Getting ON-TRAC, a team-centred design study of a reflexivity aid to support resuscitation teams' information sharingMommers, Wulterkens, Winkel
et alAdv Simul (Lond) (2025) 10 (1), 17
Abstract: Effective information sharing is crucial for emergency care teams to maintain an accurate shared mental model. This study describes the design, simulation-based testing and implementation of a team reflexivity aid to facilitate in-action information sharing during resuscitations.A five-phase team-centred iterative design process was employed. Phase 1 involved a literature review to identify in-action cognitive aids. Phase 2 focused on conceptual design, followed by simulation-based testing and modifications in phase 3. Implementation through simulation-based user training occurred in phase 4 at a large non-university teaching hospital. Phase 5 evaluated the aid among resuscitation team members in the emergency department after one year.The phase 1 literature review identified 58 cognitive aids, with only 10 designed as 'team aid'. Studies using team information screens found increase team and task performance in simulation-based environments, with no evaluations in authentic workplaces. Phase 2 resulted in a three-section team reflexivity aid, iteratively modified in three rounds of simulation-based testing (N = 30 groups) phase 3 resulted in a team reflexivity aid containing five sections: resuscitation times and intervals, patient history, interventions on a longitudinal timeline, differential diagnosis and a quick review section. Phase 4 consisted of reflexivity aid user training with simulation-based education (N = 60 sessions) and the creation of a digital entry form to store data in the patient's electronic medical record. Evaluation after one year in phase 5, (N = 84) showed perceived improvements in communication (3.82 ± 0.77), documentation (4.25 ± 0.66), cognitive load (3.94 ± 0.68), and team performance (3.80 ± 0.76) on a 5-point Likert scale. Thematic analysis of user feedback identified improvements in both teamwork and taskwork. Teamwork enhancements included better situation awareness, communication and team participation. Taskwork improvements were seen in drug administration and clinical reasoning.This study demonstrated the successful development and implementation of a Team Reflexivity Aid for Cardiac arrests using simulation methodology. This task-focused team tool improved perceived team situation awareness, communication, and overall performance. The research highlights the interplay between task- and teamwork in healthcare settings, underscoring the potential for taskwork-oriented tools to benefit team dynamics. These findings warrant further investigation into team-supportive interventions and their impact on resuscitation outcomes.© 2025. The Author(s).
Cost-effective shallow genome-wide sequencing for profiling plasma cfDNA signatures to enhance lung cancer detectionNguyen, Vo, Tran
et alFuture Oncol (2025)
Abstract: Lung cancer (LC) screening via low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) faces challenges including high false-positive rates and low patient compliance. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)-based tests offer a minimally invasive alternative but are limited by high costs and low sensitivity, particularly in early-stage detection. This study introduces a cost-effective, shallow genome-wide sequencing approach for LC detection by profiling multiple cell-free DNA (cfDNA) signatures.We developed a multimodal cfDNA assay with shallow sequencing coverage (0.5×) that integrates fragmentomic, nucleosome, end-motif, and copy number alteration analyses. A machine-learning model trained on a discovery cohort (99 LC patients, 168 healthy controls) and validated on an independent cohort (58 LC patients, 71 controls) demonstrated robust performance.The ensemble model exhibited outstanding performance, achieving an AUC of 0.97 and a specificity of 92% in both the discovery and validation cohorts, with sensitivities of 94% and 90%, respectively. Notably, it outperformed hotspot mutation-based assays and the multi-cancer SPOT-MAS assay in sensitivity across all LC stages.This assay provides a cost-effective, accurate, and minimally invasive method for LC detection, addressing the limitations of current screening methods. It represents a promising complementary tool to improve early detection and patient outcomes in LC.
Evaluation of hemodynamic changes with ultrasound cardiac output monitoring during burn wound excision and skin grafting in severely burned patients: a prospective observational studyVo, Nguyen, Le
et alInt J Burns Trauma (2025) 15 (1), 1-10
Abstract: To evaluate changes in hemodynamic parameters using the Ultrasound Cardiac Output Monitoring (USCOM) method during general anesthesia for burn wound excision and skin grafting surgery in patients with severe burns.This prospective observational study included 40 severe burn patients, aged 18-60 years, treated at the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) of Le Huu Trac National Burn Hospital (Hanoi, Vietnam). All patients underwent burn wound excision and skin grafting between June 2023 and March 2024.The average heart rate (HR) at the study time points ranged from 116.8 to 124.3 beats/min. The differences in HR at T1, T2, T3, T5, and T6 compared to T0 were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Mean arterial pressure (MAP) at the study time points ranged from 73.8 mmHg to 95.68 mmHg. The differences in MAP at T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 compared to T0 were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Cardiac Output (CO) and Cardiac Index (CI) values at all study time points were within normal ranges (6-7.04 l/min and 3.66-4.33 l/min/m2, respectively). CO and CI were highest at T0 (7.04 l/min; 4.33 l/min/m2) and lowest at T1 (6 l/min; 3.66 l/min/m2). The differences in CO and CI at T1, T2, T4, T5, and T6 compared to T0 were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Stroke Volume (SV) and Stroke Volume Index (SVI) values at all time points were within normal ranges (51.2-56.75 ml and 30.93-34.53 ml/m2). The differences in SV and SVI at T1, T4, and T5 compared to T0 were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) and Systemic Vascular Resistance Index (SVRI) values at all time points were within normal ranges (1006.03-1240.45 d.s.cm-5 and 1681.98-2060.4 d.s.cm-5.m2). SVR and SVRI were highest at T6 (1240.45 d.s.cm-5 and 2060.4 d.s.cm-5.m2) and lowest at T1 (1006.03 d.s.cm-5 and 1681.98 d.s.cm-5.m2). The differences in SVR and SVRI at T1 compared to T0 were statistically significant (P < 0.05).The study demonstrated that hemodynamic parameters, including CO, CI, SV, SVI, SVR, and SVRI, remained within normal ranges throughout the anesthesia process. However, heart rate and blood pressure tended to be elevated, reflecting the hemodynamic characteristics of burn patients. This underscores the importance of close monitoring and adaptive management during anesthesia and resuscitation to ensure hemodynamic stability tailored to the characteristics of severe burn patients.IJBT Copyright © 2025.
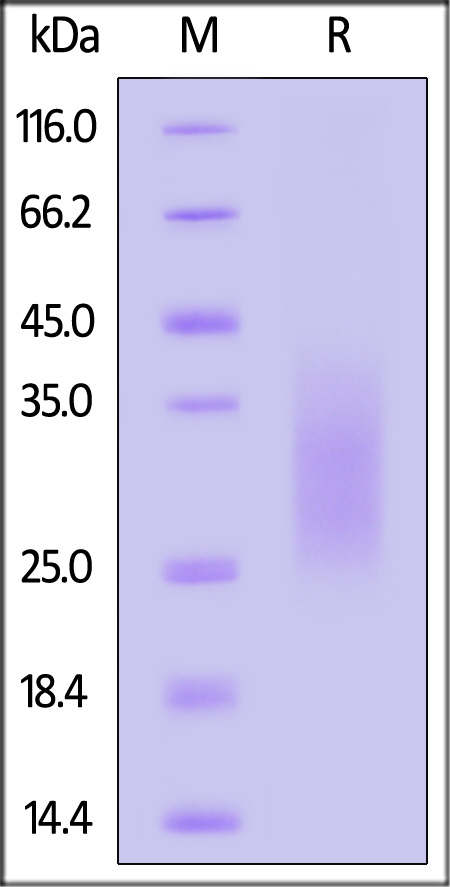
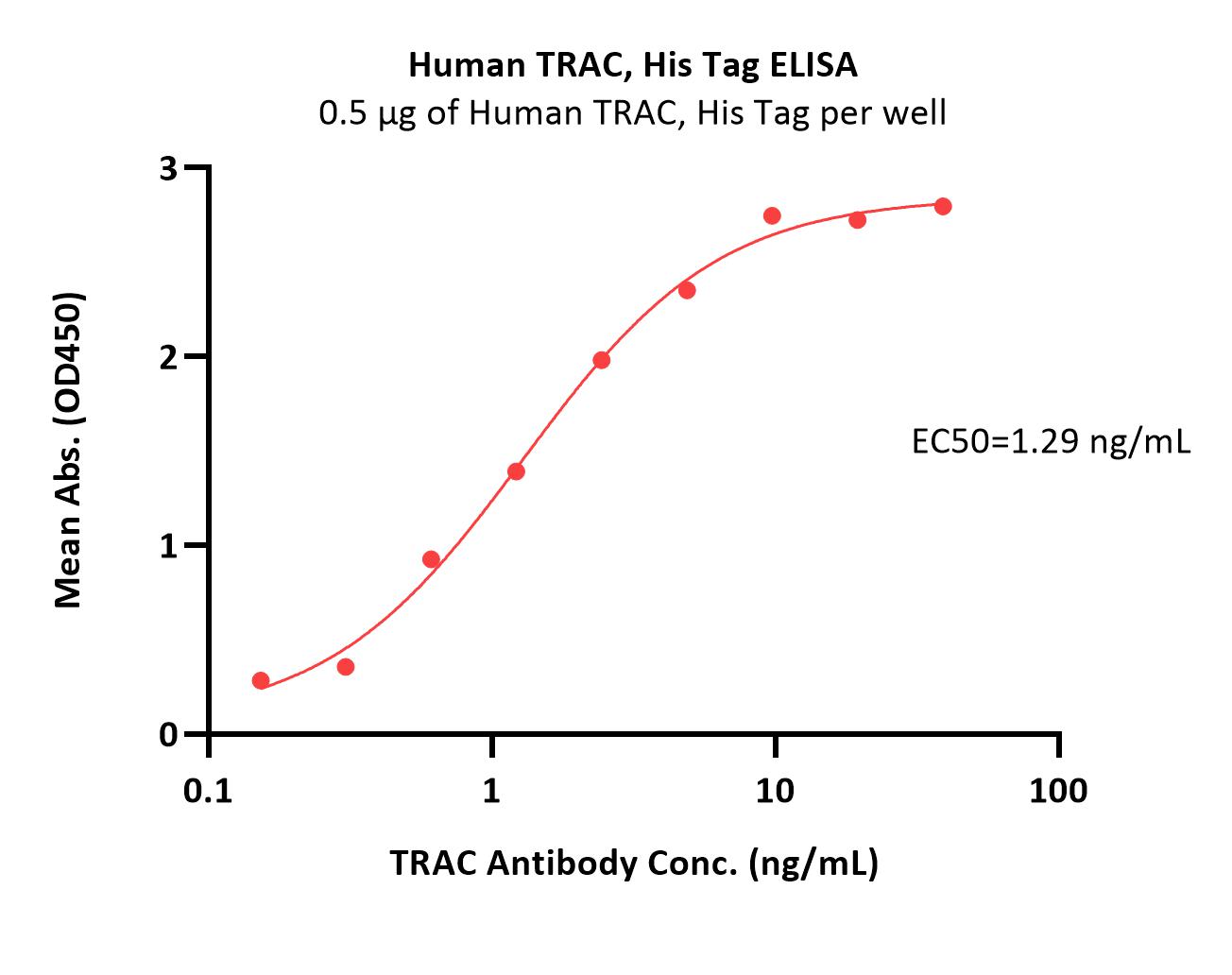
Efficient nonviral integration of large transgenes into human T cells using Cas9-CLIPTTommasi, Cappabianca, Bugel
et alMol Ther Methods Clin Dev (2025) 33 (1), 101437
Abstract: CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) combined with a nucleic acid template encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) transgene can edit human cells to produce CAR T cells with precise CAR insertion at a single locus. However, many human cells have adverse innate immune responses to foreign nucleic acids, particularly circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). Here, we introduce Cleaved, LInearized with Protein Template (Cas9-CLIPT), a circular plasmid containing a single target sequence for the Cas9 RNP, such that during manufacturing, Cas9-RNP binds and cleaves the plasmid to linearize the dsDNA in vitro. Cas9-RNP remains bound to the linearized template and is delivered to cells to promote precise knock-in via homology-directed repair with Cas9-CLIPT. Cas9-CLIPT Nanoplasmids generate up to 1.7-fold higher rates of precise knock-in relative to linearized dsDNA, reaching efficiencies up to 60% with non-homologous end joining inhibition. Cas9-CLIPT-manufactured GD2 TRAC-CAR T cells are potent against GD2+ neuroblastoma cells and exhibit an enriched stem cell memory phenotype. On several electroporation instruments and approaching clinically relevant yields, we successfully manufactured TRAC-CAR T cells using Cas9-CLIPT plasmids containing large (2-6 kb) transgenes. Cas9-CLIPT strategies have the potential to simplify donor template production and integrate large transgenes, allowing for more efficient nonviral manufacturing of multifunctional, genome-edited immune cell therapies.© 2025 The Author(s).
























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















