Discovery of crucial cytokines associated with deep vein thrombus formation by protein array analysisWang, Chi, Zeng
et alBMC Cardiovasc Disord (2024) 24 (1), 374
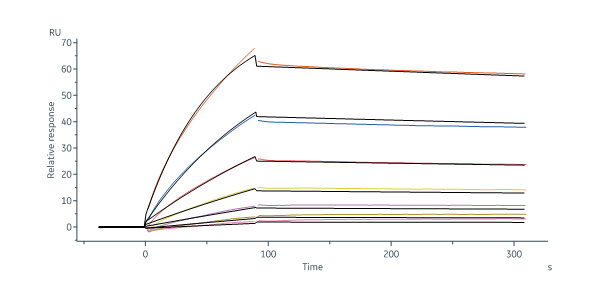
Abstract: Expanding the number of biomarkers is imperative for studying the etiology and improving venous thromboembolism prediction. In this study, we aimed to identify promising biomarkers or targeted therapies to improve the detection accuracy of early-stage deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or reduce complications.Quantibody Human Cytokine Antibody Array 440 (QAH-CAA-440) was used to screen novel serum-based biomarkers for DVT/non-lower extremity DVT (NDVT). Differentially expressed proteins in DVT were analyzed using bioinformatics methods and validated using a customized array. Diagnostic accuracy was calculated using receiver operating characteristics, and machine learning was applied to establish a biomarker model for evaluating the identified targets. Twelve targets were selected for validation.Cytokine profiling was conducted using a QAH-CAA-440 (RayBiotech, USA) quantimeter array. Cross-tabulation analysis with Venn diagrams identified common differential factors, leading to the selection of 12 cytokines for validation based on their clinical significance. These 12 biomarkers were consistent with the results of previous array analysis: FGF-6 (AUC = 0.956), Galectin-3 (AUC = 0.942), EDA-A2 (AUC = 0.933), CHI3L1 (AUC = 0.911), IL-1 F9 (AUC = 0.898), Dkk-4 (AUC = 0.88), IG-H3 (AUC = 0.876), IGFBP (AUC = 0.858), Gas-1 (AUC = 0.858), Layilin (AUC = 0.849), ULBP-2 (AUC = 0.813)and FGF-9 (AUC = 0.773). These cytokines are expected to serve as biomarkers, targets, or therapeutic targets to differentiate DVT from NDVT.EDA-A2, FGF-6, Dkk-4, IL-1 F9, Galentin-3, Layilin, Big-h3, CHI3L1, ULBP-2, Gas-1, IGFBP-5, and FGF-9 are promising targets for DVT diagnosis and treatment.© 2024. The Author(s).
In-silico screening of phytomolecules against multiple targets for wound managementThomas, Shinde, Wavhale
et alIn Silico Pharmacol (2024) 12 (1), 19
Abstract: Chronic wound healing, especially in burns, is a major medical challenge with limited treatments. This study employs computational tools to identify phytomolecules that target multiple pathways involved in wound healing. By utilizing shape analysis, molecular docking, and binding energy calculations, potential compounds are pinpointed,to address the growing problem of chronic wounds. Initially, a set of phytomolecules from the ZINC database of natural molecules was screened to find compounds with shapes similar to well-known wound healing phytomolecules like curcumin, chromogenic acid, gallic acid, and quercetin. The most promising phytomolecules identified through shape similarity were further studied through molecular docking studies on several key targets involved in wound healing, including TNF-α, FGF, and TGF-β. Among the tested phytomolecules, a ligand known as Fluorophenyl(5-(5-chloro-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxopentyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2c]pyridine-2-yl acetate) exhibited a strong affinity with favourable binding interactions for TNF-α ( - 7.1 kcal/mole), FGF (-6.9 kcal/mole), and TGF-β (-5.1 kcal/mole). Another compound, 2,4 methoxybenzylidene-(-3)-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-6-yl-4-methoxybenzoate, demonstrated a strong affinity with low binding energy for TNF-α ( - 6.8 kcal/mole) and FGF ( - 7.0 kcal/mole) targets. Isosakuranetin and Ermanin displayed moderate affinity for both TNF-α and FGF, with the highest affinity observed for the TGF-β target. These findings suggest that these identified phytomolecules hold promise as potential lead compounds for further structural modifications, with the goal of designing new molecules that can target multiple pathways involved in the wound healing process.© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Low Molecular Weight Collagen Peptide (LMWCP) Promotes Hair Growth by Activating the Wnt/GSK-3β/β-Catenin Signaling PathwayKim, Lee, Lee
et alJ Microbiol Biotechnol (2024) 34 (1), 17-28
Abstract: Low molecular weight collagen peptide (LMWCP) is a collagen hydrolysate derived from fish. We investigated the effects of LMWCP on hair growth using human dermal papilla cells (hDPCs), human hair follicles (hHFs), patch assay, and telogenic C57BL/6 mice, while also examining the underlying mechanisms of its action. LMWCP promoted proliferation and mitochondrial potential, and the secretion of hair growth-related factors, such as EGF, HB-EGF, FGF-4, and FGF-6 in hDPCs. Patch assay showed that LMWCP increased the neogeneration of new HFs in a dose-dependent manner. This result correlated with an increase in the expression of dermal papilla (DP) signature genes such as, ALPL, SHH, FGF7, and BMP-2. LMWCP upregulated phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) and β-catenin, and nuclear translocation of β-catenin, and it increased the expression of Wnt3a, LEF1, VEGF, ALP, and β-catenin. LMWCP promoted the growth of hHFs and increased the expression of β-catenin and VEGF. Oral administration of LMWCP to mice significantly stimulated hair growth. The expression of Wnt3a, β-catenin, PCNA, Cyclin D1, and VEGF was also elevated in the back skin of the mice. Furthermore, LMWCP increased the expression of cytokeratin and Keratin Type I and II. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that LMWCP has the potential to increase hair growth via activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Ultrastructural and Molecular Development of the Myotendinous Junction Triggered by Stretching Prior to Resistance ExerciseJacob, Barbosa, Rodrigues
et alMicrosc Microanal (2022)
Abstract: The myotendinous junction (MTJ) is a highly specialized region of the locomotor apparatus. Here, we investigated the ultrastructural and molecular effects in the MTJ region after static stretching prior to the ladder-based resistance training. Thirty-two male, 60-day old Wistar rats were divided into four groups: Sedentary, Resistance Training, Stretching, and Stretching-Resistance Training. The gastrocnemius muscle was processed for transmission electron microscopy techniques and Western blot assay. We observed that the static stretching prior to the ladder-based resistance training increased the MTJ components, the fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and FGF-6 protein expression. Also, we demonstrated the lower transforming growth factor expression and no difference in the lysyl oxidase expression after combined training. The MTJ alterations in response to combined training demonstrate adaptive mechanisms which can be used for the prescription or development of methods to reduce or prevent injuries in humans and promote the myotendinous interface benefit.
























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















