Influence of Distinct Maternal Cytomegalovirus-Specific Neutralizing and Fc Receptor-Binding Responses on Congenital Cytomegalovirus Transmission in HIV-Exposed NeonatesMiller, Mahant, Jenks
et alViruses (2025) 17 (3)
Abstract: Congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) is the most common infectious cause of birth defects worldwide, affecting approximately 1 in every 200 live-born infants globally. Recent work has identified potential immune correlates of protection against cCMV transmission including maternal and placentally transferred antibody levels and their function, which may inform the development of maternal active (vaccine) and passive (mono/polyclonal antibody) immunizations. However, these correlates need to also be assessed in diverse cohorts, including women living with HIV who have increased risk of cCMV transmission. Using a case-control design, we investigated whether the magnitude, specificity, function and placental transfer of maternal IgG responses are associated with protection against and/or risk of cCMV transmission in HIV/HCMV co-infection. Within 3 historical cohorts of pregnant women with HIV/HCMV co-infection, we identified 16 cCMV transmitting cases that were matched to 29 cCMV non-transmitting controls. Using a systems serology approach, we found that normalized HCMV-specific IgG binding to FcγR1α was higher in non-transmitting dyads, whereas HCMV-neutralizing antibody responses were higher in transmitting dyads. These findings suggest that engagement of FcγR1α by HCMV-specific IgG may help confer protection against cCMV transmission. Building upon previous research, our study reinforces the critical role of validating maternal humoral immune correlates of cCMV transmission risk across diverse seropositive cohorts, providing essential insights to inform and accelerate the development of effective HCMV vaccines.
Plant-derived recombinant macromolecular PAP-IgG Fc as a novel prostate cancer vaccine candidate eliciting robust immune responsesKang, Kim, Hwang
et alTransgenic Res (2025) 34 (1), 16
Abstract: Prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) is a specific protein that is highly expressed in prostate cancer. In this study, we constructed two recombinant PAP fusion genes: PAP fused to the immunoglobulin G (IgG) Fc fragment (designated PAP-Fc) and PAP-Fc fused to the endoplasmic reticulum retention sequence KDEL (designated PAP-FcK). Transgenic Nicotiana tabacum plants expressing these recombinant macromolecular proteins (MPs) were generated using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, and the presence of both genes was confirmed through genomic PCR. Western blot analysis validated the expression of PAP-Fc and PAP-FcK MPs, which were successfully purified via protein A affinity chromatography. Size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography revealed dimeric peaks for PAP-Fc (PAP-FcP) and PAP-FcK (PAP-FcKP). Bio-transmission electron microscopy demonstrated 'Y'-shaped protein particles resembling antibody structures. Moreover, PAP-FcP and PAP-FcKP exhibited a high association rate with human FcγR and FcRn. Vaccination of mice with both PAP-FcP and PAP-FcKP resulted in increased total IgG against PAP and enhanced activation of CD4+ T cells, comparable to mice immunized with PAP, which served as a positive control. These findings indicate that both plant-derived MPs can effectively induce adaptive immunity, positioning them as promising candidates for prostate cancer vaccines. Overall, plants expressing PAP-Fc and PAP-FcK represent a viable production system for antigenic macromolecule-based prostate cancer vaccines.© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Prediction of human pharmacokinetics of Fc-engineered therapeutic monoclonal antibodies using human FcRn transgenic miceHaraya, Ichikawa, Murao
et alMAbs (2025) 17 (1), 2484443
Abstract: Human FcRn transgenic mice (Tg32) have been widely used to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of mAbs and predict human pharmacokinetics. This study aims to establish an approach for predicting the human pharmacokinetics of Fc-engineered mAbs with enhanced FcRn binding mutations using Tg32 mice. MAbs were intravenously administered at 10 mg/kg in the absence or presence of IVIG (1000 mg/kg) in Tg32 mice. Pharmacokinetic parameters (CL, Q, Vc, and Vp) estimated in Tg32 mice were compared with clinical data. Optimal allometric scaling exponents were determined to improve the accuracy of human pharmacokinetic predictions for Fc-engineered mAbs. Moreover, we predicted the plasma concentration-time profile after IV injection in humans using parameters estimated based on an optimized exponent. While normal mAbs exhibited a higher CL in the presence of IVIG compared to its absence, Fc-engineered mAbs showed comparable CL in both conditions. The larger difference in CL between normal and Fc-engineered mAbs observed in the presence of IVIG closely matched clinical study results. A significant positive correlation between Tg32 mice and humans was observed in the CL of Fc-engineered mAbs in both the absence and presence of IVIG. The estimated optimal exponents for CL, Q, Vc, and Vp were 0.73, 0.60, 0.95, and 0.87, respectively. Using these exponents, the plasma mAb concentration-time profile after IV injection in humans was accurately predicted. This study establishes a robust methodology for accurately predicting the human pharmacokinetics of Fc-engineered mAbs using Tg32 mice, achieving prediction accuracy comparable to that of cynomolgus monkeys. This approach, as a viable alternative to cynomolgus monkeys, can accelerate the preclinical development of promising Fc-engineered mAbs with enhanced FcRn binding.
