PEGylated lipid screening, composition optimization, and structure-activity relationship determination for lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA deliveryLiu, Kim, Li
et alNanoscale (2025)
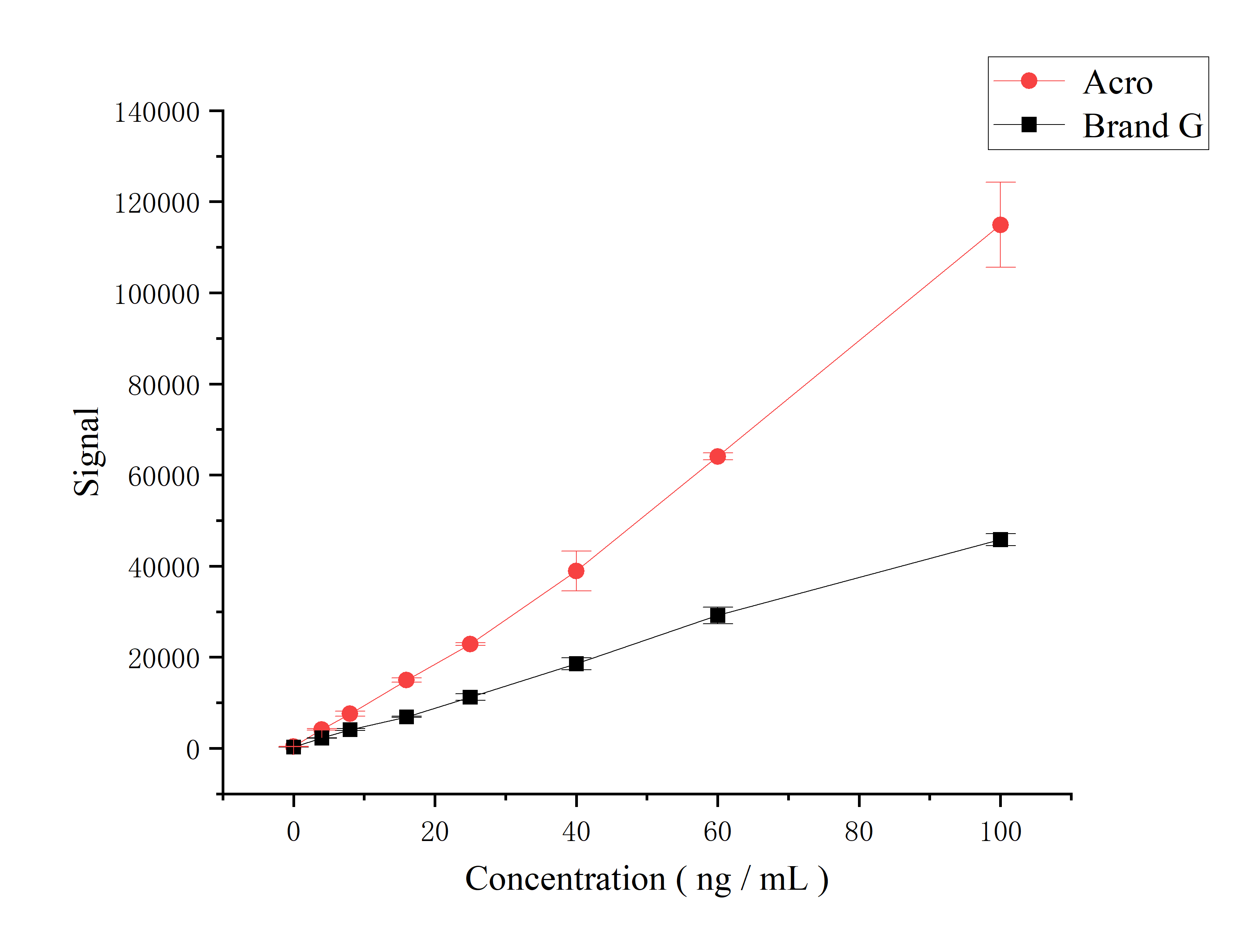
Abstract: Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as effective carriers for mRNA delivery in vaccine and therapeutic applications, attracting substantial attention since the COVID-19 pandemic. Continued efforts are crucial to optimize LNP composition for improved delivery efficacy and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms driving differences in protein expression. This study systematically screened PEGylated lipids for intramuscular mRNA delivery, followed by optimization of the formulation composition, physicochemical characterization, and investigation of the structure-activity relationship (SAR). Using a model ionizable lipid, we initially evaluated twenty-nine PEGylated lipids from four lipid families (glyceride, phosphoethanolamine (PE), cholesterol, and ceramide), each varying in linker chemistries, tail structures, or PEG molecular weights. 1,2-Dimyristoyl-rac-glycero-3-methoxypolyethylene glycol - 5000 (DMG-PEG5k) was identified as a promising candidate from this screening. Using a design of experiments (DoE) approach, we further optimized the formulation to increase in vivo transfection efficacy, achieving an increase in protein expression over the DMG-PEG2k benchmark. To explore the SAR of the DoE formulations, advanced physicochemical characterization was conducted including Laurdan assay, SAXS, Cryo-TEM, and QCM-D, alongside standard LNP analysis. Among the key factors examined, high mRNA encapsulation efficiency, LNP membrane integrity (especially under acidic conditions), and ordered internal structures were identified as the critical parameters for transfection efficiency. mRNA encapsulation efficiency increased with a lower PEG-lipid fraction. LNP membrane integrity, assessed by the generalized polarization (GP) ratio at pH 7.5 and 4.5 from the Laurdan assay, was strongly affected by the ionizable lipid ratio and, to a lesser extent, the cholesterol ratio. A lower GP7.5/GP4.5 ratio correlated with enhanced protein expression, primarily driven by a higher GP4.5 observed with lower