Simultaneous inhibition of fibroblast growth factor-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor-a with RC28-E in diabetic macular edema: a phase 2 randomised trialZhang, Cheng, Gu
et alBr J Ophthalmol (2025)
Abstract: To compare different doses and dosing regimens of RC28-E, a novel bispecific antibody that simultaneously binds vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), with conbercept in patients with diabetic macular edema (DME).Prospective, randomised, active comparator-controlled, open-label, multicentre, phase 2 clinical trial.cente PARTICIPANTS: The trial enrolled patients aged 18 years or older with centre-involving DME, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of 73 to 24 Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) letters, and central subfield thickness (CST) of 300 µm or more.Patients were assigned randomly to one of five treatment regimens: 1.0 mg RC28-E for three initial monthly doses and then every 8 weeks (1.0mgQ8); 1.0 mg RC28-E for five initial monthly doses and then on a pro re nata (PRN) basis (1.0mgPRN); 2.0 mg RC28-E for three initial monthly doses and then every 8 weeks (2.0mgQ8); 2.0 mg RC28-E for five initial monthly doses and then on a PRN basis (2.0mgPRN); or 0.5 mg conbercept for three initial monthly doses and then on a PRN basis. Assessments were made at baseline and every 4 weeks thereafter.The primary endpoint was the change in BCVA compared with baseline at 24 and 52 weeks. Secondary endpoints included the change in CST from baseline at 52 weeks; the proportion of patients who gained/lost ≥15 letters, ≥10 letters and >0 letter in BCVA; and the number of injections and safety outcomes.The trial enrolled 156 patients. Mean improvements in BCVA in the RC28-E groups at week 24 were 7.1, 11.0, 7.4 and 10.5 letters for 1.0mgQ8, 1.0mgPRN, 2.0mgQ8 and 2.0mgPRN regimens, respectively, versus 9.7 letters for the conbercept group (p=0.146). By week 52, the RC28-E groups exhibited respective mean BCVA enhancements of 5.5, 9.5, 9.2 and 9.7 letters, compared with 8.4 letters of the conbercept group (p=0.469). Mean reductions in CST in the RC28-E groups at week 52 were -163.2 µm, -136.9 µm, -142.5 µm and -153.6 µm, versus -160.7 µm for the conbercept group (p=0.948). The Per Protocol Set analysis indicated that at 24 weeks, the BCVA improvement in the 2.0mgPRN group was significantly greater than that in the conbercept group (14.0 vs 9.8, p=0.019). In patients with poor baseline glycaemic control (HbA1c ≥7.5%), the 2.0mgPRN group showed greater BCVA improvement than the conbercept group (14.4 vs 4.2, p=0.039) at week 52. During the maintenance phase, the 2.0mgPRN group had fewer injections (2.8, 95% CI 1.8 to 3.7) compared with the conbercept group (4.4, 95% CI 3.5 to 5.2). RC28-E was generally well tolerated. The incidence of ocular adverse events in study eyes was comparable between RC28-E groups (22.6% in 1.0mgQ8 group, 26.7% in 1.0mgPRN group, 34.4% in 2.0mgQ8 group, 25.0% in 2.0 mg PRN group) and conbercept group (32.3%). The number of ocular serious adverse events was 1 (1.0mgQ8), 0 (1.0mgPRN), 1 (2.0mgQ8), 2 (2.0mgPRN) and 0 (conbercept).Intravitreous RC28-E improved BCVA and CST in eyes with centre-involved DME. Compared with conbercept, the 2.0mgPRN regimen of RC28-E was recommended due to its superior efficacy in improving vision particularly for patients with poor glycaemic control, fewer treatment injections during the maintenance phase and comparable safety profile.NCT04782115.© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Long-term nucleus basalis cholinergic lesions alter the structure of cortical vasculature, astrocytic density and microglial activity in Wistar ratsOrciani, Foret, Cuello
et alNeurobiol Aging (2025) 150, 132-145
Abstract: Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons (BFCNs) are the sole source of cholinergic innervation to the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in humans and the primary source in rodents. This system undergoes early degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. BFCNs terminal synapses are involved in the regulation of the cerebral blood flow by making classical synaptic contacts with other neurons. Additionally, they are located in proximity to cortical cerebral blood vessels, forming connections with various cell types of the neurovascular unit (NVU), including vascular smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and astrocytic end-feet. However, the effects of the BFCNs input on NVU components remain unresolved. To address this issue, we immunolesioned the nucleus basalis by administering bilateral stereotaxic injections of the cholinergic immunotoxin 192-IgG-Saporin in 2.5-month-old Wistar rats. Seven months post-lesion, we observed a significant reduction in cortical vesicular acetylcholine transporter-immunoreactive synapses. This was accompanied by changes in the diameter of cortical capillaries and precapillary arterioles, as well as lower levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A). Additionally, the cholinergic immunolesion increased the density of cortical astrocytes and microglia in the cortex. At these post-BFCN-lesion stages, astrocytic end-feet exhibited an increased co-localization with arterioles. The number of microglia in the parietal cortex correlated with cholinergic loss and exhibited morphological changes indicative of an intermediate activation state. This was supported by decreased levels of proinflammatory mediators IFN-γ, IL-1β, and KC/GRO (CXCL1), and by increased expression of M2 markers SOCS3, IL4Rα, YM1, ARG1, and Fizz1. Our findings offer a novel insight: that the loss of nucleus basalis cholinergic input negatively impacts cortical blood vessels, NVU components, and microglia phenotype.Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Serum VEGF-A as a biomarker for the addition of bevacizumab to chemo-immunotherapy in metastatic NSCLCTanaka, Sugisaka, Shiraishi
et alNat Commun (2025) 16 (1), 2825
Abstract: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents in combination with immunotherapies have improved outcomes for cancer patients, but predictive biomarkers have not been elucidated. We report here a preplanned analysis in the previously reported APPLE study, a phase 3 trial evaluating the efficacy of the bevacizumab in combination with atezolizumab, plus platinum chemotherapy in metastatic, nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We investigated the correlation of serum VEGF-A and its isoforms at baseline with treatment response by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We reveal that the addition of bevacizumab significantly improves the progression-free survival in patients with the low VEGF-A level. Our results demonstrate that measuring serum VEGF-A or its isoforms may identify NSCLC patients who are likely to benefit from the addition of bevacizumab to immunotherapy. These assays are easy to measure and have significant potential for further clinical development.© 2025. The Author(s).
The anti-angiogenic effects of arctigenin on choroidal neovascularization pathogenesisShirakawa, Yasuda, Nakamura
et alJ Pharmacol Sci (2025) 158 (1), 42-51
Abstract: Neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) is an ocular disease characterized by choroidal neovascularization (CNV), resulting in severe visual impairment. Arctigenin is a natural lignan compound from Arctium lappa L. and has anti-inflammatory and vascular normalizing effects. Here, we investigated the anti-angiogenic effects of arctigenin on CNV formation. Laser-induced CNV model mice were orally administered arctigenin at 100 mg/kg once a day for 5 days before laser irradiation. Oral administration of arctigenin suppressed CNV formation, vascular leakage, and the proliferation of endothelial cells in the CNV lesions. Treatment with arctigenin at 30 μM attenuated vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced cell proliferation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMECs). Moreover, arctigenin suppressed the phosphorylation of Src, which is involved in VEGF signaling. Arctigenin also inhibited VEGF-induced mitochondrial respiratory activation. These findings suggested that daily intake of arctigenin may have beneficial effects on nAMD.Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
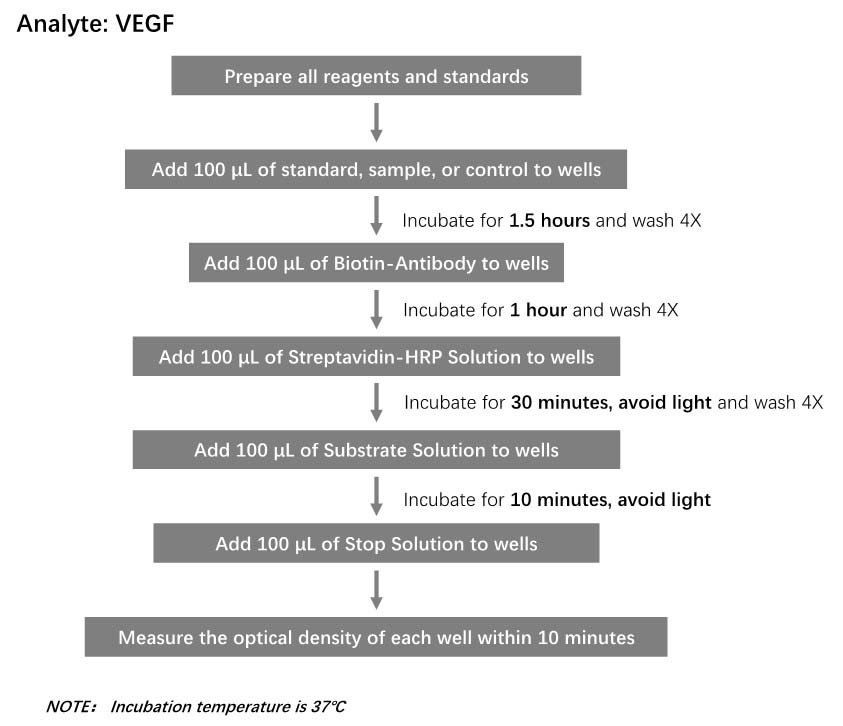
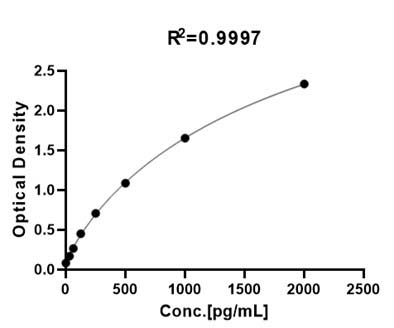
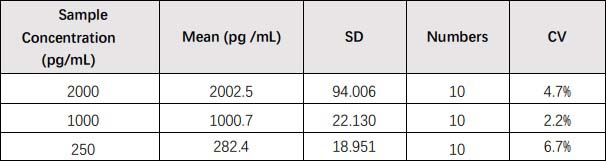
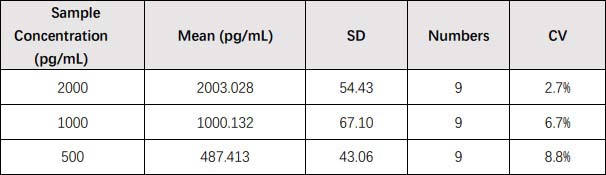























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















