Palliative middle meningeal artery embolisation for symptomatic chronic subdural haematoma in an individual with resistant thrombocytopaenia due to acute myeloid leukaemiaLangberg, Dunkerton, Shipway
et alBMJ Case Rep (2025) 18 (3)
Abstract: An older male presented with intermittent headaches, reduced mobility and transient facial weakness. CT head scan revealed acute-on-chronic subdural haematoma (cSDH), causing mass effect and midline shift. A background of progressive acute myeloid leukaemia was reported, characterised by severe thrombocytopaenia resistant to haematological therapies. The risk of neurosurgical intervention was deemed to be excessive.Right middle meningeal artery embolisation (MMAE) was pursued to arrest repeated subdural haemorrhage and prevent symptomatic neurological deterioration. The patient was discharged home the following day. Interval CT head showed almost complete resolution of the right cSDH. Symptoms improved and the patient was able to return to living independently at home.MMAE may be an effective intervention in patients with cSDH who are unsuitable candidates for surgery, and where the goal is to maintain functional independence, quality of life and prevent acute neurological decline and disability.© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2025. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
NIR-II aza-BODIPY Platform for the Development of a Fluorescent Antibody Drug ConjugateChazeau, Pipier, Wegner
et alJ Med Chem (2025)
Abstract: Real-time imaging of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offers valuable insights for assessing tumor targeting specificity, monitoring therapeutic efficacy, and detecting off-target accumulation that may cause adverse effects. To enable precise tracking, we developed a versatile fluorescent platform based on an NIR-II emitting aza-BODIPY dye, which can be site-specifically grafted onto an IgG1 antibody to generate well-defined fluorescent ADCs. As a proof of concept, we synthesized an HER2-targeting trastuzumab immunoconjugate bearing a NIR-II aza-BODIPY fluorophore. The cytotoxic monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) payload was introduced in the final step, resulting in a trackable and homogeneous ADC suitable for both in vitro and in vivo investigations. The resulting Trastu-azaNIRII-MMAE selectively accumulated in HER2-positive subcutaneous tumors, significantly reducing the tumor growth. Using NIR-II optical imaging, a single injection of the NIR-II-ADC allowed for the detection of the conjugate over a period of more than one month, highlighting its potential for long-term tracking and therapeutic applications.
Therapeutically targeting endometrial cancer in preclinical models by ICAM1 antibody-drug conjugatesXie, Sun, Yao
et alGynecol Oncol (2025) 196, 16-27
Abstract: The incidence of mortality and morbidity from endometrial cancer (EC) is increasing annually, and there is a paucity of effective targeted therapies for the condition. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) represent a promising approach to tumor-targeted therapy. In this study, we aim to identify a novel molecular target for the preclinical development of EC-targeted ADCs.Through quantitative and unbiased bioinformatics analyses intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM1) was identified as a potential cell membrane target. Two ADCs, ICAM1-MMAE and ICAM1-DXd, were subsequently developed by conjugating ICAM1 monoclonal antibodies with microtubule inhibitors and DNA topoisomerase inhibitors, respectively. The preclinical efficacy and biosafety of these ICAM1 ADCs were validated in both in vitro and in vivo models. Furthermore, transcriptomic analysis was conducted to elucidate the therapeutic effects of the ICAM1 ADCs.Quantitative flow screening and bioinformatics analyses revealed significant overexpression of ICAM1 in EC. ICAM1-MMAE and ICAM1-DXd were developed using clinically effective linkers and payloads. In preclinical models, ICAM1 ADCs showed superior antitumor efficacy compared to standard chemotherapy, achieving sustained tumor regression with an excellent safety profile in both subcutaneous and orthotopic xenograft models. Transcriptomic analysis further revealed that ICAM1-DXd potently activated tumor immunity.ICAM1 was identified as a promising cell membrane protein target for ADC development in EC. As-synthesized ICAM1 ADCs demonstrated potent antitumor activity, favorable biosafety profiles in vitro and in vivo, and the ability to activate tumor immunity. These findings support the potential of ICAM1 ADCs as a therapeutic strategy and warrant further investigation in clinical studies.Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
PK/PD of Positively Charged ADC in MiceChang, Le, Liu
et alPharmaceutics (2025) 17 (3)
Abstract: Background/Objectives: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) show significant promise in oncology but often suffer from a narrow therapeutic window. Introducing a positive charge on the antibody is one proposed strategy to enhance tumor distribution and efficacy of ADC. Accordingly, this study evaluates the pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacology of an ADC developed using a positively charged (+5) version of anti-HER2 antibody trastuzumab conjugated with vc-MMAE linker-payload. Methods: A positively charged variant of trastuzumab was generated and conjugated to vc-MMAE. In vitro cytotoxicity assays were performed in cell lines with varying HER2 expression levels: N87 (high), MCF-7 (low), and MDA-MB-468 (non-expressing). In vivo biodistribution of wild-type (WT) and positively charged (+5) ADC was investigated in plasma, tumors, liver, and spleen. A pilot efficacy and toxicity study was also conducted in N87 tumor-bearing mice. Results: The charged ADC showed differential potency and PK behavior compared to the WT ADC. The charged ADC had similar potency in N87 cells but demonstrated ~20-fold and ~60-fold higher potency in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468 cells. Plasma exposures of all the analytes were found to be reduced following the administration of charged ADC. However, total antibody exposure was found to increase in liver, spleen, and low antigen-expressing MCF-7 tumors. Tumor payload exposures were found to be significantly reduced for the charged ADCs, but liver and spleen displayed higher peak concentrations and increased tissue-to-plasma exposure ratios for the payload, suggesting preferential distribution of ADC with high drug-antibody ratio (DAR) to liver and spleen. Consistent with reduced tumor exposures, charged ADC showed lower efficacy in N87 tumor-bearing mice. No overt toxicity was observed for the charged ADC. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that while positively charged ADCs may be more potent in vitro, their efficacy in vivo may be compromised due to altered PK behavior. Thus, introducing a positive charge into the antibody framework may not be a viable strategy for improving the therapeutic potential of ADCs.
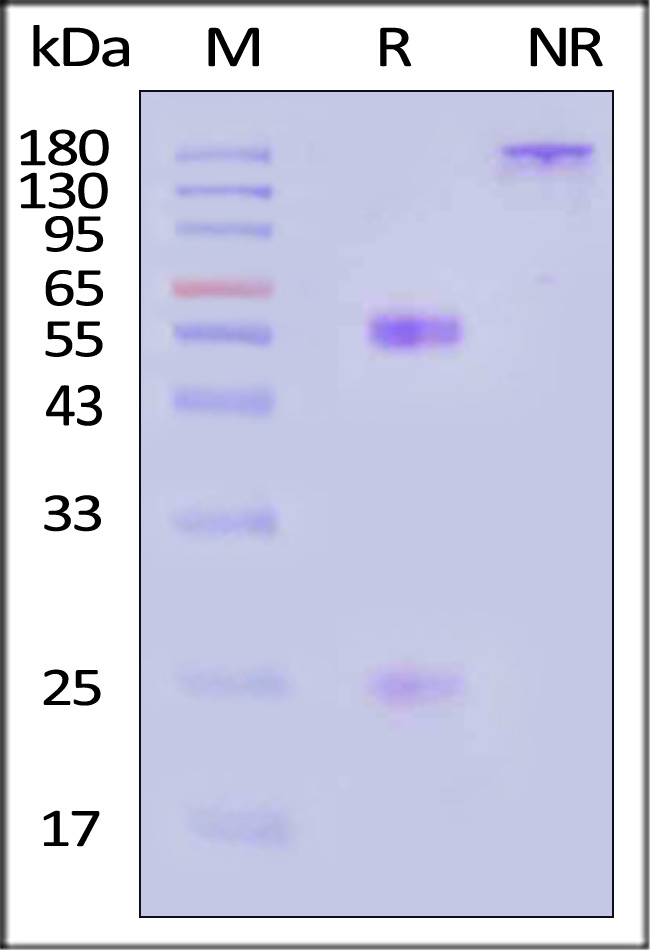
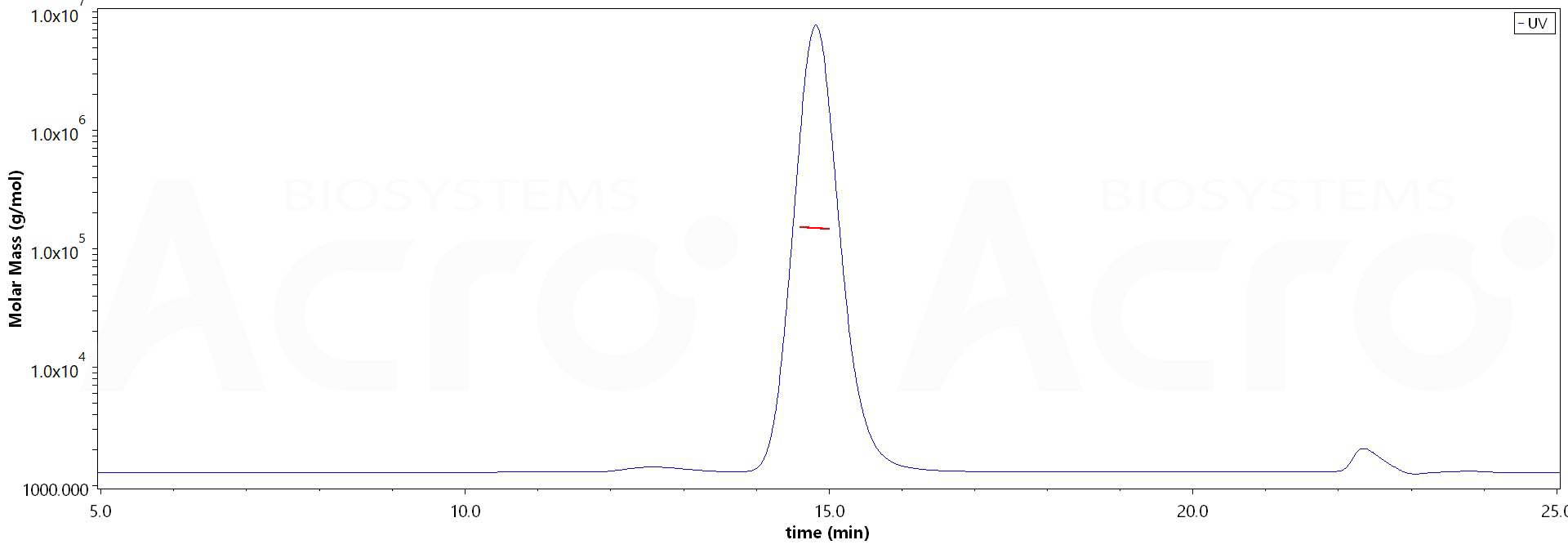
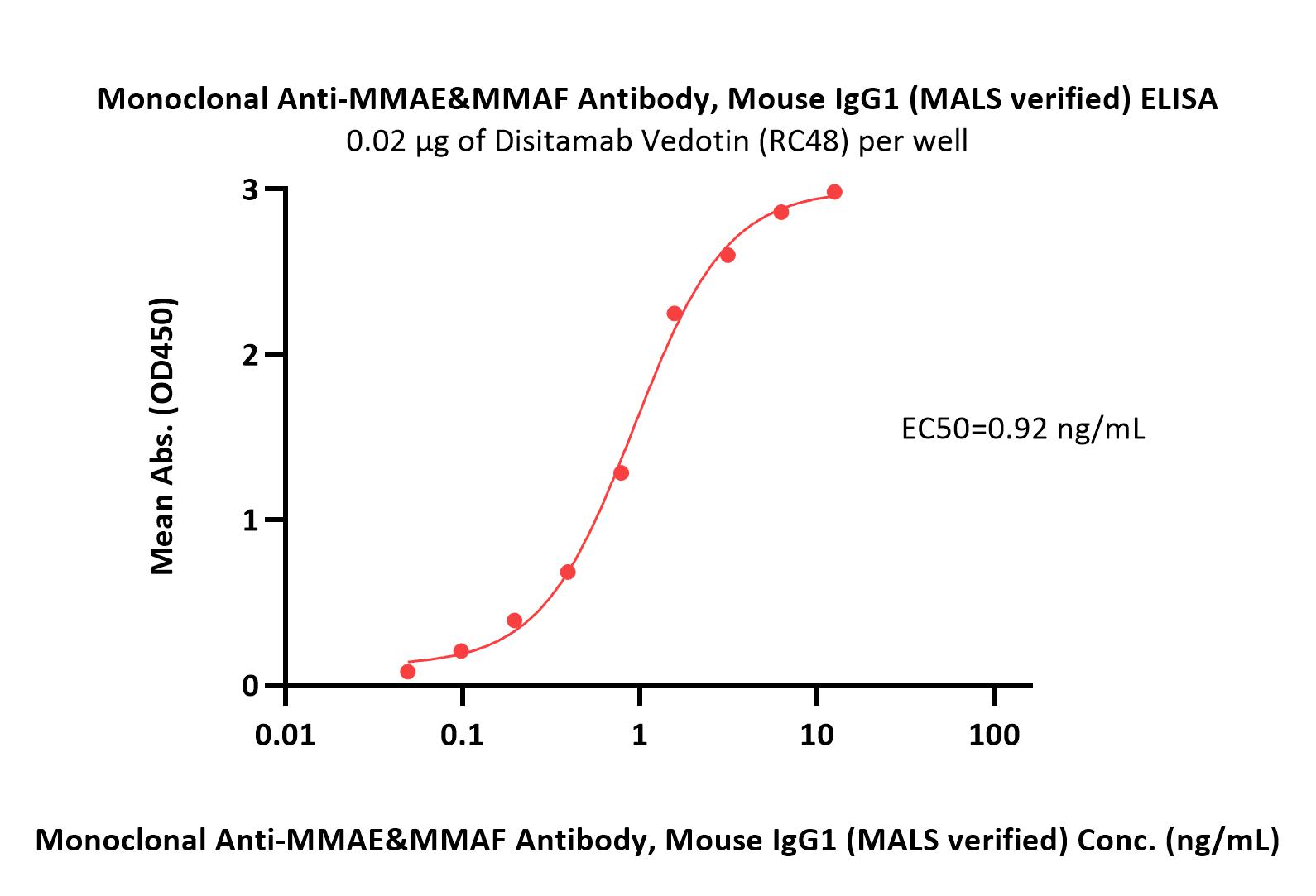
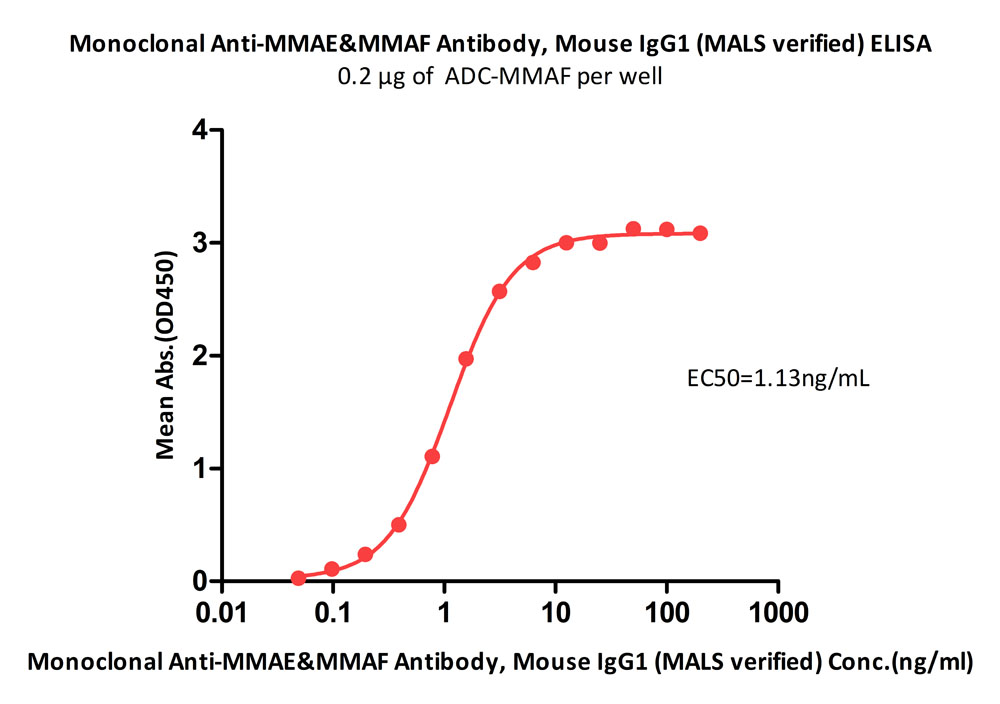
 +添加评论
+添加评论






















































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















