表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein (HLH-H82E8) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Gly 25 - Ile 308 (HLA-A*02:01) & Ile 21 - Met 119 (B2M) & SLYNTVATL peptide (Accession # AAA59606.1 (HLA-A*02:01) & P61769 (B2M) & SLYNTVATL).
Predicted N-terminus: Gly 25 & Ser
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)
Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein is produced by co-expression of HLA and B2M loaded with HIV Gag peptide.
This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus, followed by an Avi tag (Avitag™).
The protein has a calculated MW of 36.3 kDa and 13.7 kDa. The protein migrates as 40-43 kDa and 14 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
标记(Labeling)
Biotinylation of this product is performed using Avitag™ technology. Briefly, the single lysine residue in the Avitag is enzymatically labeled with biotin.
蛋白标记度(Protein Ratio)
Passed as determined by the HABA assay / binding ELISA.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>95% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)

Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
SEC-MALS
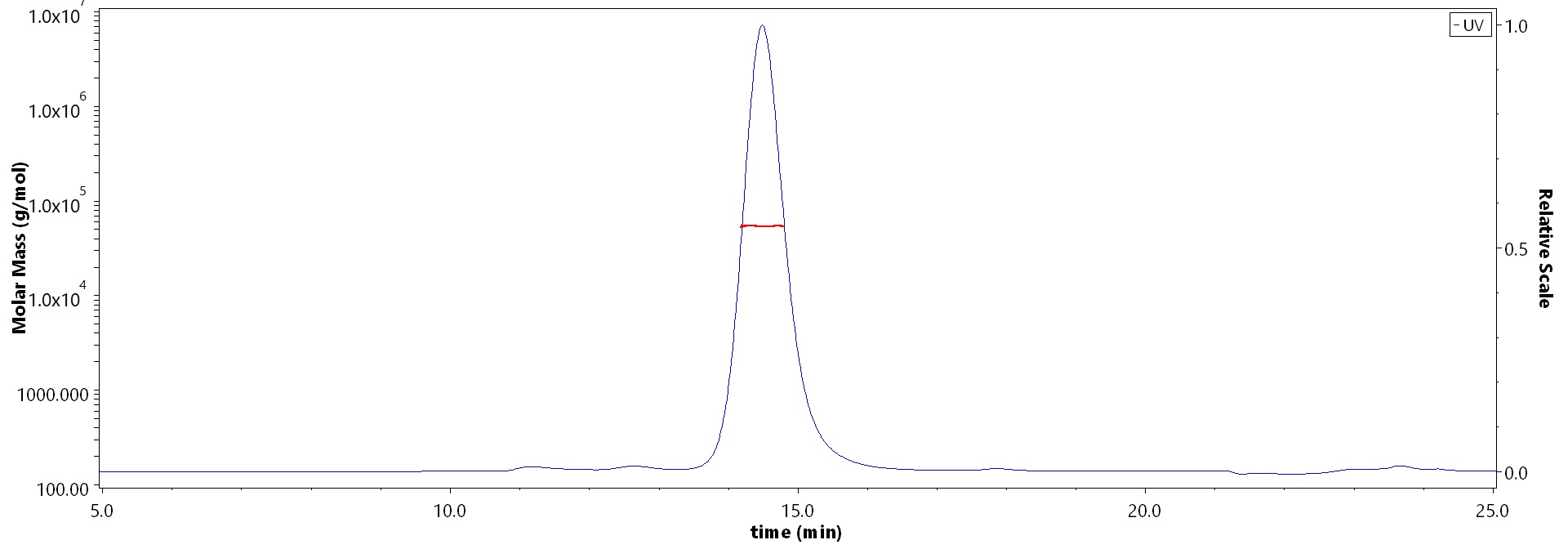
The purity of Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein (Cat. No. HLH-H82E8) is more than 95% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 48-58 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
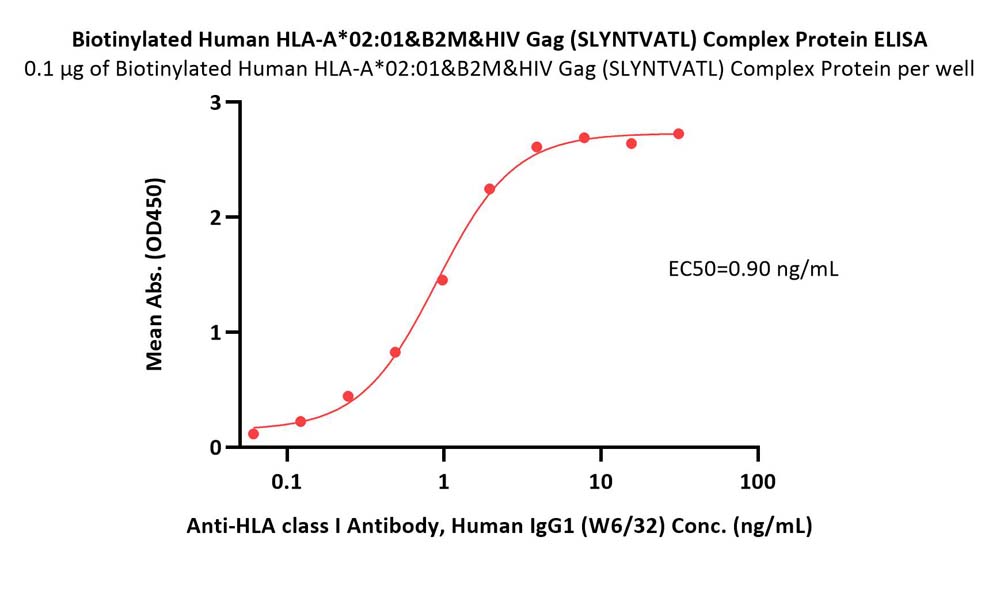
Immobilized Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein (Cat. No. HLH-H82E8) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) on streptavidin (Cat. No. STN-N5116) precoated (0.5 μg/well) plate can bind Anti-HLA class I Antibody, Human IgG1 (W6/32) with a linear range of 0.1-2 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
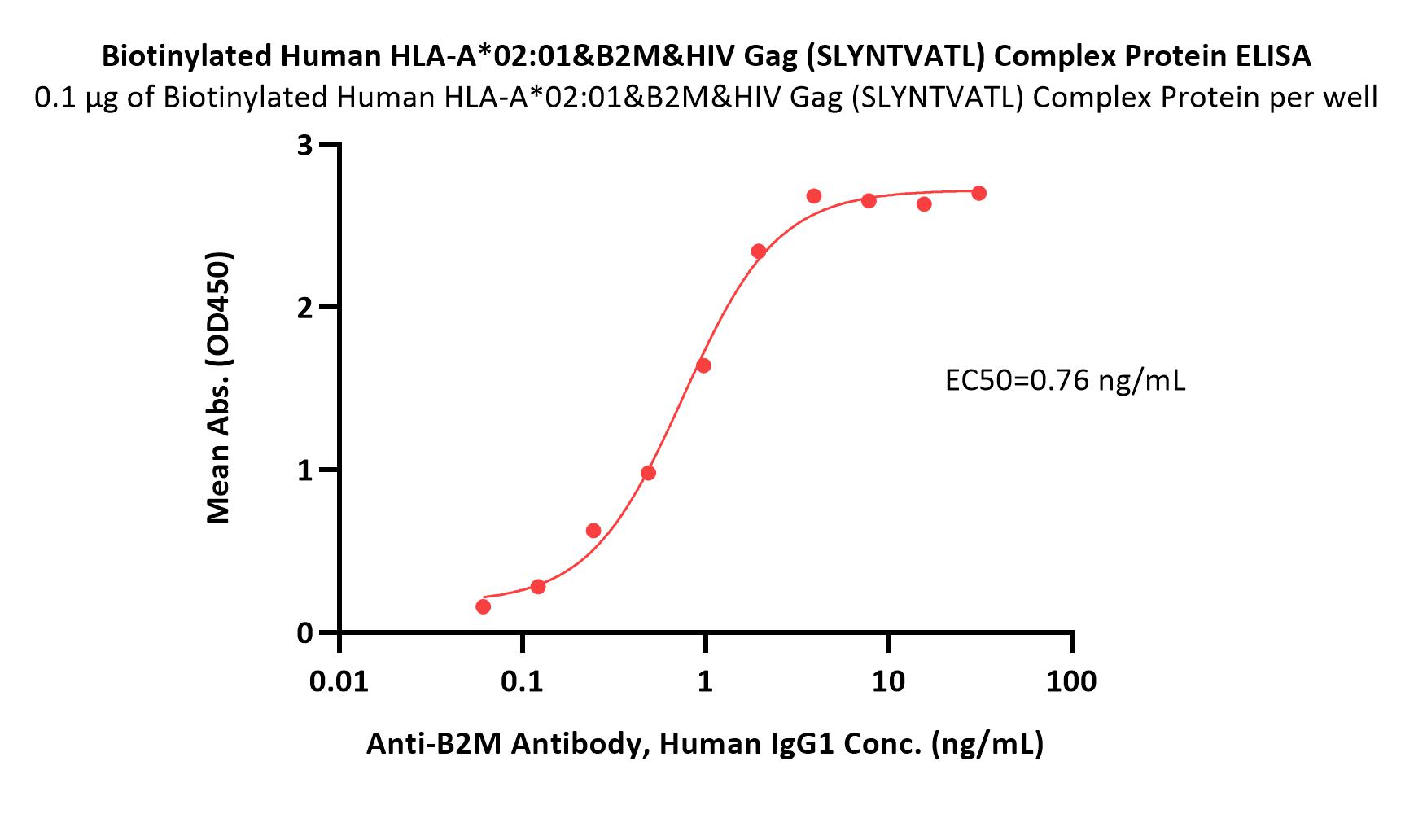
Immobilized Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein (Cat. No. HLH-H82E8) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) on streptavidin (Cat. No. STN-N5116) precoated (0.5 μg/well) plate can bind Anti-B2M Antibody, Human IgG1 with a linear range of 0.1-2 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-SPR

HIV Gag TCR captured on Protein A Chip can bind Biotinylated HumanHLA-A*02:01&B2M&HIV Gag (SLYNTVATL) Complex Protein (Cat. No. HLH-H82E8) with an affinity constant of 0.345 nM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). It can be transmitted via the exchange of a variety of body fluids from infected people, such as blood, breast milk, semen and vaginal secretions, And from a mother to her child during pregnancy and delivery. This disease can be managed by treatment regimens composed of a combination of antiretroviral (ARV) drugs. The Human HLA-A*0201 HIV (SLYNTVATL) complex protein is a complex of HLA-A*0201 of the MHC Class I, B2M, and SLYNTVATL peptide of the HIV.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















