产品参数(Product Specifications)
| Assay Type | Sandwich-ELISA |
| Analyte | IL-4 |
| Format | 96T(8×12 strips) |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Regulatory Status | RUO |
| Sensitivity | <0.391pg/mL |
| Standard Curve Range | 0.391 pg/mL-25 pg/mL |
| Assay Time | 2 hr 50 min |
| Suitable Sample Type | For the quantitative determination of human IL-4 in Cell Culture Supernatants, Plasma, Serum. |
| Sample volume | 100 uL |
产品概述(Product Overview)
resDetect™ Human Interleukin-4 (IL-4) ELISA Kit (Residue Testing) is based on the ELISA sandwich method and is used to detect and quantitatively determine GMP human IL-4 in cell culture supernatants, serum, and plasma. The kit contains GMP human IL-4 (ACROBiosystems, cat#GMP-L04H26) to ensure accurate assay results and is designed to provide a reliable solution for CAR-T product quality assessment during drug development and CMC quality control stages. It can also be used as a universal detection tool for the quantitative determination of human IL-4.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for details of reconstitution instruction and specific concentration.
存储(Storage)
1. Unopened kit should be stored at 2℃-8℃ upon receiving.
2. Find the expiration date on the outside packaging and do not use reagents past their expiration date.
3. The opened kit should be stored per components table. The shelf life is 30 days from the date of opening.
组分(Materials Provided)
| ID | Components | Size |
| CRS004-C01 | Pre-coated Anti-IL-4 Antibody Microplate | 1 plate(8×12 strips) |
| CRS004-C02 | Human IL-4 Standard | 20 μg |
| CRS004-C03 | Biotin-Anti-IL-4 Antibody | 50 μL |
| CRS004-C04 | Streptavidin-HRP | 50 μL |
| CRS004-C05 | 10xWashing Buffer | 50 mL |
| CRS004-C06 | 2xDilution Buffer | 50 mL |
| CRS004-C07 | Substrate Solution | 12 mL |
| CRS004-C08 | Stop Solution | 7 mL |
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
典型数据-Typical Data Please refer to DS document for the assay protocol.

For each experiment, a standard curve needs to be set for each micro-plate, and the specific OD value may vary depending on different laboratories, testers, or equipments. The following example data is for reference only.
验证(Validation)
稀释线性(Dilution Linearity)
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples spiked with high concentrations of human IL-4 were serially diluted with calibrator diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
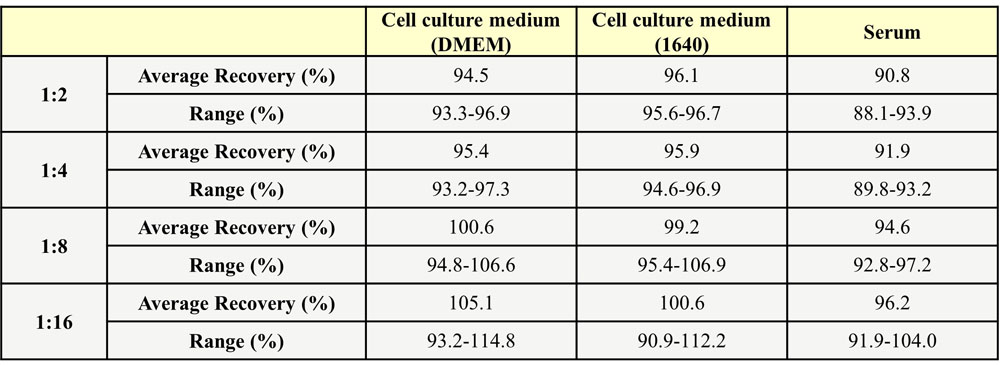
批内差异(Intra-Assay Statistics)
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision, Intra-Assay Precision CV<10%.
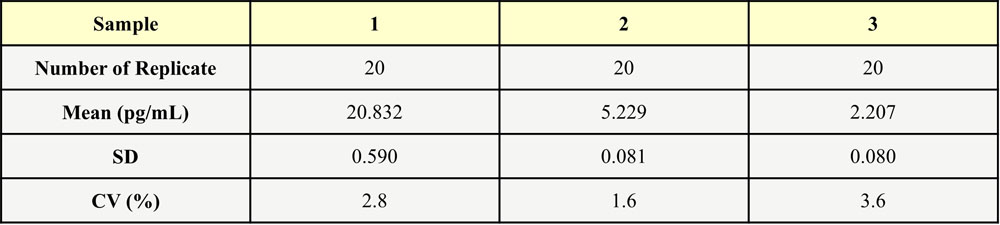
批间差异(Inter-Assay Statistics)
Three samples of known concentration were tested in three separate assays to assess inter-assay precision, Inter-Assay Precision CV<10%.
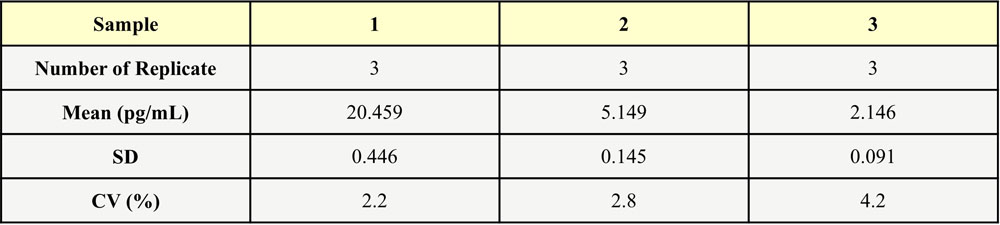
回收率(Recovery)
Three parts of blank serum were added with different concentrations of human IL-4, and the serum without human IL-4 was used as background to calculate the recovery rate. The range of the recovery rate is 80.9-97.7%, and the average recovery is 86.3%.

背景(Background):IL-4
Interleukin-4, is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells (Th0 cells to Th2 cells). In the presence of IL-4 and IL-13, cytokines that are produced in a Th-2 type response, particularly during allergy and parasitic infections, macrophages become differentially activated, And this cytokine is a ligand for interleukin 4 receptor. The interleukin 4 receptor also binds to IL13, which may contribute to many overlapping functions of this cytokine and IL13. STAT6, a signal transducer and activator of transcription, has been shown to play a central role in mediating the immune regulatory signal of this cytokine. Recently, researcher found that the cytokine IL-4 plays a key role in development of innate CD8+ T cells in the thymus of several gene-deficient mouse strains, including Itk, KLF2, CBP and Id3, without previous exposure to antigen.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















