Immunotherapies Targeting CD123 and CD303: A New Frontier in Treating Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell NeoplasmGalati, Zanotta, Florio
et alInt J Mol Sci (2025) 26 (6)
Abstract: Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a rare and aggressive hematologic malignancy characterized by the overexpression of CD123 and CD303 surface antigens. These molecular markers play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases and developing targeted therapies. Traditional treatment options for BPDCN have demonstrated limited effectiveness, highlighting the need for new and innovative therapeutic strategies. Recent advances in immunotherapy, particularly therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bispecific T-cell engagers, and CAR T-cell therapy, have provided promising alternatives. Tagraxofusp, the first FDA-approved CD123-targeted therapy, has significantly improved patient outcomes. Additionally, emerging CD303-targeting strategies offer the potential for further advancements. Despite these breakthroughs, challenges such as treatment resistance and toxicity remain. This review explores the latest developments in BPDCN treatment, emphasizing the potential of CD123 and CD303 as targets for precision medicine interventions. The ongoing evolution of targeted immunotherapies holds promise for improving patient survival and redefining treatment paradigms in hematologic malignancies.
Refining the interactions between microglia and astrocytes in Alzheimer's disease pathologyChen, Xu, Wang
et alNeuroscience (2025) 573, 183-197
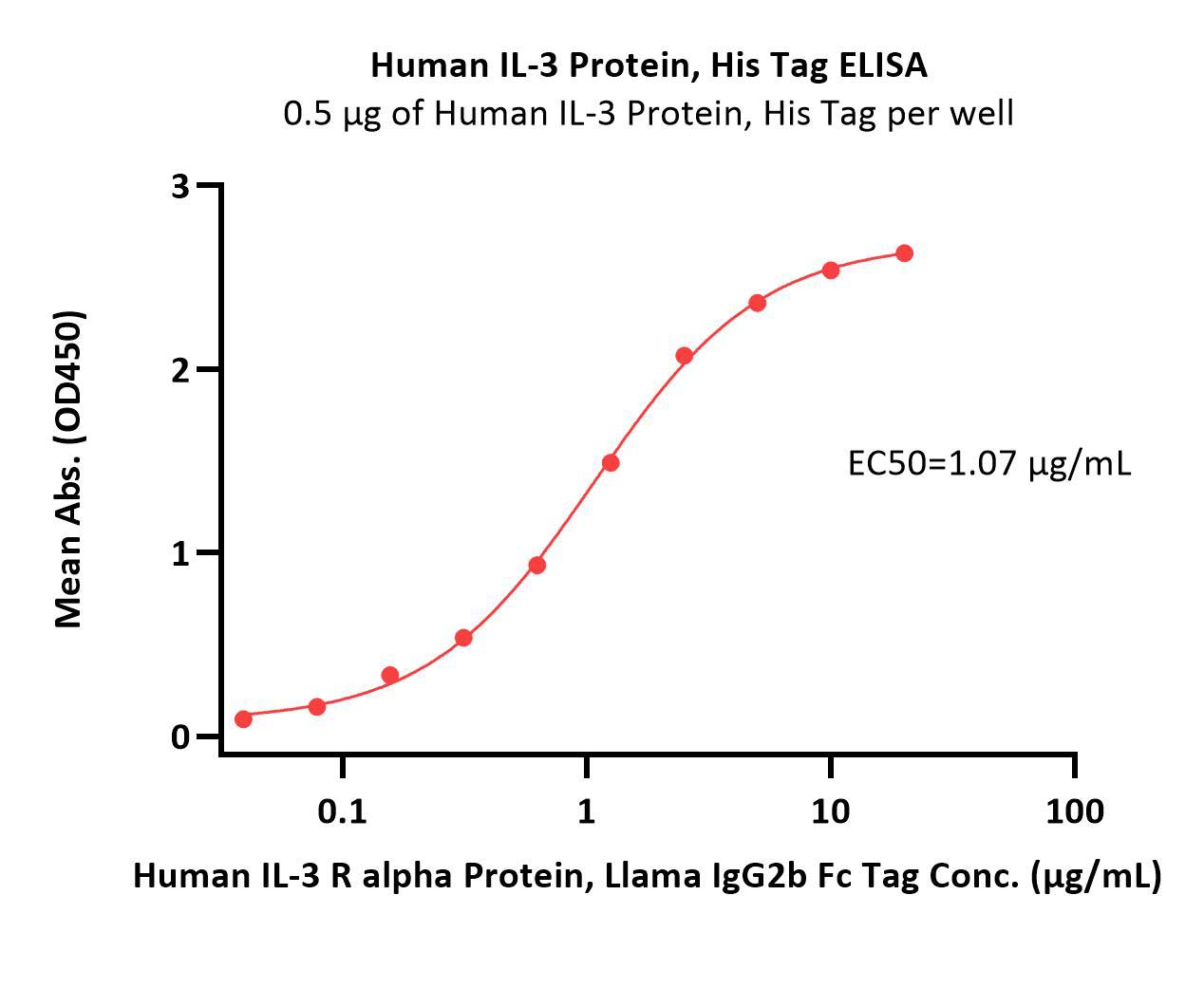
Abstract: Microglia and astrocytes are central to the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer's Disease (AD), working both independently and collaboratively to regulate key pathological processes such as β-amyloid protein (Aβ) deposition, tau aggregation, neuroinflammation, and synapse loss. These glial cells interact through complex molecular pathways, including IL-3/IL-3Ra and C3/C3aR, which influence disease progression and cognitive decline. Emerging research suggests that modulating these pathways could offer therapeutic benefits. For instance, recombinant IL-3 administration in mice reduced Aβ plaques and improved cognitive functions, while C3aR inhibition alleviated Aβ and tau pathologies, restored synaptic function, and corrected immune dysregulation. However, the effects of these interactions are context-dependent. Acute C3/C3aR activation enhances microglial Aβ clearance, whereas chronic activation impairs it, highlighting the dual roles of glial signaling in AD. Furthermore, C3/C3aR signaling not only impacts Aβ clearance but also modulates tau pathology and synaptic integrity. Given AD's multifactorial nature, understanding the specific pathological environment is crucial when investigating glial cell contributions. The interplay between microglia and astrocytes can be both neuroprotective and neurotoxic, depending on the disease stage and brain region. This complexity underscores the need for targeted therapies that modulate glial cell activity in a context-specific manner. By elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying microglia-astrocyte interactions, this research advances our understanding of AD and paves the way for novel therapeutic strategies aimed at mitigating neurodegeneration and cognitive decline in AD and related disorders.Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Lienal Polypeptide Decreases Immune Thrombocytopenia in a Mouse Model by Upregulating Cytokine Production and Increasing the Levels of CD4+, CD8+, and T Regulatory CellsYue, Xie, Wang
et alJ Interferon Cytokine Res (2025)
Abstract: Primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a condition marked by immune-mediated inadequate platelet production or excessive destruction. This study investigates the effects of Lienal polypeptide injection (LP) on T lymphocyte subgroups in the spleen and thymus, megakaryocyte counts in the bone marrow, and cytokine levels related to megakaryocyte development in mice with antibody-induced ITP, aiming to elucidate potential therapeutic mechanisms. We first assessed the effects of LP on Meg-01 megakaryocytic cells regarding proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation using Methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays, Western blot analysis, and flow cytometry for apoptosis and CD41 expression as a differentiation marker. Following this, LP was administered intraperitoneally at 60 mg/(kg·d) for 11 days to ITP mice. We quantified peripheral blood platelets and bone marrow megakaryocytes, measured spleen and thymus indices, and assessed serum levels of stem cell factor (SCF), interleukin-3 (IL-3), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and platelet factor-4 (PF-4) via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Flow cytometry quantified T-helper cells (CD4+), cytotoxic T cells (CD8+), and regulatory T cells (Tregs). LP significantly induced apoptosis in Meg-01 cells while not markedly affecting differentiation. In ITP mice, LP effectively prevented platelet decline without affecting megakaryocyte counts or maturity. Increased SCF, IL-3, and IL-6 levels, alongside decreased PF-4 levels, correlated with enhanced platelet production. Moreover, CD4+/CD8+ ratios and Treg populations increased, contributing to reduced platelet destruction. In conclusion, LP exerts a protective effect in ITP by modulating SCF, IL-3, IL-6, and PF-4 levels and restoring the balance of T cell subtypes, elucidating its therapeutic potential.
Carbon Dioxide Selectivity over Ethane in Promising Bis Tri (Fluoromethylsulfonyl) Imide-Based Ionic LiquidsQuaye, Henni, Shirif
Molecules (2025) 30 (5)
Abstract: This research addresses the critical challenge of CO2 capture by exploring innovative ways to avoid ethane (C2H6) co-absorption in natural gas sweetening operations. The solubility of Ethane (C2H6) was measured in three ionic liquids (ILs) with similar anions, 1-decyl-3-methyl imidazolium bis (trifluoro methylsulfonyl imide) [IL-1], 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoro methylsulfonyl imide) [IL-2], and triethytetra-decyl ammonium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl imide) [IL-3]. The solubility experiments were investigated at 303.15 K and 343.15 K with pressures reaching 1.2 MPa. Among the ILs, [IL-2] exhibited the highest ethane absorption capacity due to its extended alkyl chain. The Peng-Robinson equation of state (PR-EoS) and three (3) distinct mixing rules provided robust correlations for the solubility data. Results demonstrate the inferior performance of [IL-1], [IL-2], and [IL-3] compared to Selexol/Genosorb 1753. The selectivity of Ethane (C2H6) over CO2 was determined, with the overall selectivity ranking as follows: [IL-1] > [IL-3] > [IL-2]. A comparison of these selectivity values with published IL data indicated that these three ILs are most effective when used in applications targeting CO2 capture in the absence of Ethane (C2H6), such as in the case of flue gas. They will most probably be used with an amine blend. Additionally, the Enthalpy and entropy of absorption provided valuable insights, demonstrating Ethane's weaker interactions and lower solubility than CO2. These findings emphasize the critical role of IL structure in determining ethane solubility and highlight the potential of customized ILs for optimizing gas-separation processes.

 +添加评论
+添加评论























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















