分子别名(Synonym)
CD19,B4,CVID3,MGC12802
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
APC-Labeled Human CD19 (20-291), His Tag (CD9-HA2H5) is produced via conjugation of APC to Human CD19 (20-291), His Tag with a new generation site-specific technology under optimal conditions with a proprietary technology. Human CD19 (20-291), His Tag is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Pro 20 - Lys 291 (Accession # P15391-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Pro 20
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 33.7 kDa.
偶联(Conjugate)
APC
Excitation Wavelength: 640 nm
Emission Wavelength: 661 nm
应用说明(Application)
Please note that this product is NOT compatible to streptavidin detection system.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, 0.5% BSA, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please protect from light and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
活性(Bioactivity)-FACS
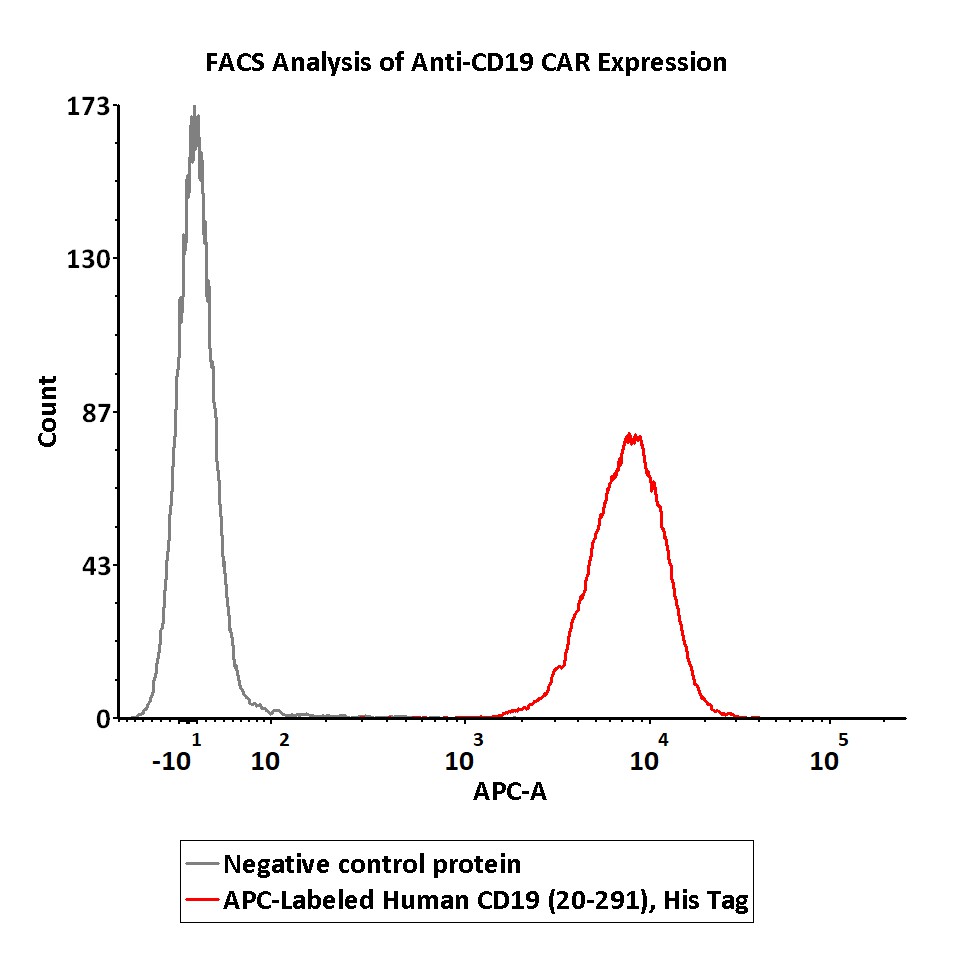
5e5 of anti-CD19 CAR-293 cells were stained with 100 μL of 1:50 dilution (2 μL stock solution in 100 μL FACS buffer) of APC-Labeled Human CD19 (20-291), His Tag (Cat. No. CD9-HA2H5) and negative control protein respectively. APC signal was used to evaluate the binding activity (QC tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 is also known as CD19 (Cluster of Differentiation 19), is a single-pass type I membrane protein which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. CD19 is expressed on follicular dendritic cells and B cells. In fact, it is present on B cells from earliest recognizable B-lineage cells during development to B-cell blasts but is lost on maturation to plasma cells. It primarily acts as a B cell co-receptor in conjunction with CD21 and CD81. Upon activation, the cytoplasmic tail of CD19 becomes phosphorylated, which leads to binding by Src-family kinases and recruitment of PI-3 kinase. As on T cells, several surface molecules form the antigen receptor and form a complex on B lymphocytes. The (almost) B cell-specific CD19 phosphoglycoprotein is one of these molecules. The others are CD21 and CD81. These surface immunoglobulin (sIg)-associated molecules facilitate signal transduction. On living B cells, anti-immunoglobulin antibody mimicking exogenous antigen causes CD19 to bind to sIg and internalize with it. The reverse process has not been demonstrated, suggesting that formation of this receptor complex is antigen-induced. This molecular association has been confirmed by chemical studies. Mutations in CD19 are associated with severe immunodeficiency syndromes characterized by diminished antibody production. CD19 has been shown to interact with: CD81, CD82, Complement receptor 2, and VAV2.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining












