Ligand-induced ubiquitination unleashes LAG3 immune checkpoint function by hindering membrane sequestration of signaling motifsJiang, Dai, Huang
et alCell (2025)
Abstract: Lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3) has emerged as a promising cancer immunotherapy target, but the mechanism underlying LAG3 activation upon ligand engagement remains elusive. Here, LAG3 was found to undergo robust non-K48-linked polyubiquitination upon ligand engagement, which promotes LAG3's inhibitory function instead of causing degradation. This ubiquitination could be triggered by the engagement of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC class II) and membrane-bound (but not soluble) fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1). LAG3 ubiquitination, mediated redundantly by the E3 ligases c-Cbl and Cbl-b, disrupted the membrane binding of the juxtamembrane basic residue-rich sequence, thereby stabilizing the LAG3 cytoplasmic tail in a membrane-dissociated conformation enabling signaling. Furthermore, LAG3 ubiquitination is crucial for the LAG3-mediated suppression of antitumor immunity in vivo. Consistently, LAG3 therapeutic antibodies repress LAG3 ubiquitination, correlating with their checkpoint blockade effects. Moreover, patient cohort analyses suggest that LAG3/CBL coexpression could serve as a biomarker for response to LAG3 blockade. Collectively, our study reveals an immune-checkpoint-triggering mechanism with translational potential in cancer immunotherapy.Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Tumor-intrinsic PRMT5 upregulates FGL1 via methylating TCF12 to inhibit CD8+ T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity in liver cancerSun, Yuan, Sun
et alActa Pharm Sin B (2025) 15 (1), 188-204
Abstract: Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) acts as an oncogene in liver cancer, yet its roles and in-depth molecular mechanisms within the liver cancer immune microenvironment remain mostly undefined. Here, we demonstrated that disruption of tumor-intrinsic PRMT5 enhances CD8+ T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity both in vivo and in vitro. Further experiments verified that this effect is achieved through downregulation of the inhibitory immune checkpoint molecule, fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1). Mechanistically, PRMT5 catalyzed symmetric dimethylation of transcription factor 12 (TCF12) at arginine 554 (R554), prompting the binding of TCF12 to FGL1 promoter region, which transcriptionally activated FGL1 in tumor cells. Methylation deficiency at TCF12-R554 residue downregulated FGL1 expression, which promoted CD8+ T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Notably, combining the PRMT5 methyltransferase inhibitor GSK591 with PD-L1 blockade efficiently inhibited liver cancer growth and improved overall survival in mice. Collectively, our findings reveal the immunosuppressive role and mechanism of PRMT5 in liver cancer and highlight that targeting PRMT5 could boost checkpoint immunotherapy efficacy.© 2025 The Authors.
Development of Novel Peptide-Based Radiotracers for Detecting FGL1 Expression in TumorsXu, Zhang, Pan
et alMol Pharm (2025) 22 (3), 1605-1614
Abstract: A novel immune checkpoint, FGL1, is a potentially viable target for tumor immunotherapy. The development of FGL1-targeted PET probes could provide significant insights into the immune system's status and the evaluation of treatment efficacy. A ClusPro 2.0 server was used to analyze the interaction between FGL1 and LAG3, and the candidate peptides were identified by using the Rosetta peptide derivate protocol. Three candidate peptides targeting FGL1, named FGLP21, FGLP22, and FGLP23, with a simulated affinity of -9.56, -8.55, and -8.71 kcal/mol, respectively, were identified. The peptides were readily conjugated with p-NCS-benzyl-NODA-GA, and the resulting compounds were successfully labeled with 68Ga in approximately 70% yields and radiochemical purity greater than 95%. In vitro competitive cell-binding assay demonstrated that all probes bound to FGL1 with IC50 ranging from 100 nM to 160 nM. Among the probes, PET imaging revealed that 68Ga-NODA-FGLP21 exhibited the best tumor imaging performance in mice bearing FGL1 positive Huh7 tumor. At 60 min p.i., the tumor uptake of 68Ga-NODA-FGLP21 was significantly higher than those of 68Ga-NODA-FGLP22 and 68Ga-NODA-FGLP23, respectively (2.51 ± 0.11% ID/g vs 1.00 ± 0.16% ID/g and 1.49 ± 0.05% ID/g). Simultaneously, the tumor-to-muscle uptake ratios of the former were also higher than those of the latter, respectively (19.40 ± 2.30 vs 9.65 ± 0.62 and 12.45 ± 0.72). In the presence of unlabeled FGLP21, the uptake of 68Ga-NODA-FGLP21 in Huh7 xenograft decreased to 0.81 ± 0.09% ID/g at 60 min p.i., which is similar to that observed in the FGL1 negative U87 MG tumor (0.46 ± 0.03% ID/g). The results were consistent with the immunohistochemical analysis and ex vivo autoradiography. No significant radioactivity was accumulated in normal organs, except for kidneys. In summary, a preclinical study confirmed that the tracer 68Ga-NODA-FGLP21 has the potential to specifically detect FGL1 expression in tumors with good contrast to the background.
Genetic insights into CRP levels in Indian adolescents: confirming adult genetic associationsNair, Bandesh, Giri
et alMol Genet Genomics (2025) 300 (1), 17
Abstract: CRP is a biomarker of acute inflammation linked to metabolic complications. Given the rising prevalence of these conditions in India, we investigated the genetic basis of CRP levels in Indian adolescents, an underrepresented group in genetic studies, to identify early markers of metabolic risk. We performed a two-phased genome-wide association study (GWAS; N = 5052) and an independent Exome-wide association study (ExWAS; N = 4547), to identify both common and rare genetic variants associated with CRP levels. The study identified intergenic variants near CRP and CRPP1 genes, and APOC1 gene as the key regulators of CRP levels establishing the universality of these associations. The GWAS identified the variant rs4247360 (PITPNC1) to be associated at a suggestive significance. The ExWAS single variant association identified novel associations in genes FGL1 (rs35431851), C19orf45 (rs608144, rs475923, rs484870), TRAPPC12 (rs11686212) and KIAA0087 (rs17153822). The SKATO analysis of the rare variants highlighted the role of loss of function and missense variants in genes EPS15, CCDC15, ZNF286A, ELF1, B3GNT8, ZNF850, MAP2, and PSG2. The GWAS and ExWAS in the present study validated the association of 56 variants previously reported for CRP levels. The meta-analysis with the CRP GWAS earlier reported in Indian adults revealed the shared genetic architecture of CRP levels across age groups. The gene-set enrichment analysis highlighted the role of CRP-associated genes in inflammatory and cardiometabolic pathways. The study enhances understanding of genetic predispositions to inflammation and metabolic disorders confirming known associations, identifying novel loci, and validating shared genetic architecture across age-groups, guiding targeted prevention for at-risk youth.© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
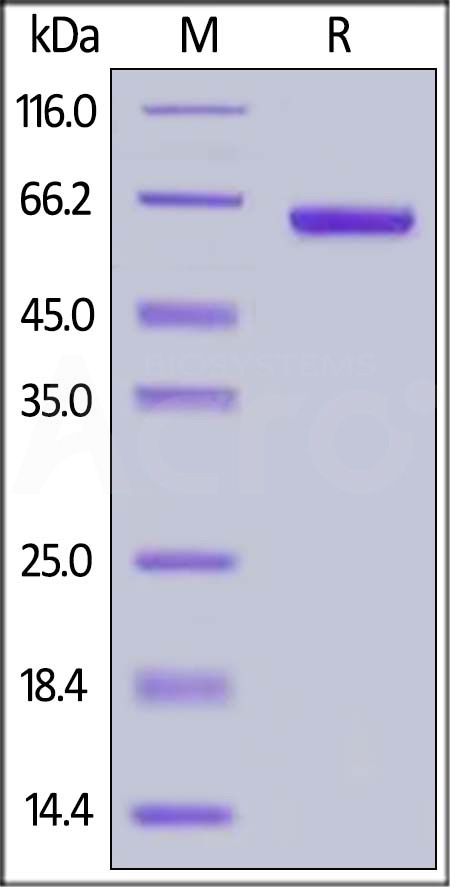
























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining

