ionizable lipid and higher cholesterol fractions. Overall, balancing the ratios of all LNP components is critical for maximizing LNP functionality. This study presents a systematic evaluation and characterization of LNPs with different PEG-lipid moieties, deepens SAR understanding, and provides valuable guidelines for rationally designing more effective next-generation LNPs.
Classification of red beet and sugar beet for drought tolerance using morpho-physiological and stomatal traitsKaya, Ergin
PeerJ (2025) 13, e19133
Abstract: Drought is a global phenomenon that endangers agricultural production by creating water scarcity. Selecting drought-tolerant cultivars, varieties, and species is essential for maintaining the food supply and advancing breeding efforts. The study aimed to compare red beet (Beta vulgaris L. var. cruenta) and sugar beet (B. vulgaris L. var. altissima Döll.) for drought tolerance at the early growth stage considering morpho-physiological and stomatal parameters. Three red beet cultivars (Bicores, BT Pancina, and Yakut) and three sugar beet cultivars (Mohican, Orthega KWS, and Valentina) were subjected to various drought stress (Control, 10%, and 20% PEG-6000) for 30 days at the four-leaf stage. Fresh and dry plant weight, leaf area, dry matter, chlorophyll content (SPAD), leaf temperature, relative water content, membrane stability index, stomatal density, and size were investigated. The results revealed that the cultivars exhibited different responses to drought stress, and a greater percentage reduction in morphological parameters was observed in red beet cultivars. Drought markedly reduced the fresh and dry weights, leaf area, relative water content, membrane stability, and stomatal size. Enhanced dry matter and stomatal density were identified. The stomatal density increased from 158 to 215 mm-2 while the stomatal size decreased from 433 to 342 µm2 in the plants subjected to 20% PEG. Moderate drought stress effectively distinguished drought-tolerant sugar beet and red beet genotypes. It was concluded that sugar beet appeared to be more drought-tolerant than red beet and that the membrane stability index, relative water content, and stomatal density could be effectively used for selecting drought-tolerant beet genotypes.©2025 Kaya and Ergin.
