背景(Background)
Residual host cell DNA refers to fragments of DNA from the host organism that are left behind after a biological process such as the production of a biopharmaceutical product or the cultivation of a cell line. This residual DNA can potentially contaminate the final product and affect its safety and efficacy. In the context of biopharmaceutical production, regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA have set limits on the amount of residual host cell DNA that is acceptable in a final product. These limits vary depending on the type of product and the route of administration, and residue host cell DNA quantitation kits are designed to ensure that the final product is safe for human use.
产品描述(Product Details)
Pichia pastoris resDNA Quantitation Kit is designed for quantitative detection of residual Pichia pastoris DNA in biopharmaceuticals (Antibodies, Vaccines, etc.). Based on real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) method, this kit makes the detection of the residual DNA from Pichia pastoris rapid and reliable. The lower limit of quantitation is 3 fg/µL. All procedures are typically in less than 4 hours.
Use the kit after you extract host cell DNA from test samples. To achieve the best performances, resDNA Sample Preparation Kit Ⅱ(Magnetic Beads) (Cat. No. OPA-R024) is recommended for DNA extraction.
产品特性(Features)
- High sensitivity for optimal product safety: LLOD (1 fg/µL) for detection of residue host cell DNA
- High specificity: No cross-reactivity with unrelated DNA
- Validation: ICH Q2(R2) as Validation of Analytical Procedures
- High-quality: This kit is manufactured in GMP-like facility and alignment with the ISO 13485 standard.
应用说明(Application)
The kit is used for quantitative detection of residual Pichia pastoris DNA in biopharmaceuticals.
For use in quality control/manufacturing process only.
It is for research use only.
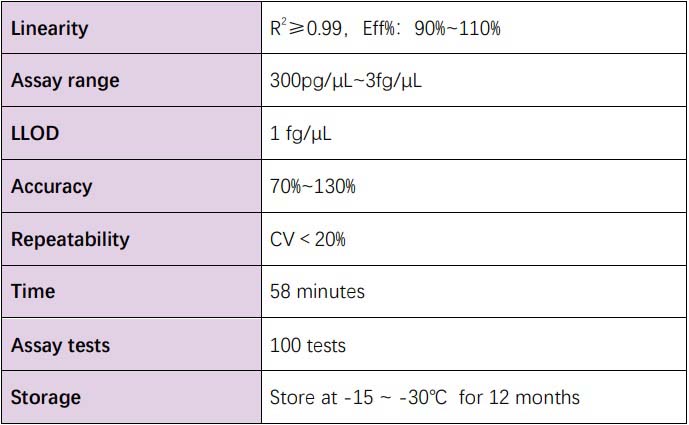
技术参数(Technical Specifications)
使用提示(Attention)
If your experimental process requires sample preparation, please purchase and conduct the experiment using the sample preparation kits recommended in the table to ensure that the buffers used in both the sample preparation and resDNA detection are consistent.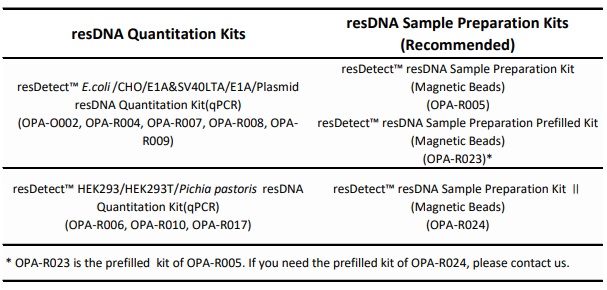
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
典型数据-Typical Data Please refer to DS document for the assay protocol.
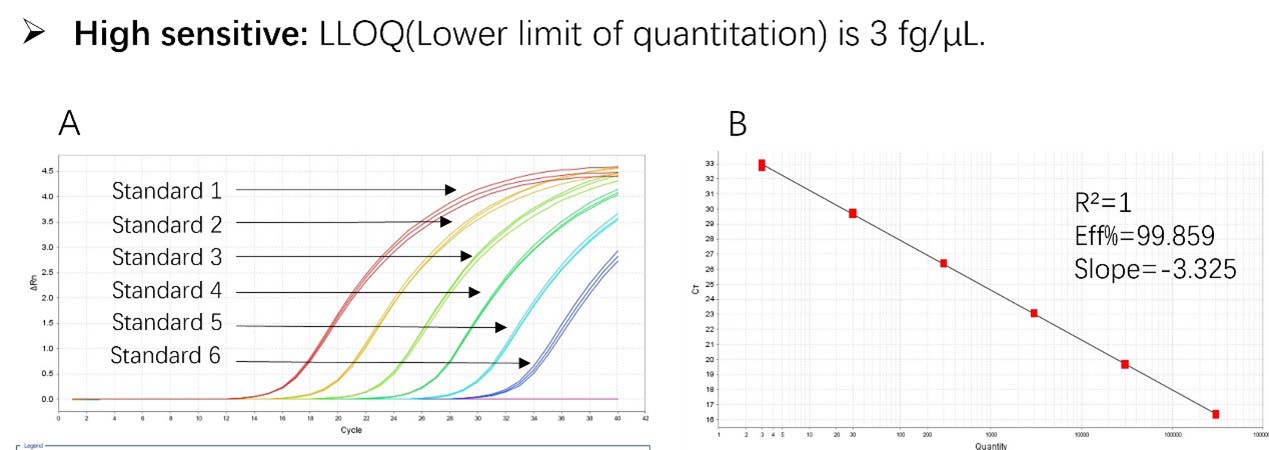
Figure 1. High sensitivity and broad dynamic range using the Pichia pastoris resDNA Quantitation Kit. (A) Typical analysis results obtained with Standard 1 (300 pg/μL) to 6 (3 fg/μL). (B) The standard curve of the 10-fold dilution series. PCR efficiency should be 90-110%.
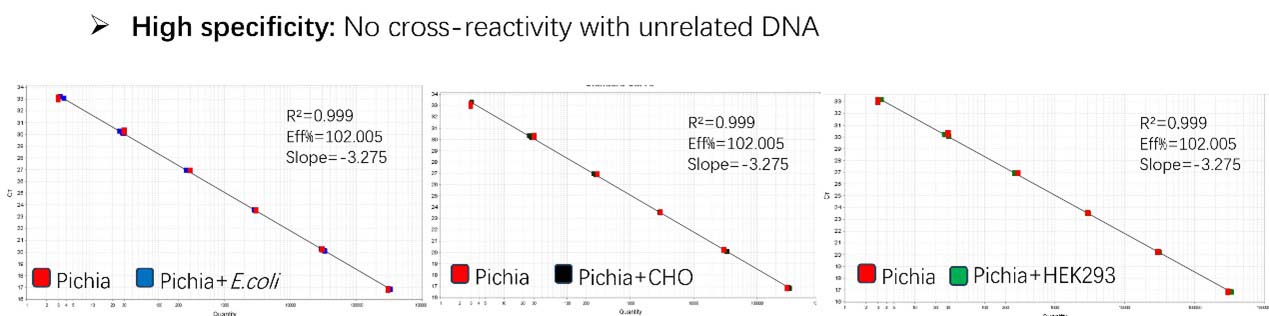
Figure 2. Assay specificity. Standard curves generated using 10-fold serial dilution of Pichia pastoris genomic DNA (included in the kit) in the presence of DNA (CHO, E. coli and HEK293).
组分(Materials Provided)
| ID | Components | Size |
| OPA-R017-01 | 2×qPCR Master Mix | 1.0 mL×2 |
| OPA-R017-02 | Pichia Primer & Probe Mix | 700 μL |
| OPA-R017-03 | Pichia DNA Control(3ng/μL) | 100 μL |
| OPA-R017-04 | Dilution Buffer | 1.5 mL×3 |
| OPA-R017-05 | DNase/RNase-free Water | 1.0 mL |























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















