分子别名(Synonym)
B7-H4,VTCN1,B7S1,B7h.5
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Canine B7-H4, His Tag (B74-C52H8) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Phe 29 - Ala 258 (Accession # XP_038547815.1).
Predicted N-terminus: Phe 29
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 27.2 kDa. The protein migrates as 44-55 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>95% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
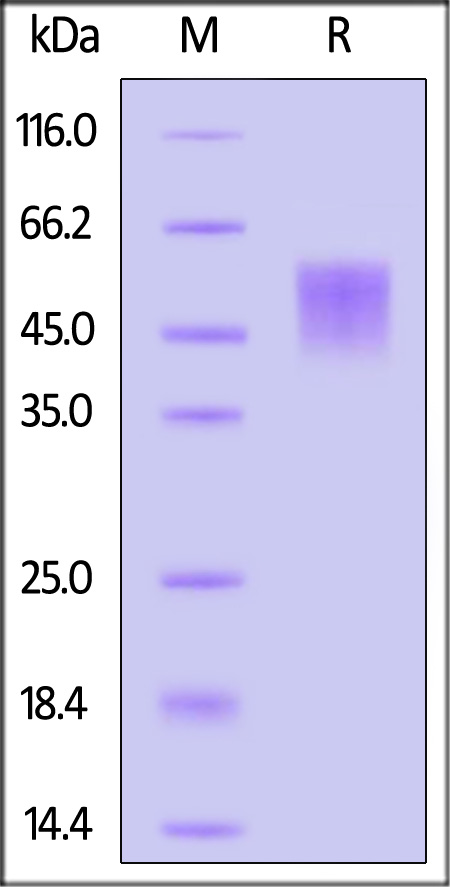
Canine B7-H4, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90%.
SEC-MALS
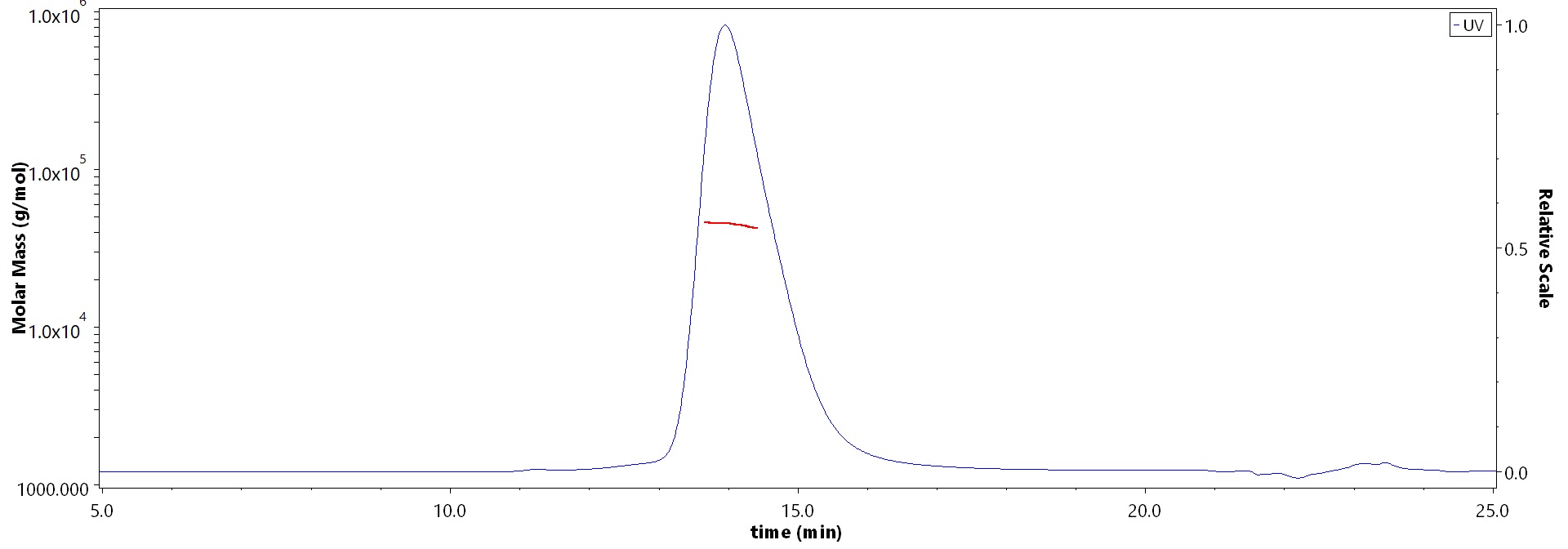
The purity of Canine B7-H4, His Tag (Cat. No. B74-C52H8) is more than 95% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 38-50 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
