分子别名(Synonym)
FGF2,BFGF,FGFB,FGF basic,HBGF-2
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human FGF basic (154aa) Protein, premium grade (BFF-H5115) is expressed from E. coli cells. It contains AA Ala 135 - Ser 288 (Accession # NP_001997.5).
Predicted N-terminus: Met
It is produced under our rigorous quality control system that incorporates a comprehensive set of tests including sterility and endotoxin tests. Product performance is carefully validated and tested for compatibility for cell culture use or any other applications in the early preclinical stage. When ready to transition into later clinical phases, we also offer a custom GMP protein service that tailors to your needs. We will work with you to customize and develop a GMP-grade product in accordance with your requests that also meets the requirements for raw and ancillary materials use in cell manufacturing of cell-based therapies.
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries no "tag".
The protein has a calculated MW of 17.3 kDa. The protein migrates as 15-17 kDa when calibrated against Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE).
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 0.01 EU per μg by the LAL method.
宿主蛋白残留(Host Cell Protein)
<0.5 ng/µg of protein tested by ELISA.
宿主核酸残留(Host Cell DNA)
<0.02 ng/μg of protein tested by qPCR.
无菌(Sterility)
Negative
支原体(Mycoplasma)
Negative.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
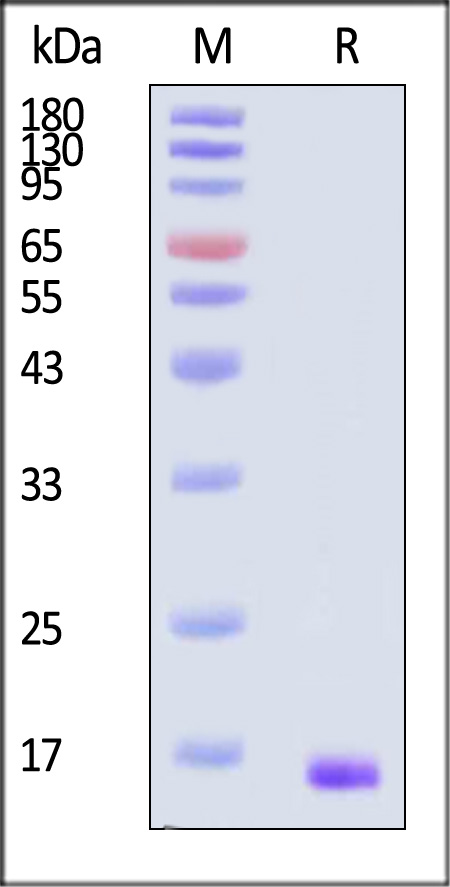
Human FGF basic (154aa) Protein, premium grade on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95% (With Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker).
SEC-MALS
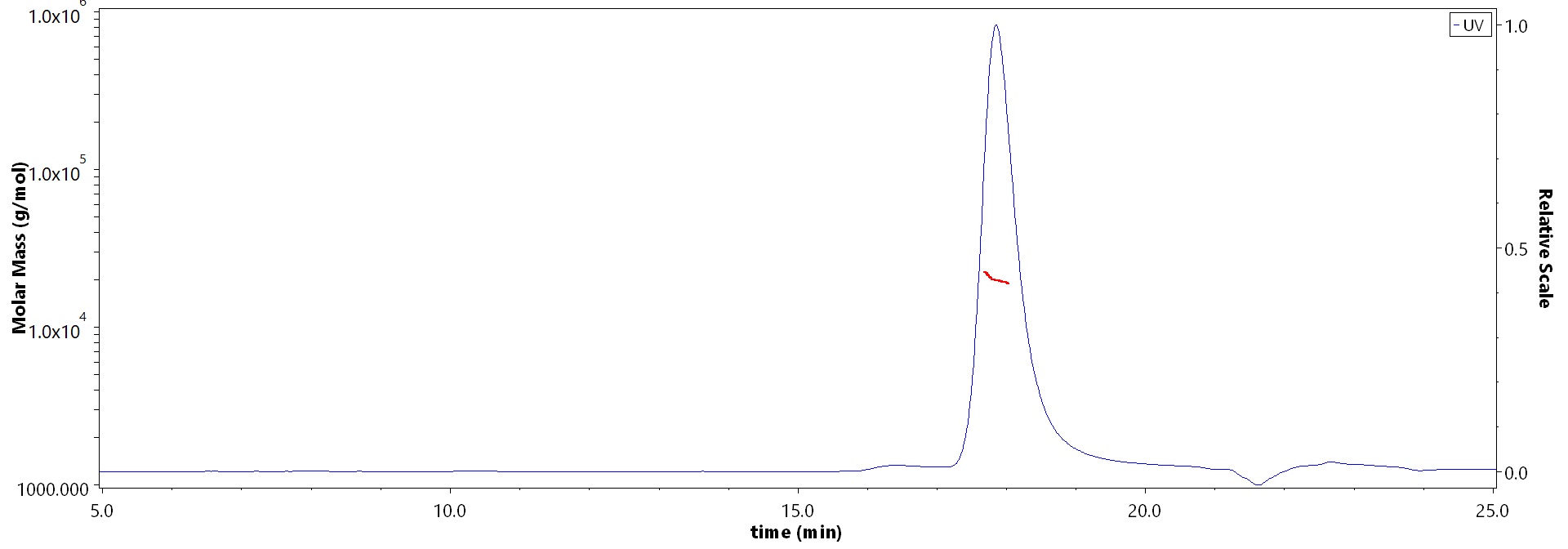
The purity of Human FGF basic (154aa) Protein, premium grade (Cat. No. BFF-H5115) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 15-25 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
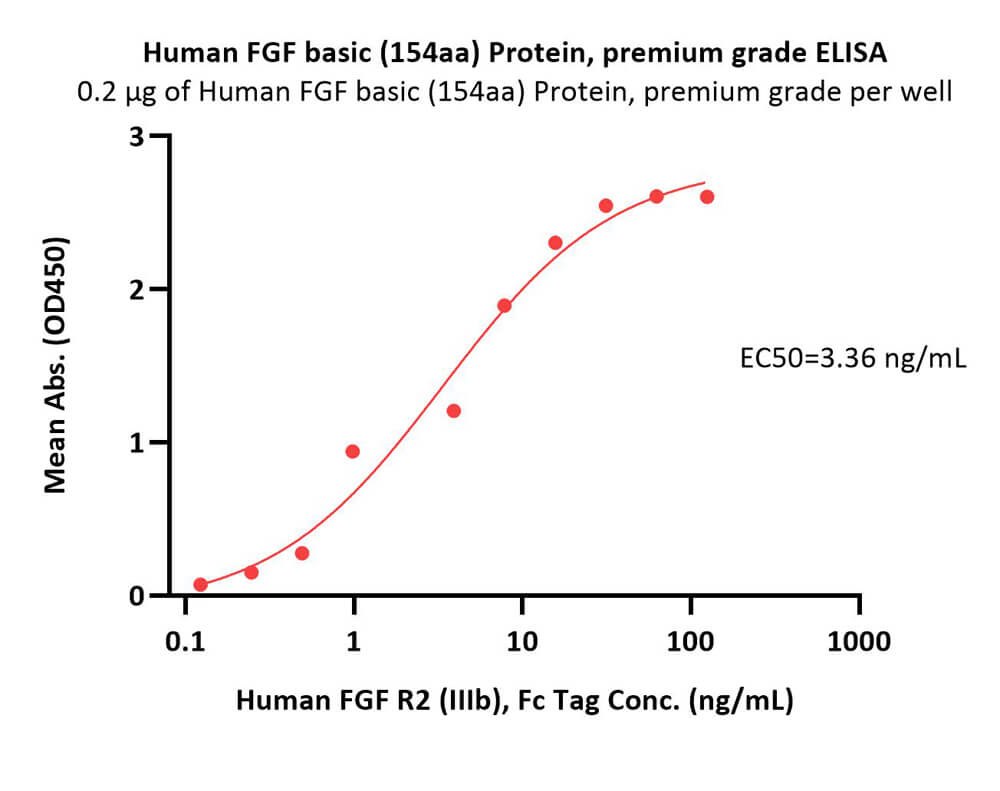
Immobilized Human FGF basic (154aa) Protein, premium grade (Cat. No. BFF-H5115) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human FGF R2 (IIIb), Fc Tag (Cat. No. FGB-H5256) with a linear range of 0.2-8 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
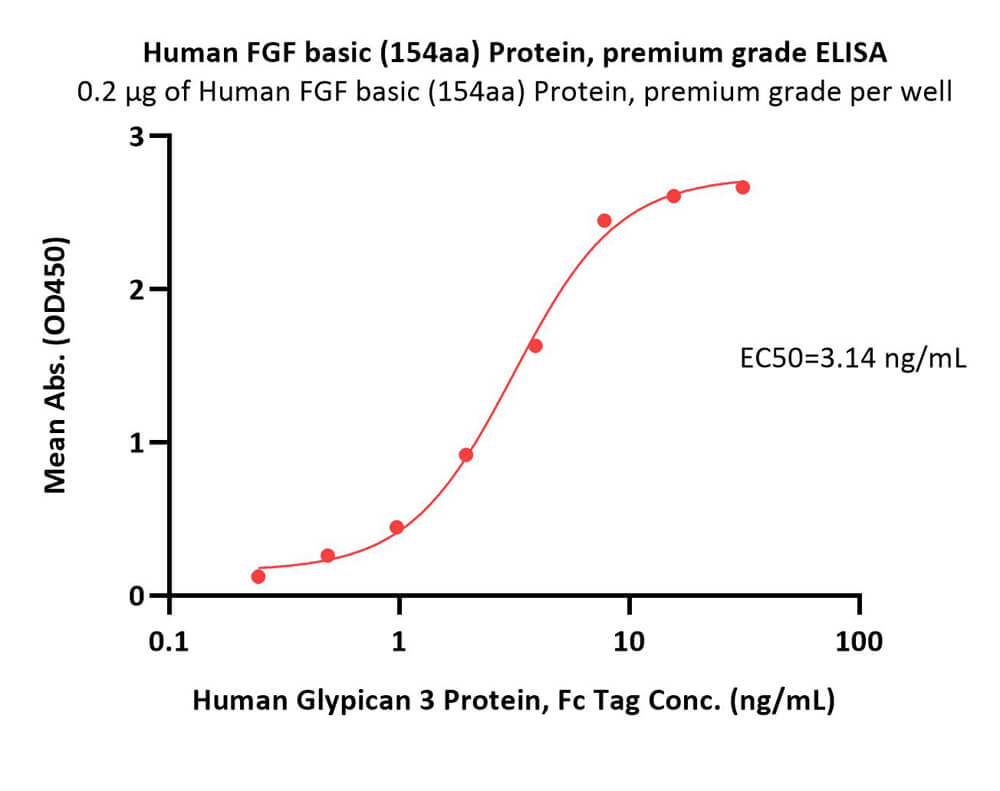
