分子别名(Synonym)
DDPAC,FTDP-17,MAPT,MSTD,MTBT1,Tau,PHF-tau,TAU
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human Tau Protein, Tag Free (TAU-H5114) is expressed from E. coli cells. It contains AA Gln 244 - Glu 372 (Accession # P10636-8).
Predicted N-terminus: Met
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries no "tag".
The protein has a calculated MW of 13.8 kDa. The protein migrates as 16-17 kDa when calibrated against Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE).
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 0.01 EU per μg by the LAL method.
无菌(Sterility)
Negative
支原体(Mycoplasma)
Negative.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Supplied as 0.2 μm filtered solution in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH7.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
运输(Shipping)
This product is supplied and shipped with dry ice, please inquire the shipping cost.
存储(Storage)
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- The product MUST be stored at -70°C or lower upon receipt;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions.
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
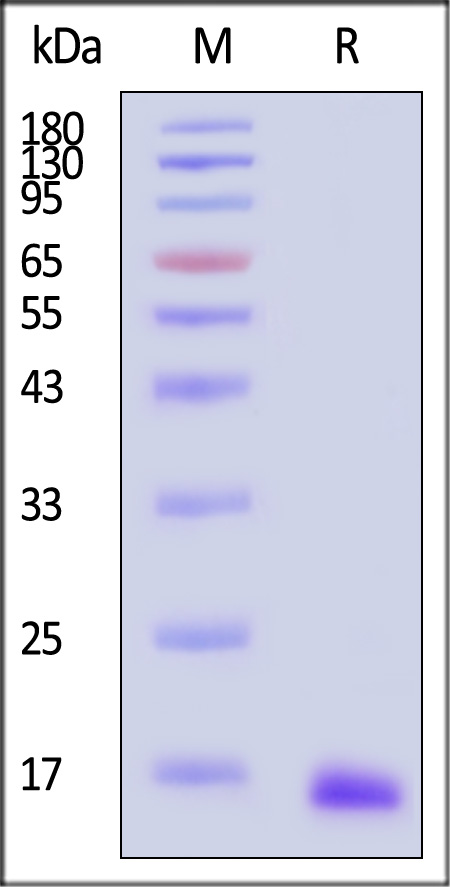
Human Tau Protein, Tag Free on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95% (With Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker).
SEC-MALS
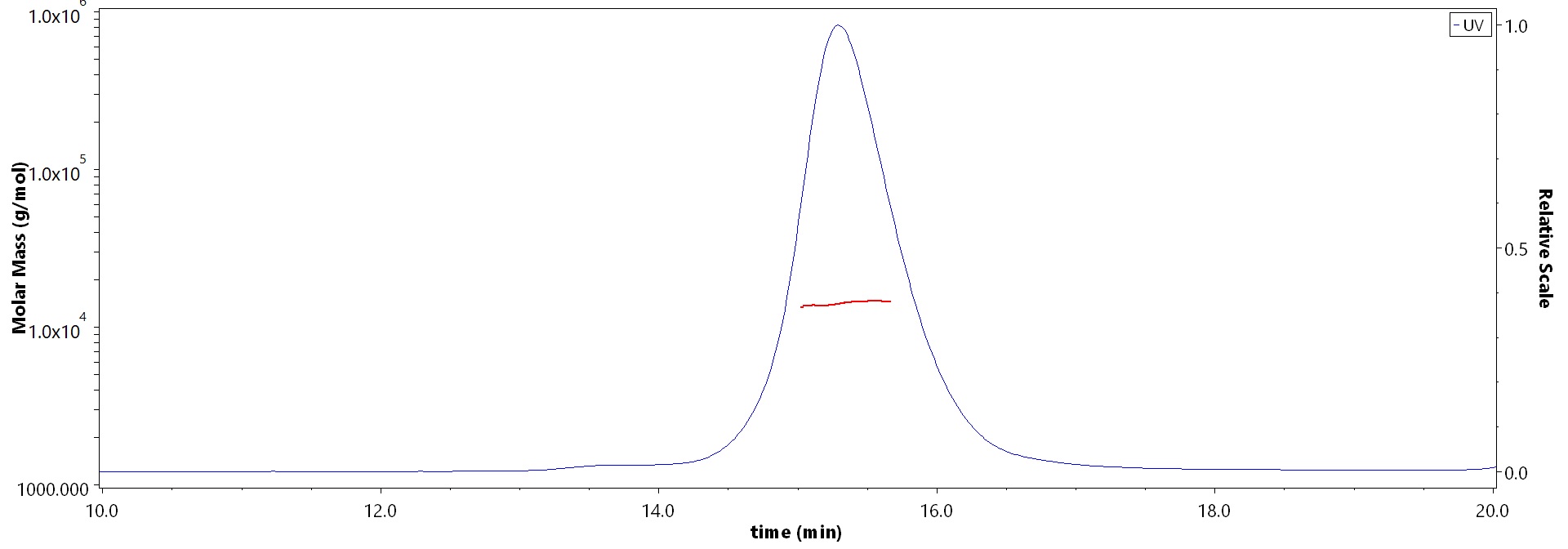
The purity of Human Tau Protein, Tag Free (Cat. No. TAU-H5114) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 12-20 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
背景(Background)
This gene encodes the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) whose transcript undergoes complex, regulated alternative splicing, giving rise to several mRNA species. MAPT transcripts are differentially expressed in the nervous system, depending on stage of neuronal maturation and neuron type. MAPT gene mutations have been associated with several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining











