A fusion intermediate gp41 immunogen elicits neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1Lai, Hock, Radzimanowski
et alJ Biol Chem (2014) 289 (43), 29912-26
Abstract: The membrane-proximal external region (MPER) of the human immunodeficiency virus, type 1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein subunit gp41 is targeted by potent broadly neutralizing antibodies 2F5, 4E10, and 10E8. These antibodies recognize linear epitopes and have been suggested to target the fusion intermediate conformation of gp41 that bridges viral and cellular membranes. Anti-MPER antibodies exert different degrees of membrane interaction, which is considered to be the limiting factor for the generation of such antibodies by immunization. Here we characterize a fusion intermediate conformation of gp41 (gp41(int)-Cys) and show that it folds into an elongated ∼ 12-nm-long extended structure based on small angle x-ray scattering data. Gp41(int)-Cys was covalently linked to liposomes via its C-terminal cysteine and used as immunogen. The gp41(int)-Cys proteoliposomes were administered alone or in prime-boost regimen with trimeric envelope gp140(CA018) in guinea pigs and elicited high anti-gp41 IgG titers. The sera interacted with a peptide spanning the MPER region, demonstrated competition with broadly neutralizing antibodies 2F5 and 4E10, and exerted modest lipid binding, indicating the presence of MPER-specific antibodies. Although the neutralization potency generated solely by gp140(CA018) was higher than that induced by gp41(int)-Cys, the majority of animals immunized with gp41(int)-Cys proteoliposomes induced modest breadth and potency in neutralizing tier 1 pseudoviruses and replication-competent simian/human immunodeficiency viruses in the TZM-bl assay as well as responses against tier 2 HIV-1 in the A3R5 neutralization assay. Our data thus demonstrate that liposomal gp41 MPER formulation can induce neutralization activity, and the strategy serves to improve breadth and potency of such antibodies by improved vaccination protocols.© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
HIV antigen incorporation within adenovirus hexon hypervariable 2 for a novel HIV vaccine approachMatthews, Fatima, Tang
et alPLoS One (2010) 5 (7), e11815
Abstract: Adenoviral (Ad) vectors have been used for a variety of vaccine applications including cancer and infectious diseases. Traditionally, Ad-based vaccines are designed to express antigens through transgene expression of a given antigen. However, in some cases these conventional Ad-based vaccines have had sub-optimal clinical results. These sub-optimal results are attributed in part to pre-existing Ad serotype 5 (Ad5) immunity. In order to circumvent the need for antigen expression via transgene incorporation, the "antigen capsid-incorporation" strategy has been developed and used for Ad-based vaccine development in the context of a few diseases. This strategy embodies the incorporation of antigenic peptides within the capsid structure of viral vectors. The major capsid protein hexon has been utilized for these capsid incorporation strategies due to hexon's natural role in the generation of anti-Ad immune response and its numerical representation within the Ad virion. Using this strategy, we have developed the means to incorporate heterologous peptide epitopes specifically within the major surface-exposed domains of the Ad capsid protein hexon. Our study herein focuses on generation of multivalent vaccine vectors presenting HIV antigens within the Ad capsid protein hexon, as well as expressing an HIV antigen as a transgene. These novel vectors utilize HVR2 as an incorporation site for a twenty-four amino acid region of the HIV membrane proximal ectodomain region (MPER), derived from HIV glycoprotein gp41 (gp41). Our study herein illustrates that our multivalent anti-HIV vectors elicit a cellular anti-HIV response. Furthermore, vaccinations with these vectors, which present HIV antigens at HVR2, elicit a HIV epitope-specific humoral immune response.
Evaluating the immunogenicity of a disulfide-stabilized, cleaved, trimeric form of the envelope glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1Beddows, Schülke, Kirschner
et alJ Virol (2005) 79 (14), 8812-27
Abstract: The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope glycoprotein (Env) complex comprises three gp120 exterior glycoproteins each noncovalently linked to a gp41 transmembrane glycoprotein. Monomeric gp120 proteins can elicit antibodies capable of neutralizing atypically sensitive test viruses in vitro, but these antibodies are ineffective against representative primary isolates and the gp120 vaccines failed to provide protection against HIV-1 transmission in vivo. Alternative approaches to raising neutralizing antibodies are therefore being pursued. Here we report on the antibody responses generated in rabbits against a soluble, cleaved, trimeric form of HIV-1(JR-FL) Env. In this construct, the gp120 and gp41 moieties are covalently linked by an intermolecular disulfide bond (SOS gp140), and an I559P substitution has been added to stabilize gp41-gp41 interactions (SOSIP gp140). We investigated the value of DNA priming and compared the use of membrane-bound and soluble priming antigens and of repeat boosting with soluble and particulate protein antigen. Compared to monomeric gp120, SOSIP gp140 trimers elicited approximately threefold lower titers of anti-gp120 antibodies. Priming with DNA encoding a membrane-bound form of the SOS gp140 protein, followed by several immunizations with soluble SOSIP gp140 trimers, resulted in antibodies capable of neutralizing sensitive strains at high titers. A subset of these sera also neutralized, at lower titers, HIV-1(JR-FL) and some other primary isolates in pseudovirus and/or whole-virus assays. Neutralization of these viruses was immunoglobulin mediated and was predominantly caused by antibodies to gp120 epitopes, but not the V3 region.
Stabilization of the soluble, cleaved, trimeric form of the envelope glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1Sanders, Vesanen, Schuelke
et alJ Virol (2002) 76 (17), 8875-89
Abstract: The envelope glycoprotein (Env) complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 has evolved a structure that is minimally immunogenic while retaining its natural function of receptor-mediated virus-cell fusion. The Env complex is trimeric; its six individual subunits (three gp120 and three gp41 subunits) are associated by relatively weak, noncovalent interactions. The induction of neutralizing antibodies after vaccination with individual Env subunits has proven very difficult, probably because they are inadequate mimics of the native complex. Our hypothesis is that a stable form of the Env complex, perhaps with additional modifications to rationally alter its antigenic structure, may be a better immunogen than the individual subunits. A soluble form of Env, SOS gp140, can be made that has gp120 stably linked to the gp41 ectodomain by an intermolecular disulfide bond. This protein is fully cleaved at the proteolysis site between gp120 and gp41. However, the gp41-gp41 interactions in SOS gp140 are too weak to maintain the protein in a trimeric configuration. Consequently, purified SOS gp140 is a monomer (N. Schülke, M. S. Vesanen, R. W. Sanders, P. Zhu, D. J. Anselma, A. R. Villa, P. W. H. I. Parren, J. M. Binley, K. H. Roux, P. J. Maddon, J. P. Moore, and W. C. Olson, J. Virol. 76:7760-7776, 2002). Here we describe modifications of SOS gp140 that increase its trimer stability. A variant SOS gp140, designated SOSIP gp140, contains an isoleucine-to-proline substitution at position 559 in the N-terminal heptad repeat region of gp41. This protein is fully cleaved, has favorable antigenic properties, and is predominantly trimeric. SOSIP gp140 trimers are noncovalently associated and can be partially purified by gel filtration chromatography. These gp140 trimers are dissociated into monomers by anionic detergents or heat but are relatively resistant to nonionic detergents, high salt concentrations, or exposure to a mildly acidic pH. SOSIP gp140 should be a useful reagent for structural and immunogenicity studies.

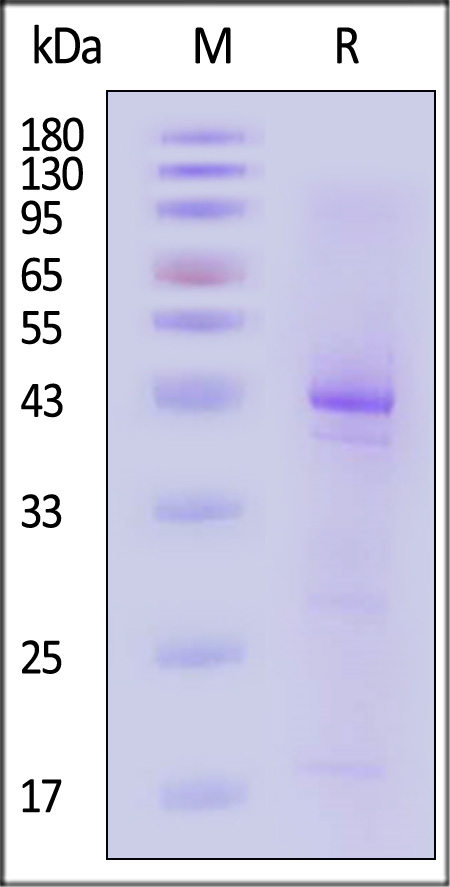
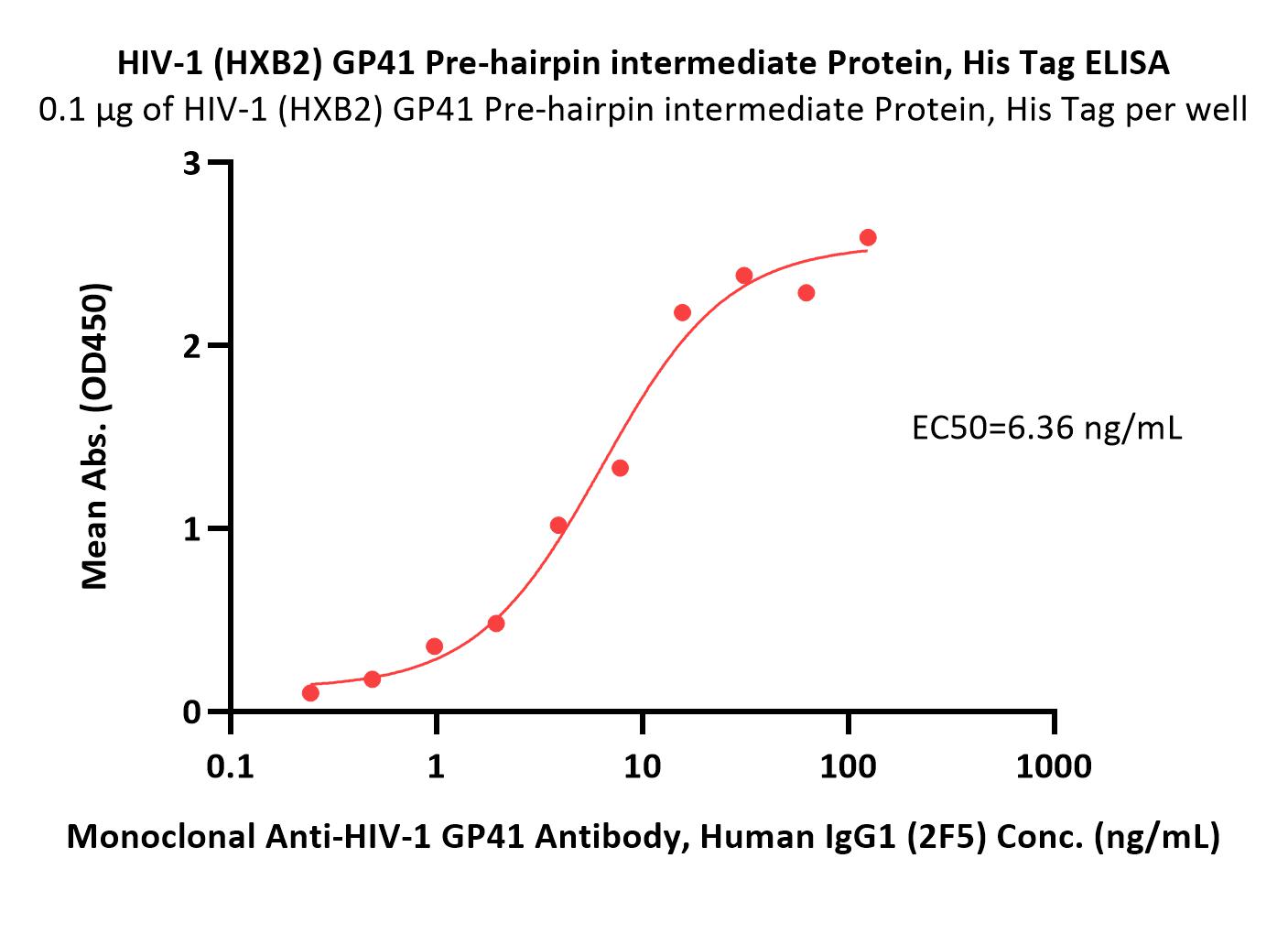
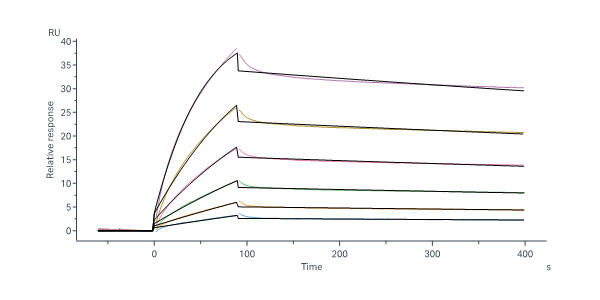























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