Immobilized Human FGF basic (154aa) Protein, premium grade (Cat. No. BFF-H5115) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human Glypican 3 Protein, Fc Tag (Cat. No. GP3-H5258) with a linear range of 0.2-8 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
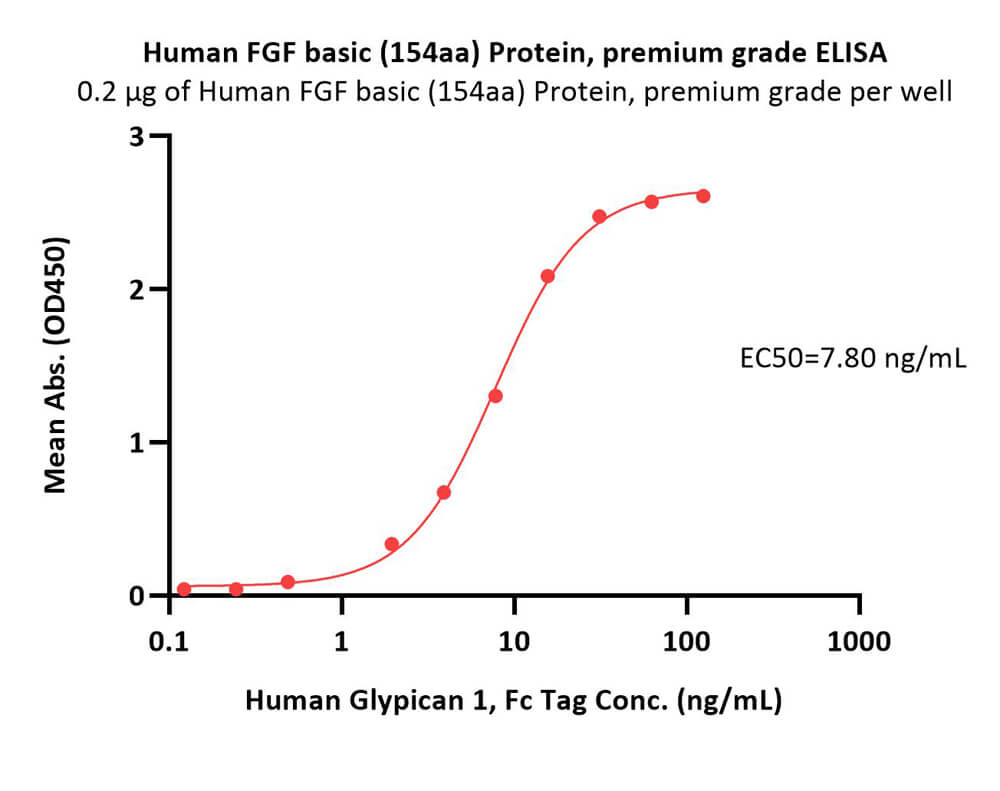
Immobilized Human FGF basic (154aa) Protein, premium grade (Cat. No. BFF-H5115) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human Glypican 1, Fc Tag (Cat. No. GP1-H5254) with a linear range of 0.2-8 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
FGF basic (also known as FGF2 and HBGF-2) is an 18-34 kDa, heparin-binding member of the FGF superfamily of molecules (1-3). Superfamily members are characterized by the presence of a centrally placed beta -trefoil structure. FGF acidic (FGF-1) and FGF basic (FGF2) were the first two identified FGFs, and the designations acidic and basic refer to their relative isoelectric points. Human FGF basic is 288 amino acids (aa) in length. There are multiple start sites, four of which utilize atypical CUG codons, and one that initiates at an AUG start site (4 - 6). The four CUG start sites generate high molecular weight (HMW) FGF basic. There is a 34 kDa, 288 aa form, a 24 kDa, 210 aa form, a 22.5 kDa, 201 aa form, and a 22 kDa, 196 aa form. All are retained intracellularly, undergo extensive methylation, and possess one or more nuclear localization signals (NLS) (7-9). The AUG initiating form is 18 kDa and 155 aa in length. There is no signal sequence (ss). It is, however, secreted directly through the plasma membrane via a mechanism that appears to be dependent upon tertiary structure (10). In place of a ss, there is purportedly a 9 aa N-terminal prosegment that precedes a 146 aa mature segment (11). Early isolations of 18 kDa bovine FGF basic yielded 146 aa molecules, an effect attributed to the presence of acid proteases (12). The molecule contains a heparin-binding site (aa residues 128-144), and undergoes phosphorylation at Ser117 (13). There is also an ill-defined C-terminal NLS that may be more “functional” (or 3-dimensional) than structural (7). Human 146 aa FGF basic is 97% aa identical to mouse FGF basic (14).























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