A self-accelerating 'copper bomb' strategy activated innate and adaptive immune response against triple-negative breast cancerXu, Zhou, Hong
et alBioact Mater (2025) 49, 193-206
Abstract: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) presents therapeutic challenges due to its aggressive, drug-resistance, and low immunological reactivity. Cuproptosis, an emerging therapeutic modality, is a promising strategic intervention for treating TNBC. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of cuproptosis is compromised by tumor adaptations, including the Warburg effect, increased intracellular glutathione (GSH), and copper efflux, thus breaking the barrier of cuproptosis is the basis for developing cuproptosis-based clinical therapies. Herein, a self-accelerating strategy utilizing a pH-responsive copper framework encapsulating glucose oxidase (GOx), modified with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and tumor-penetrating peptide (tLyp1) has been developed. Upon reaching the acidic tumor microenvironment, the released GOx increases intracellular acidity and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The elevated intracellular GSH and H2O2 serve as "fuel" to amplify the copper-based catalytic within tumor cells. Concurrently, the reduction of copper efflux proteins (ATP7B) and the depletion of GSH lead to copper overload in tumor cells, leading to cuproptosis via copper overload, mitochondrial disruption, and Fe-S protein instability. This constellation of interrelated events constitutes a potent "Copper Bomb," which concurrently triggers the immune system and effectively kills the tumor. It robustly engages innate and adaptive immunity via the release of mitochondrial DNA, facilitating the cGAS-STING pathway and precipitating immunogenic cell death. This process reverses the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, eliminates tumor cells, and suppresses metastasis, thus offering a novel therapeutic modality for the comprehensive treatment of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).© 2025 The Authors.
Chemical composition, in vitro gas production, and nutrient degradability of carob leaves as a sustainable feed for ruminants in Tunisia and PalestineGhzayel, Ammar, Zoabi
et alFront Vet Sci (2025) 12, 1433814
Abstract: Carob leaves may be a potential roughage source for ruminants in arid areas. The nutritive value of this feedstuff may be considerably enhanced by the application of solid-phase chemical treatments. This study aimed to evaluate the nutritive value of carob leaves collected from Tunisia and Palestine untreated or treated with urea or sodium hydroxide (NaOH), or supplemented with polyethylene glycol (PEG) on chemical composition and in vitro ruminal fermentation.Carob leaf samples were collected from either Palestine or Tunisia, and were used either untreated (control) or treated with urea, NaOH at 4% or PEG at 100 mg/g (dry matter (DM) basis), and analyzed for chemical composition. Carob leaves were incubated in vitro in diluted rumen fluid fermentation for 48 h, measuring fermentation gasses [methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2)], DM degradability and fermentation kinetics.Results showed a significant country × treatment interaction for most measured parameters, indicating that treatment effects are constrained by the origin of the leaves. Palestine untreated carob leaves had higher (p < 0.001) crude fat, crude protein (CP) and neutral detergent fiber (NDF), but less nonstructural carbohydrate (NSC), acid detergent fiber (ADF) and acid detergent lignin than Tunisia leaves. Tunisia carob leaves had higher concentration (p < 0.01) of flavonoids and tannins than leaves from Palestine. Of the three treatments tested, the addition of PEG increased (p < 0.01) the gas production during the incubation in diluted rumen fluid of carob leaves and this effect was greater with leaves from Palestine than with those from Tunisia. The other treatments had less noticeable effects, which were different when applied to the leaves from one or another country, given the significance of the interaction country × treatment detected for most of the variables studied. PEG, NaOH and urea treatments of carob leaves can be applied to enhance the ruminal fermentation and energy value of this feedstuff. However, the effects of these treatments are highly dependent on the parent material, and seem to be more effective when applied to a low digestible material.Copyright © 2025 Ghzayel, Ammar, Zoabi, Abou Aziz, Kholif, Adegbeye, Ben Abdallah, de Haro-Martí, Lopez and Chahine.


























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