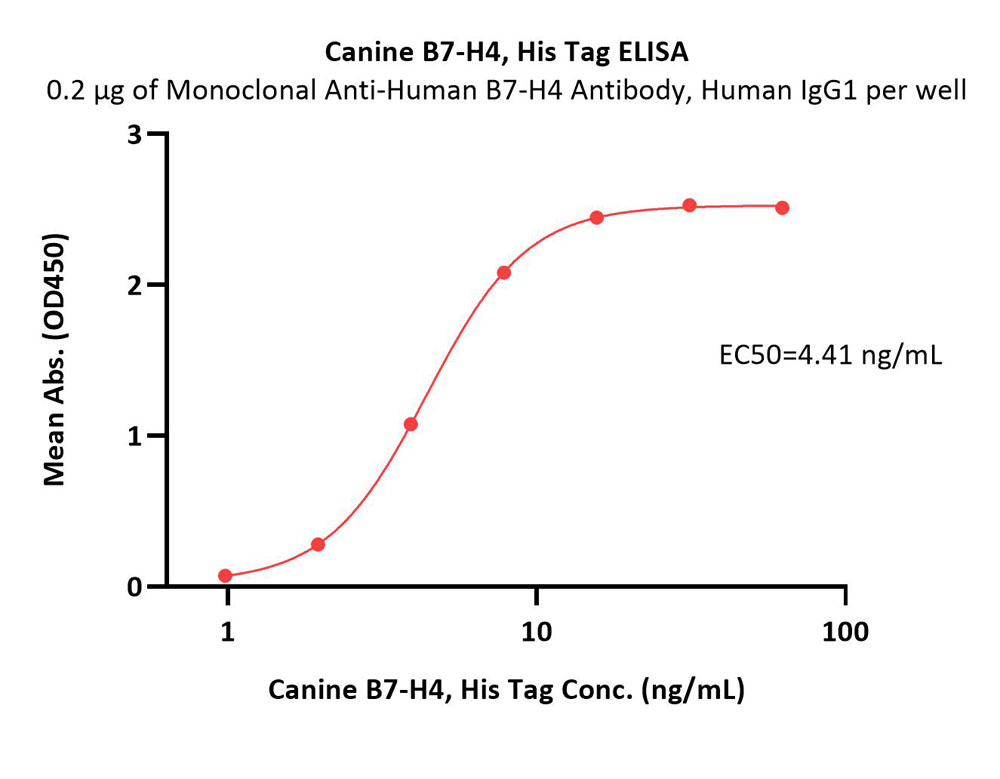
Immobilized Monoclonal Anti-Human B7-H4 Antibody, Human IgG1 at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Canine B7-H4, His Tag (Cat. No. B74-C52H8) with a linear range of 1-16 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
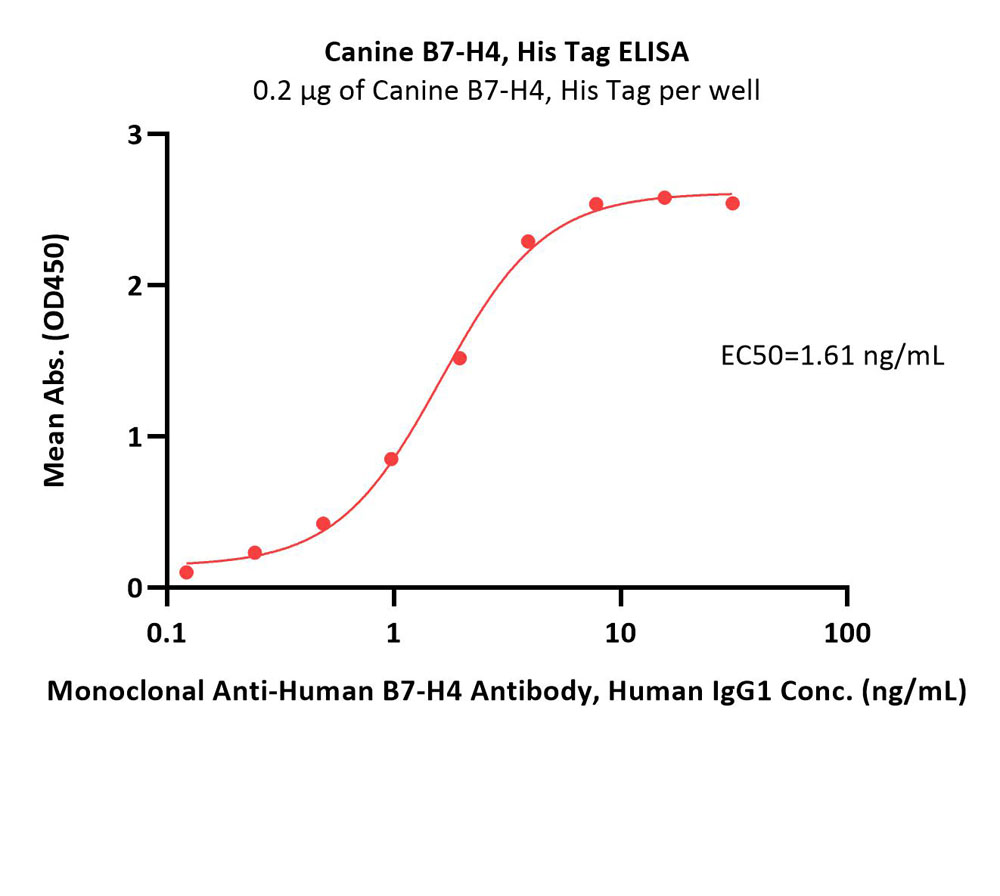
Immobilized Canine B7-H4, His Tag (Cat. No. B74-C52H8) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-Human B7-H4 Antibody, Human IgG1 with a linear range of 0.1-8 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-SPR
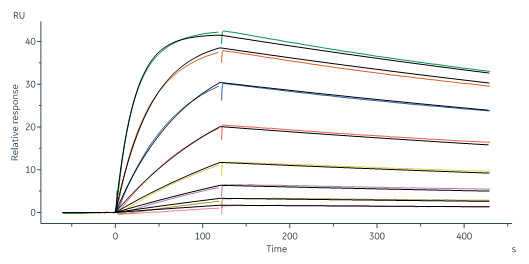
Anti-B7-H4 antibody, Human IgG1 captured on CM5 chip via Anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can bind Canine B7-H4, His Tag (Cat. No. B74-C52H8) with an affinity constant of 8.59 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
V-set domain-containing T-cell activation inhibitor 1 (VTCN1) is also known as Immune costimulatory protein B7-H4, Protein B7S1, T-cell costimulatory molecule B7x, B7H4, which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and BTN/MOG family. VTCN1 contains two Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. The expression of VTCN1 is up-regulated by IL6 and IL10 and is inhibited by GM-CSF and IL4 on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). VTCN1 / B7-H4 negatively regulates T-cell-mediated immune response by inhibiting T-cell activation, proliferation, cytokine production and development of cytotoxicity. VTCN1 involved in promoting epithelial cell transformation.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















