分子别名(Synonym)
Spike,S protein RBD,Spike glycoprotein Receptor-binding domain,S glycoprotein RBD,Spike protein RBD
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag (SPD-C82En) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Arg 319 - Lys 537 (Accession # QHD43416.1 (Y449H, E484K, N501Y)). The mutations Y449H, E484K, N501Y were identified in the SARS-CoV-2 variant C.1.2.
Predicted N-terminus: Arg 319
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus, followed by an Avi tag (Avitag™)
The protein has a calculated MW of 28.2 kDa. The protein migrates as 32-38 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
标记(Labeling)
Biotinylation of this product is performed using Avitag™ technology. Briefly, the single lysine residue in the Avitag is enzymatically labeled with biotin.
蛋白标记度(Protein Ratio)
Passed as determined by the HABA assay / binding ELISA.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
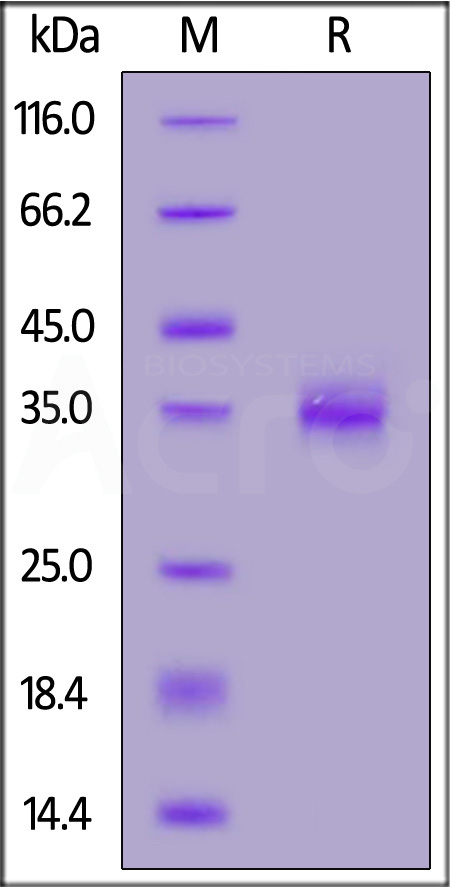
Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
SEC-MALS
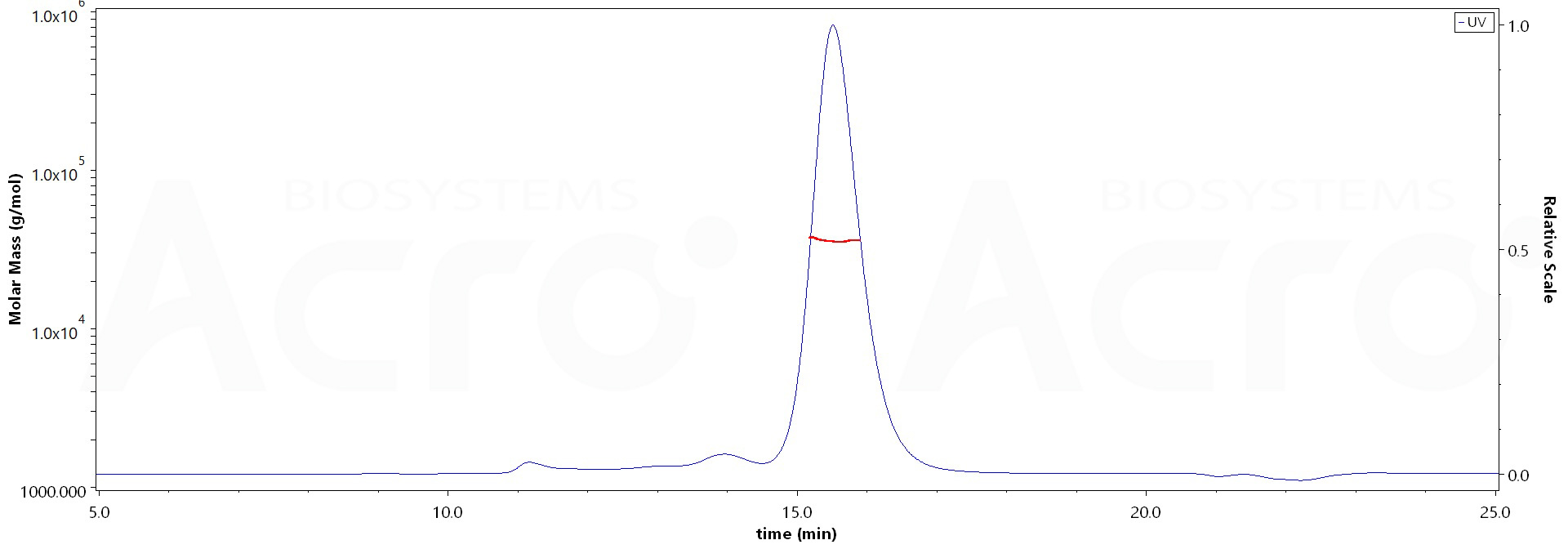
The purity of Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag (Cat. No. SPD-C82En) is more than 85% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 28-42 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
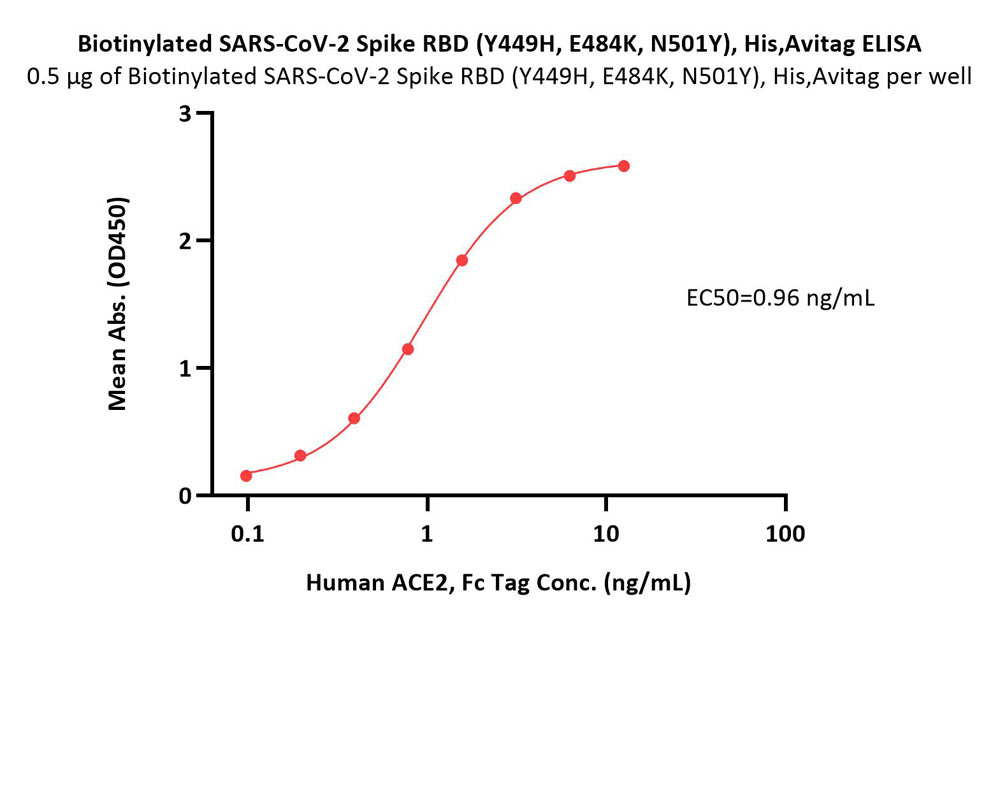
Immobilized Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag (Cat. No. SPD-C82En) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) on streptavidin (Cat. No. STN-N5116) precoated (0.5 μg/well) plate can bind Human ACE2, Fc Tag (Cat. No. AC2-H5257) with a linear range of 0.1-2 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
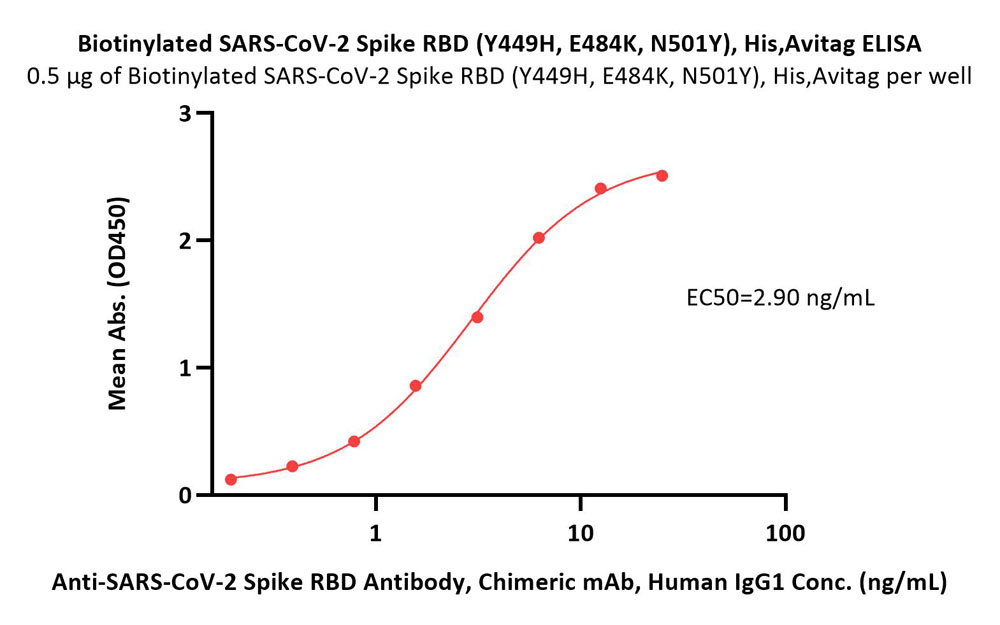
Immobilized Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag (Cat. No. SPD-C82En) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) on streptavidin (Cat. No. STN-N5116) precoated (0.5 μg/well) plate can bind Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody, Chimeric mAb, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. S1N-M122) with a linear range of 0.2-6 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
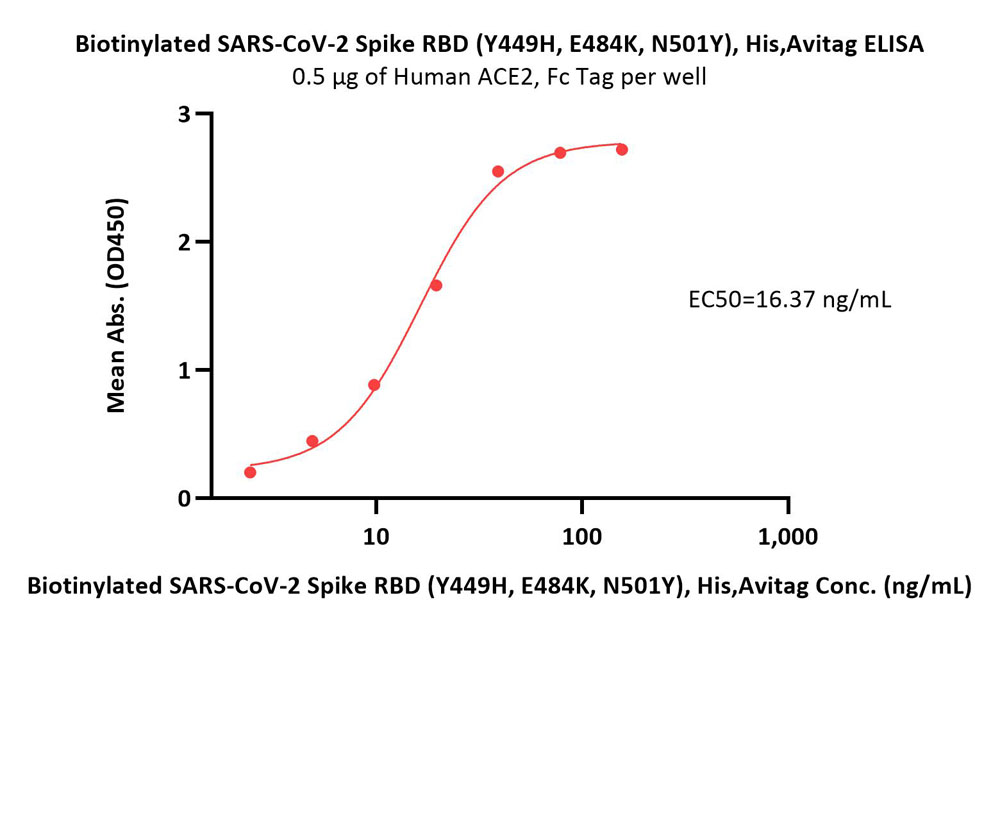
Immobilized Human ACE2, Fc Tag (Cat. No. AC2-H5257) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag (Cat. No. SPD-C82En) with a linear range of 2-39 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
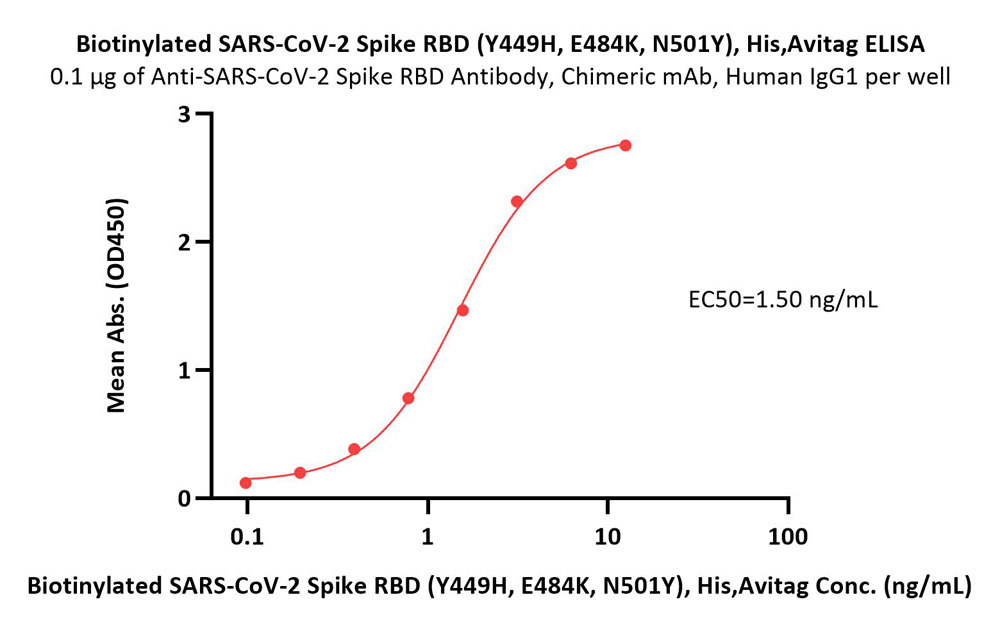
Immobilized Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody, Chimeric mAb, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. S1N-M122) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Protein (Y449H, E484K, N501Y), His,Avitag (Cat. No. SPD-C82En) with a linear range of 0.1-3 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol

- 774XXXXXXX
- I have been using the unconjugated FMC63 for a while and as soon as we knew about the conjugated FMC63 we wanted to use this as it will be saving us 1.5 hours in the staining procedure. We used this antibody and we were able to see a better seperation of positive and negative poulations. Its easy to use and 1:25 dilution works really well. I will recommend this 200%
 >
>- 2022-2-26

- 156XXXXXXX8
- 该抗体目前主要用于细胞转染后阳性细胞转染效率检测,实验过程中抗体的高灵敏度及识别特异性,能够真实有效的反映出结果的准确性,且重复性,后期实验需要将会继续订购。
 >
>- 2022-12-13
背景(Background)
It's been reported that Coronavirus can infect the human respiratory epithelial cells through interaction with the human ACE2 receptor. The spike protein is a large type I transmembrane protein containing two subunits, S1 and S2. S1 mainly contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which is responsible for recognizing the cell surface receptor. S2 contains basic elements needed for the membrane fusion.The S protein plays key parts in the induction of neutralizing-antibody and T-cell responses, as well as protective immunity.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining

