Role of Antibody Glycosylation in Health, Disease, and TherapyNimmerjahn
Handb Exp Pharmacol (2025)
Abstract: Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies are an essential component of humoral immunity protecting the host from recurrent infections. Among all antibody isotypes, IgG antibodies have a uniquely long half-life, can basically reach any tissue in the body, and have the ability to kill opsonized target cells, which has made them the molecule of choice for therapeutic interventions in cancer and autoimmunity. Moreover, IgG antibodies in the form of pooled serum IgG preparations from healthy donors are used to treat chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, providing evidence that serum IgG antibodies can have an active immunomodulatory activity. Research over the last two decades has established that the single sugar moiety attached to each IgG heavy chain plays a very important role in modulating the pro- and anti-inflammatory activities of IgG. Moreover, specific sugar moieties such as sialic acid and galactose residues can serve as highly specific biomarkers for ongoing inflammatory processes. This chapter will summarize how different sugar residues in the IgG sugar moiety change upon inflammation and how such changes may translate to altered IgG function and hence maybe useful for optimizing or modulating the function of therapeutic antibodies.© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.

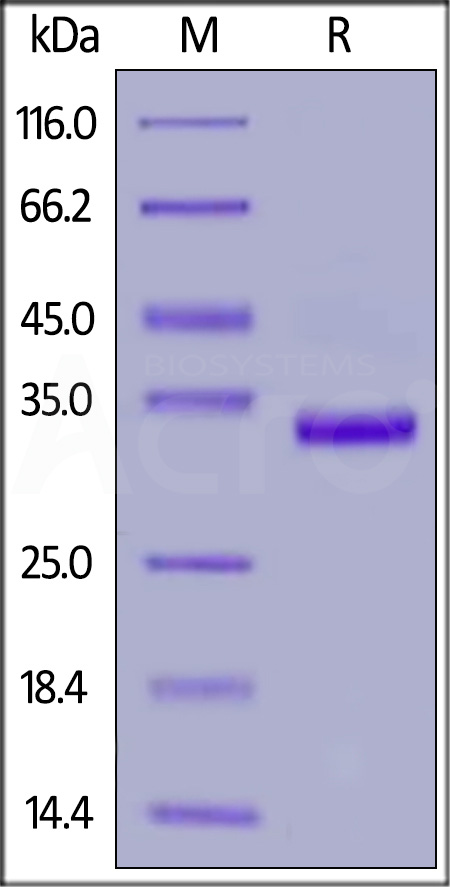
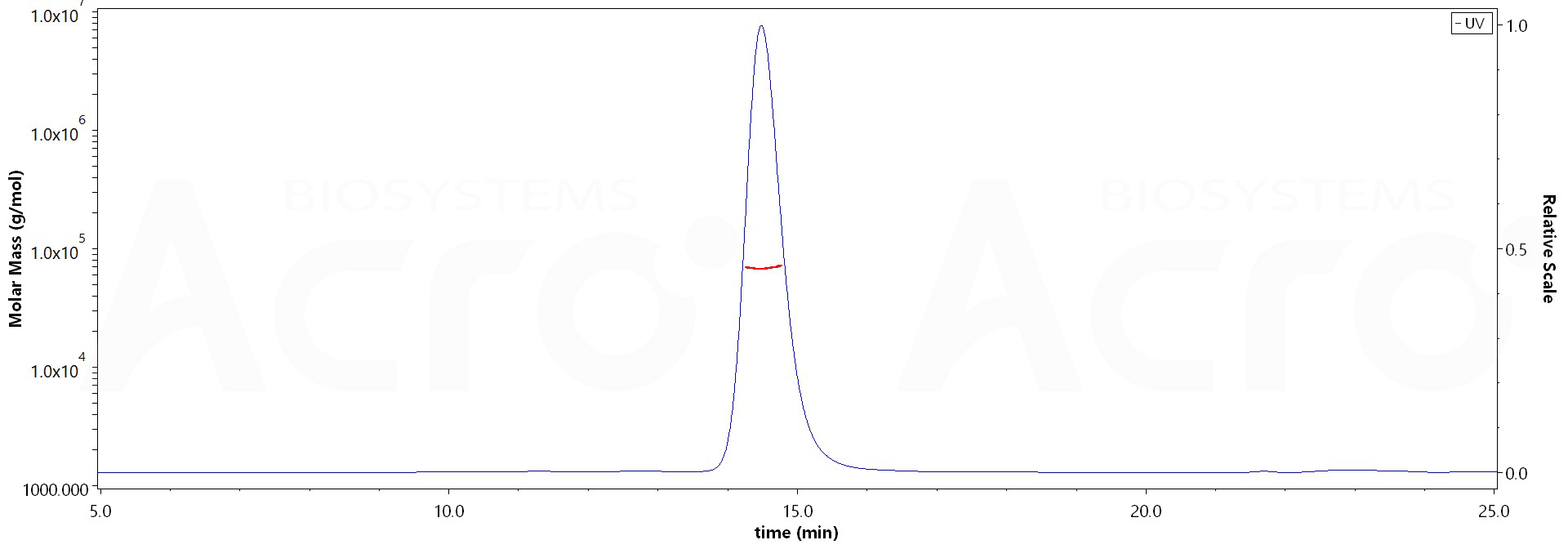























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















