Synthesis of (S)-4-Methylgeranyl Esters, the Pheromone Components of the Ponerine Ant, Holcoponera striatula, and their (R)-IsomersTashiro, Watanabe
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem (2025)
Abstract: (2E,4S)-3,4,7-Trimethylocta-2,6-dien-1-yl octanoate [(S)-1], decanoate [(S)-2], and dodecanoate [(S)-3] are the main trail pheromone components of the Dufour's gland secretion of the ponerine ant, Holcoponera striatula. We synthesized these pheromone components from an optically active alcohol, (R)-5, by using Johnson-Claisen rearrangement reaction as the key step for constructing a methyl-branched alkyl chain. The alcohol (R)-5 was prepared by using the enzymatic resolution of its racemate. To investigate the biological activity of the enantiomers of these pheromone components, we synthesized the antipodes (R)-1, (R)-2, and (R)-3.© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry.
Apoptotic Receptors and CD107a Expression by NK Cells in an Interaction Model with Trophoblast CellsMikhailova, Sokolov, Grebenkina
et alCurr Issues Mol Biol (2024) 46 (8), 8945-8957
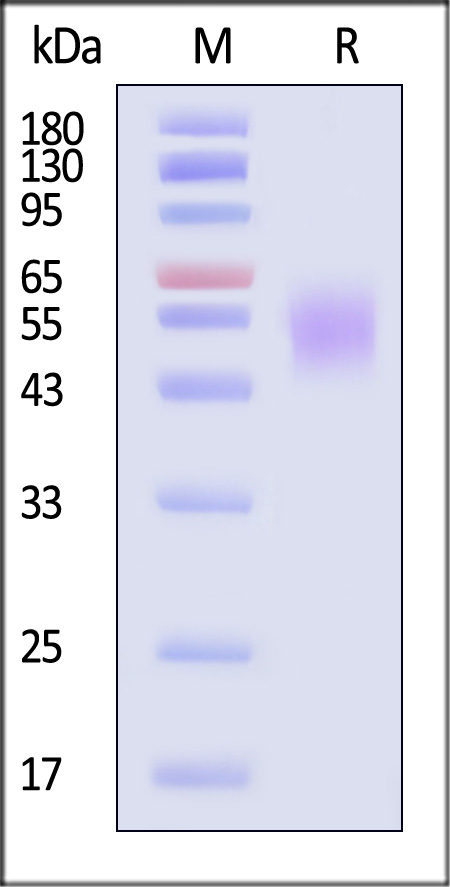
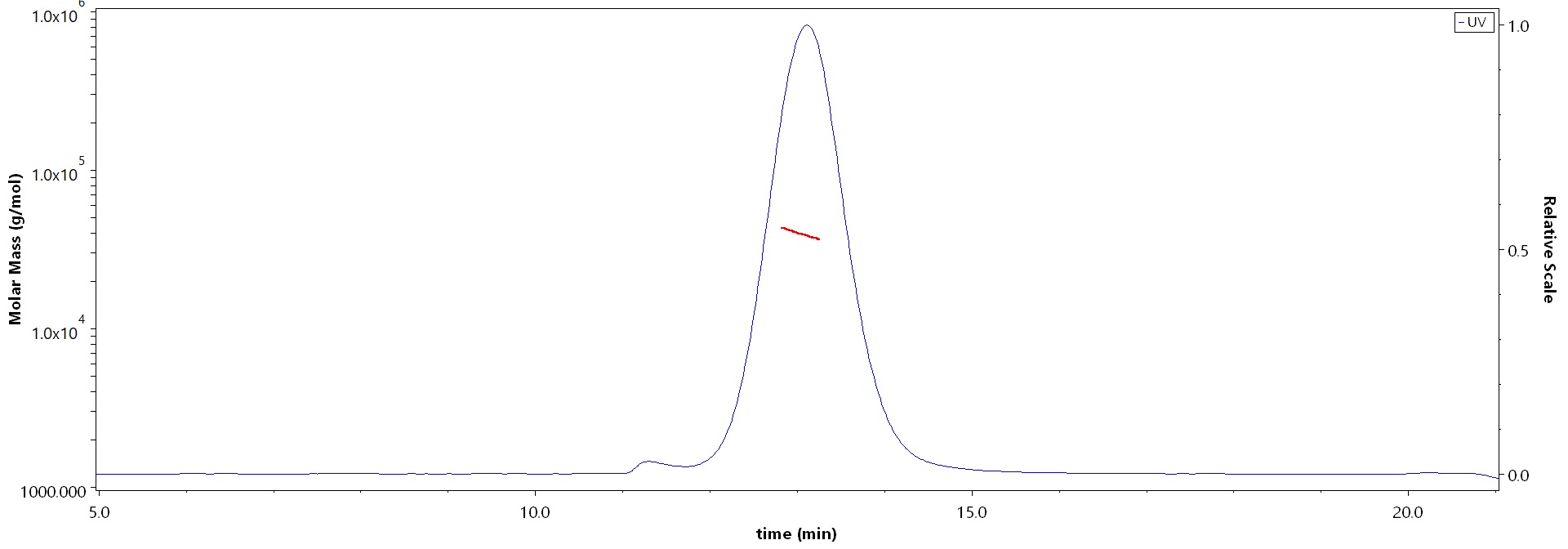
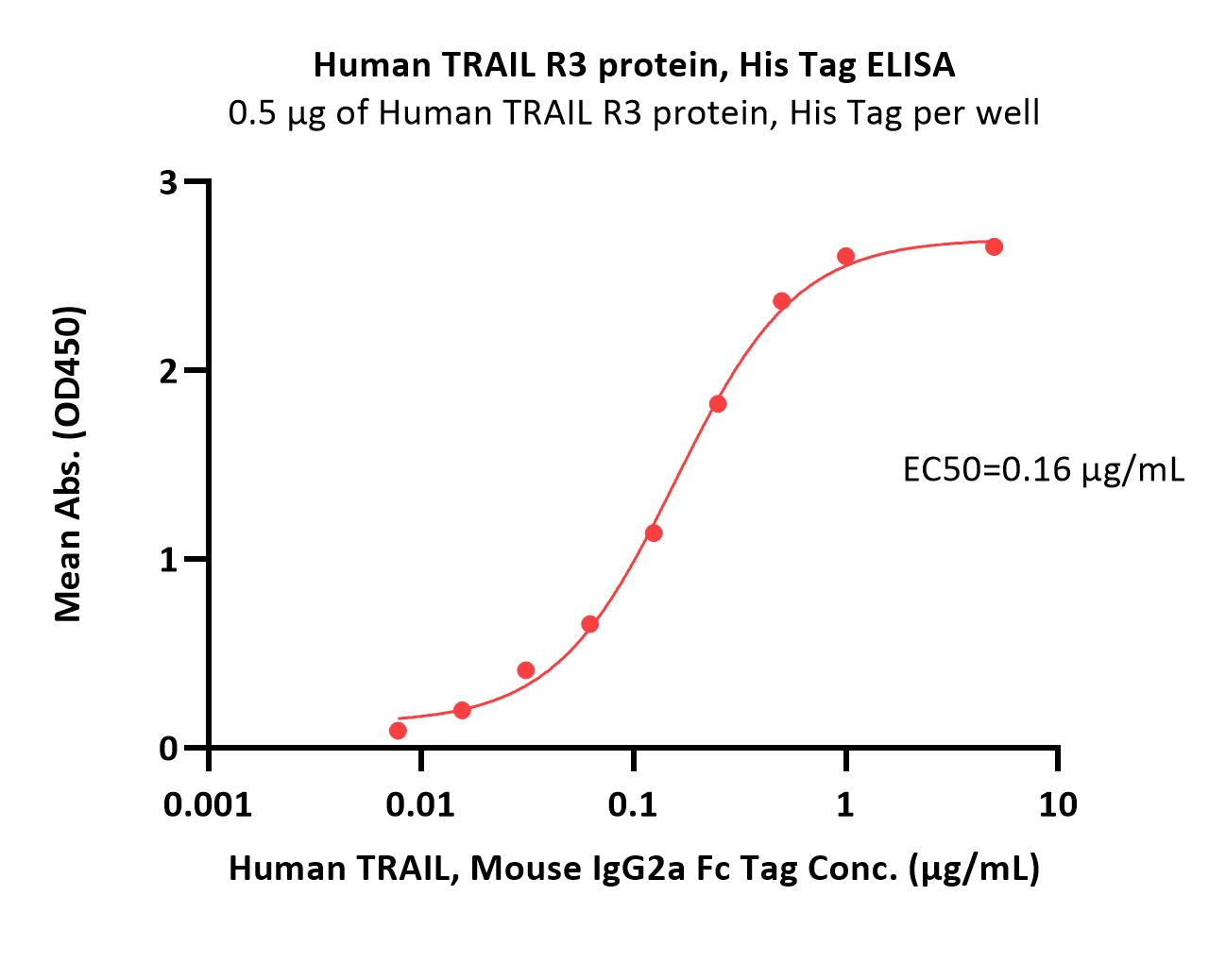
Abstract: Natural killer cells (NK cells) exert cytotoxicity towards target cells in several ways, including the expression of apoptosis-mediating ligands (TRAIL, FasL). In addition, NK cells themselves may be susceptible to apoptosis due to the expression of TRAIL receptors. These receptors include TRAIL-R1 (DR4), TRAIL-R2 (DR5), capable of inducing apoptosis, and TRAIL-R3 (DcR1), TRAIL-R4 (DcR2), the so-called "decoy receptors", which lack an intracellular domain initiating activation of caspases. Of particular interest is the interaction of uterine NK cells with cells of fetal origin, trophoblasts, which are potential targets for natural killer cells to carry out cytotoxicity. The aim of this work was to evaluate the expression of proapoptotic receptors and their ligands as well as CD107a expression by NK cells in a model of interaction with trophoblast cells. To evaluate NK cells, we used cells of the NK-92 line; cells of the JEG-3 line were used as target cells. The cytokines IL-1β, IL-15, IL-18, TNFα, IL-10, TGFβ and conditioned media (CM) of the first and third trimester chorionic villi explants were used as inducers. We established that cytokines changed the expression of apoptotic receptors by NK cells: in the presence of TNFα, the amount and intensity of Fas expression increased, while in the presence of TGFβ, the amount and intensity of expression of the DR5 receptor decreased. Soluble chorionic villi factors alter the expression of TRAIL and FasL by NK-92 cells, which can reflect the suppression of the TRAIL-dependent mechanism of apoptosis in the first trimester and stimulating the Fas-dependent mechanism in the third trimester. In the presence of trophoblast cells, the expression of TRAIL and DcR1 by NK cells was reduced compared to intact cells, indicating an inhibitory effect of trophoblast cells on NK cell cytotoxicity. In the presence of chorionic villi CM and trophoblast cells, a reduced number of NK-92 cells expressing DR4 and DR5 was found. Therefore, soluble factors secreted by chorionic villi cells regulate the resistance of NK cells to death by binding TRAIL, likely maintaining their activity at a certain level in case of contact with trophoblast cells.
Efficacy and safety of tetrandrine in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysisXu, Li, Ye
et alZhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban (2024) 53 (4), 519-526
Abstract: To explore the efficacy and safety of tetrandrine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Randomized controlled studies of tetrandrine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis were searched in CNKI, VIP, Wanfang database, SinoMed, PubMed, Springer, Web of Science and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trails databases. A meta-analysis was conducted using R 3.5.3 software to evaluate the clinical outcomes, including the total effective rate, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), rheumatoid factor (RF), visual analogue scale (VAS), disease activity score (DAS), tender joint count (TJC), swollen joint count (SJC), and morning stiffness duration, as well as adverse events of rheumatoid arthritis patients.A total of 10 articles were included in the study. The meta-analysis indicated that tetrandrine significantly improved the total effective rate (OR=3.27, 95%CI: 2.01-5.37, P<0.01), ESR (SMD=1.12, 95%CI: 0.06-2.19, P<0.05), CRP (SMD=0.75, 95%CI: 0.28-1.22, P<0.01), VAS (SMD=0.64, 95%CI: 0.29-1.00, P<0.01), TJC (SMD=1.16, 95%CI: 0.58-1.74, P<0.01), SJC (SMD=0.85, 95%CI: 0.40-1.31, P<0.01), and morning stiffness (SMD=1.09, 95%CI: 0.68-1.50, P<0.01). However, no statistical significance was found in RF (SMD=1.70, 95%CI: -1.10-4.51, P>0.05) and DAS (SMD=0.26, 95%CI: -0.59-1.11, P>0.05). The overall incidence of adverse events associated with tetrandrine treatment for rheumatoid arthritis was 20% (95%CI: 12%-27%, I2=60%, P<0.05), with mild severity and favorable outcomes.Tetrandrine is effective in the treatment of RA patients with a mild degree of adverse events.
Mapping trends and hotspots regarding the use of telenursing for elderly individuals with chronic diseases: A bibliometric analysisYuan, Wang, Tao
et alMedicine (Baltimore) (2024) 103 (9), e37313
Abstract: Telenursing is receiving extensive attention from scholars and medical staff. However, there are few studies on the knowledge structure of telenursing for elderly individuals with chronic diseases. This study aims to demonstrate current research status and development trend of telenursing for elderly individuals with chronic diseases through a visual analysis of CiteSpace, so as to provide a more comprehensive perspective for future researches.Literature about telenursing for elderly patients with chronic diseases from 2002 to 2022 was retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection using CiteSpace 6.1.R3.A total of 375 records were obtained. Annual publication and citation frequency gradually increased over the investigated period, reaching a peak in 2022. Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare was the most prolific and the most cited journal. The United States was the most productive country, the University of Melbourne was the most productive institution, and the author CHEN C ranked the highest in the number of publications. The most popular keywords were "care," "telemedicine," "management," "older adult," "chronic disease," "health," and "heart failure," which had a high frequency and centrality. The keywords "telehealth," "randomized controlled trail," "chronic obstructive pulmonary disease," "implementation" and "time" showed the strongest citation burst. The keywords were clustered to form 10 labels. The article published in 2010 by Chaudhry SI was cited the most. The top 3 cited journals were all special journal of telemedicine.This study revealed current research status and development trend of telenursing for elderly individuals with chronic diseases. The bibliometric analysis of telenursing expands the knowledge field of telemedicine and provides new insights into the management of elderly patients with chronic diseases.Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















