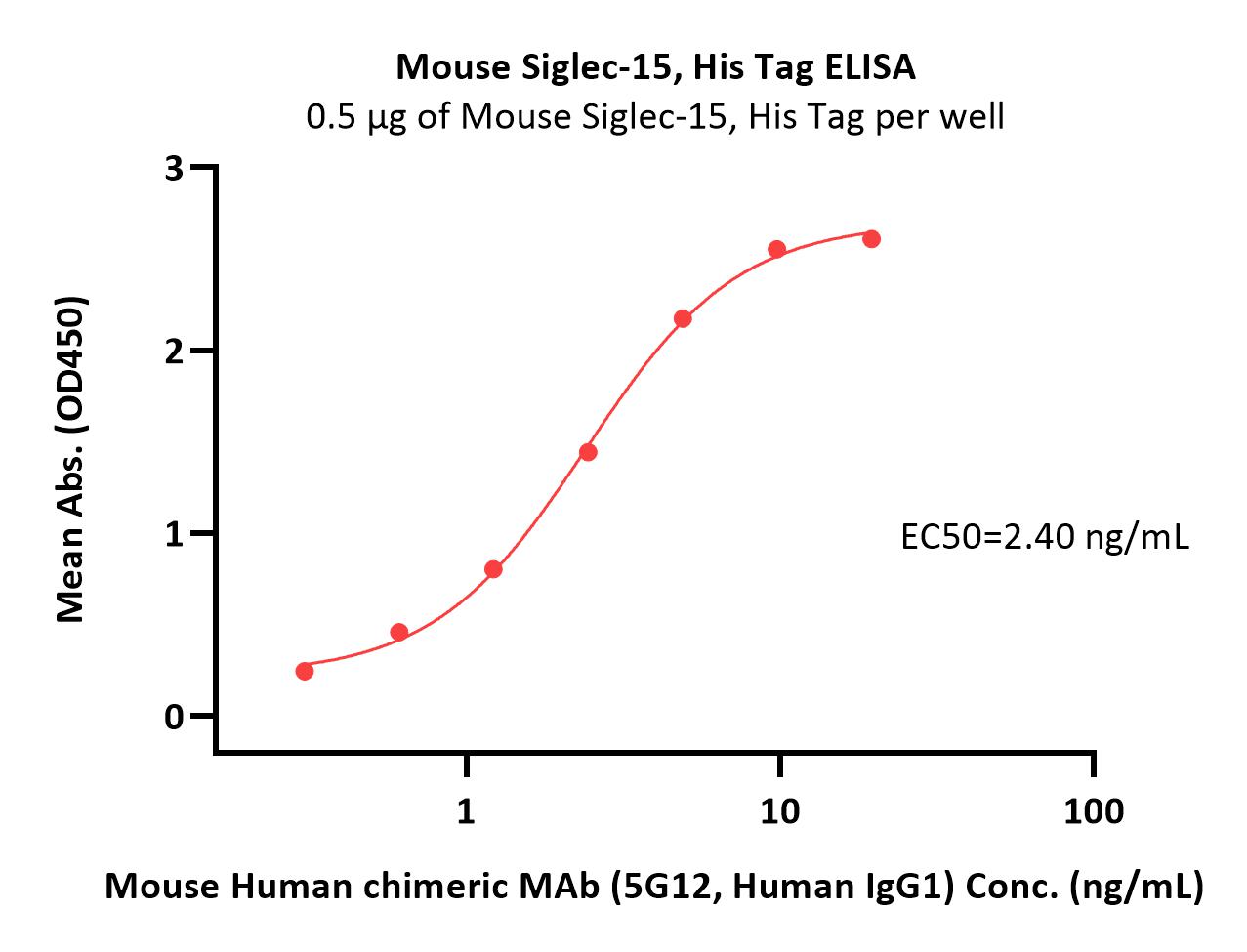
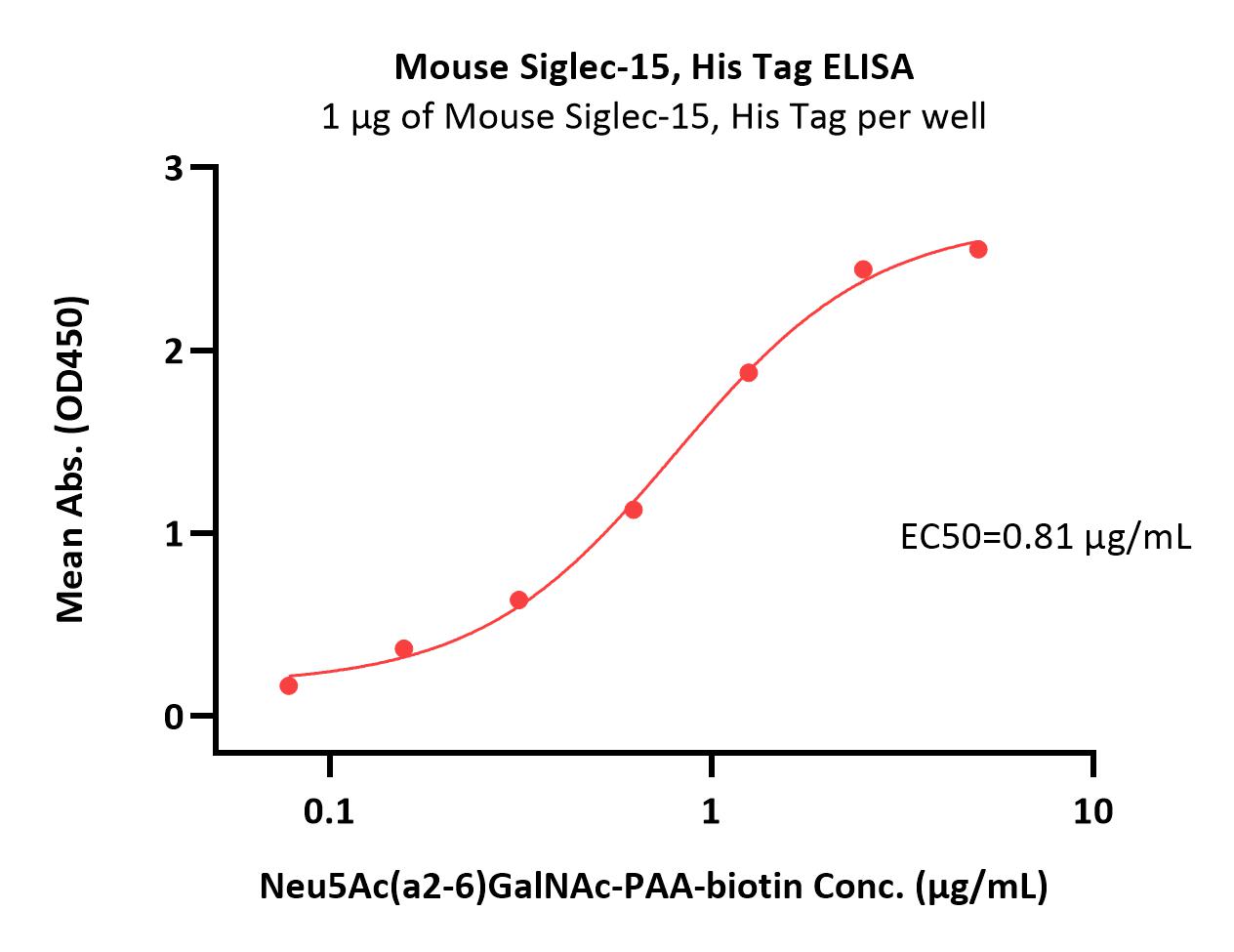
Abstract: As an important member of the Siglec family, SIGLEC-15 plays an important role in osteoclast differentiation, bone remodeling, and tumor immune evasion. In the tumor microenvironment, SIGLEC-15 functions independently of the B7-H1/PD-1 pathway. In this study, the SIGLEC-15 fusion protein (SIGLEC-15-Fc) was successfully expressed and purified using a eukaryotic expression system. This protein was then used as an antigen to immunize camelids, inducing the production of specific nanobodies (VHHs) targeting SIGLEC-15. The resulting nanobodies exhibited a molecular weight of approximately 15 kDa. After screening, we identified two nanobody strains, Nb1C8 and Nb2D7, both of which bind SIGLEC-15 without competition. We confirmed the nanobodies' high affinity and stability through Octec platform and stability analyses. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated that Nb1C8 and Nb2D7 specifically binds to SIGLEC-15 which naturally expressed on bladder cancer cells. This study marks the first development of nanobodies specifically targeting SIGLEC-15, providing a solid foundation for the development of SIGLEC-15-related diagnostic tools and antibody therapeutics.Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Targeting Siglec-15 mediates mitochondrial retrograde regulation of cervical cancer developmentWang, Li, He
et alTissue Cell (2025) 93, 102713
Abstract: Cervical cancer (CCA) is the predominant cause of fatalities from gynecologic malignancies, with metastasis responsible for 80 % of cancer-related mortalities. This study preliminarily examined the involvement of Sialic Acid Binding Ig Like Lectin 15 (Siglec-15) in the development of CCA and its probable mechanisms. We assessed the capacity of Siglec-15 to modulate CCA progression by establishing knockdown and overexpression Siglec-15 cell lines, supplemented with animal models, using both in vivo and in vitro dual investigations. Our findings indicate that Siglec-15 is significantly expressed in CCA cell lines and is intimately associated with the proliferation, migration, and invasion capabilities of CCA cells, as well as mitochondrial ROS homeostasis. The suppression of Siglec-15 expression markedly reduced tumor growth in mice, potentially due to Siglec-15's role in regulating the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, which mediates the retrograde regulation of mitochondrial ROS homeostasis. Siglec-15 may emerge as a novel therapeutic target and prognostic marker for patients with CCA.Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Ltd.

 +添加评论
+添加评论






















































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining