抗体来源(Source)
Monoclonal Anti-Human CD19 Antibody, Mouse IgG2a (FMC63) is a monoclonal antibody recombinantly expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293), which provides higher batch consistency and long term security of supply.
应用(Application)
Flow Cytometry (Evaluation of the expression of CD19 on Human cells).
克隆号(Clone)
FMC63
种属(Species)
Mouse
亚型(Isotype)
Mouse IgG2a | Mouse kappa
特异性(Specificity)
This product is a specific antibody specifically reacts with CD19 protein.
种属反应性(Reactivity)
Human
免疫原(Immunogen)
Human prolymphocytic leukaemia cell line JVM3.
偶联(Conjugate)
APC
Excitation Wavelength: 640 nm
Emission Wavelength: 661 nm
同型对照(Isotype Control)
The Isotype control is sold separately and you can search for Cat. No. DNP-AFM487 for product information.
推荐稀释比(Recommended Dilution)
1:20
制剂(Formulation)
Supplied as 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS, 0.2% BSA, 0.03% Proclin 300, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
存储(Storage)
Please protect from light and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- Store at 2-8 °C for 12 months.
活性(Bioactivity)-FACS
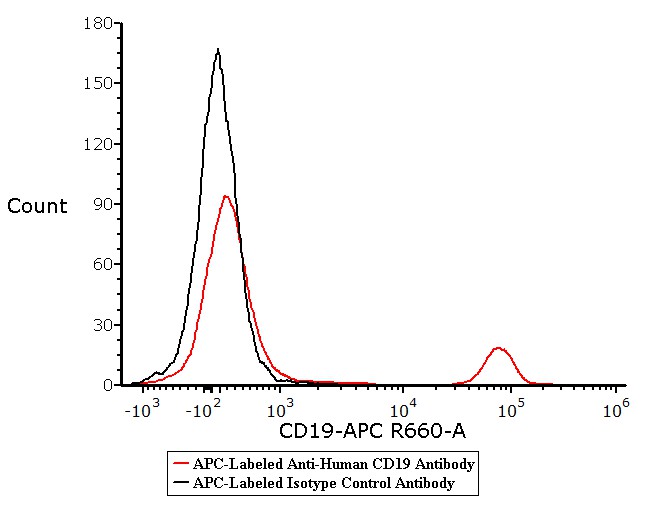
Flow cytometric analysis of Human peripheral blood lymphocytes respectively staining with APC-Labeled Monoclonal Anti-Human CD19 Antibody Mouse IgG2a (Cat. No. FABm004-02) at 1:20 dilution (5 μL of the antibody stock solution corresponds to labeling of 2.5e5 cells in a final volume of 100 µL), compared with isotype control antibody. APC signal was used to evaluate the binding activity (QC tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 is also known as CD19 (Cluster of Differentiation 19), is a single-pass type I membrane protein which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains. CD19 is expressed on follicular dendritic cells and B cells. In fact, it is present on B cells from earliest recognizable B-lineage cells during development to B-cell blasts but is lost on maturation to plasma cells. It primarily acts as a B cell co-receptor in conjunction with CD21 and CD81. Upon activation, the cytoplasmic tail of CD19 becomes phosphorylated, which leads to binding by Src-family kinases and recruitment of PI-3 kinase. As on T cells, several surface molecules form the antigen receptor and form a complex on B lymphocytes. The (almost) B cell-specific CD19 phosphoglycoprotein is one of these molecules. The others are CD21 and CD81. These surface immunoglobulin (sIg)-associated molecules facilitate signal transduction. On living B cells, anti-immunoglobulin antibody mimicking exogenous antigen causes CD19 to bind to sIg and internalize with it. The reverse process has not been demonstrated, suggesting that formation of this receptor complex is antigen-induced. This molecular association has been confirmed by chemical studies. Mutations in CD19 are associated with severe immunodeficiency syndromes characterized by diminished antibody production. CD19 has been shown to interact with: CD81, CD82, Complement receptor 2, and VAV2.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining












