Bayesian spatiotemporal modelling and mapping of malaria risk among children under five years of age in GhanaTakramah, Afrane, Aheto
BMC Infect Dis (2025) 25 (1), 430
Abstract: Malaria is a significant public health problem, particularly among children aged 6-59 months who bear the greatest burden of the disease. Malaria transmission is high and more pronounced in poor tropical and subtropical areas of the world. Climate change is positively correlated with the geographical distribution of malaria vectors. There is substantial evidence of spatial and temporal differences in under-five malaria risk. Thus, the study aimed to create intelligent maps of smooth relative risk of malaria in children under-5 years in Ghana that highlight high and low malaria burden in space and time to support malaria prevention, control, and elimination efforts.The study extracted and merged data on malaria among children aged 6-59 months from the 2014 Ghana Demographic and Health Surveys (GDHS), 2016 and 2019 Ghana Malaria Indicator Surveys (GMIS). The outcome variable of interest was the count of children aged 6-59 months with a positive test on the rapid diagnostic test (RDT) result. Bayesian Hierarchical spatiotemporal models were specified to estimate and map spatiotemporal variations in the relative risk of malaria. The existence of local clustering was assessed using the local indicator of spatial association (LISA), and the points were mapped to display significant local clusters, hotpot, and cold spot communities.The number of positive malaria cases in children aged 6-59 months decreased marginally from 946.7 (36.4%) in 2014 to 603.6 (22.9) in 2019 DHS survey periods. Smooth relative risk of malaria among children aged 6-59 months has consistently increased in the Northern and Eastern regions between 2014 and 2019. Socioeconomic and climatic factors such as household size [Posterior Mean: -0.198 (95% CrI: 3.52, 80.95)], rural area [Posterior Mean: 1.739 (95% CrI: 0.581, 2.867)], rainfall [Posterior Mean: 0.003 (95% CrI: 0.001, 0.005)], and maximum temperature [Posterior Mean: -1.069 (95% CrI: -2.135, -0.009)] were all shown as statistically significant predictors of malaria risk in children aged 6-59 months. Hot spot DHS clusters (enumeration areas) with a significantly high relative risk of malaria among children aged 6-59 months were repeatedly detected in the Ashanti region between 2014 and 2019.The findings of the study would provide policymakers with practical and insightful information for the equitable distribution of scarce health resources targeted at reducing the burden of malaria and its associated mortality among children under five years.© 2025. The Author(s).
Evaluating longitudinal cytomegalovirus-specific humoral immune responses and association with DNAemia risk in seropositive lung transplant recipientsHarnois, Barfield, Dennis
et alJHLT Open (2024) 5, 100113
Abstract: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is the most common viral infection among lung transplant recipients and is associated with chronic lung allograft dysfunction. There is a need for better therapeutics as well as biomarkers to enable effective stratification of CMV seropositive patient risk for developing CMV DNAemia to inform prophylaxis duration.CMV-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) binding and functional responses were evaluated in a discovery cohort of longitudinal plasma samples from 51 CMV seropositive human lung transplant recipients, collected as part of the clinical trials in organ transplantation (CTOT)-20 and CTOT-22 consortium studies. Pre-transplant plasma from an additional 43 CMV seropositive lung transplant recipients was evaluated as a validation cohort.In the discovery cohort with longitudinal samples, pre-transplant plasma IgG binding to CMV surface glycoproteins glycoprotein H (gH)/glycoprotein L (gL), gH/gL/glycoprotein O (gO), and pentameric complex, as well as neutralization of CMV in epithelial cells, is associated with increased risk of CMV DNAemia post-prophylaxis. However, these results were not confirmed by the validation cohort.While quantification of pre-transplant CMV-specific antibody responses showed association with DNAemia in the discovery cohort, additional clinical variables and/or known risk factors for CMV, such as patient CMV-specific T-cell responses, may need to be considered in combination with humoral immunity to effectively stratify risk of CMV DNAemia.© 2024 International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation.
Herpes simplex virus 1 envelope glycoprotein C shields glycoprotein D to protect virions from entry-blocking antibodiesHull, Pritchard, Nicola
J Virol (2025)
Abstract: Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) gD interaction with the host cell receptor nectin-1 triggers the membrane fusion cascade during viral entry. Potent neutralizing antibodies to gD prevent receptor-binding or prevent gD interaction with gH/gL critical for fusion. HSV has many strategies to evade host immune responses. We investigated the ability of virion envelope gC to protect envelope gD from antibody neutralization. HSV-1 lacking gC was more sensitive to neutralization by anti-gD monoclonal antibodies than a wild-type rescuant virus. gD in the HSV-1 gC-null viral envelope had enhanced reactivity to anti-gD antibodies compared to wild type. Soluble nectin-1 bound similar to HSV-1 particles regardless of the presence of gC in the envelope. However, entry of HSV-1 ΔgC was more sensitive to inhibition by soluble nectin-1 receptor. The viral membrane protein composition of HSV-1 ΔgC is equivalent to that of wild type, suggesting that the lack of gC is responsible for the increased reactivity of gD-specific antibodies and the consequent increased susceptibility to neutralization by those antibodies. Together, the results suggest that gC in the HSV-1 envelope shields both receptor-binding domains and gH/gL-interacting domains of gD from neutralizing antibodies, facilitating HSV cell entry.IMPORTANCEHSV-1 causes lifelong infections. There is no vaccine and no cure. Understanding HSV immune evasion strategies is an important goal. HSV-1 gC is a multi-functional envelope glycoprotein. This study suggests that virion gC physically shields neighboring gD from antibodies, including neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. This mechanism may allow HSV to escape immune detection, promoting HSV infection in the host.
Metabolic Engineering of E. coli for Enhanced Diols Production from AcetateRicci, Cen, Zu
et alACS Synth Biol (2025)
Abstract: Effective employment of renewable carbon sources is highly demanded to develop sustainable biobased manufacturing. Here, we developed Escherichia coli strains to produce 2,3-butanediol and acetoin (collectively referred to as diols) using acetate as the sole carbon source by stepwise metabolic engineering. When tested in fed-batch experiments, the strain overexpressing the entire acetate utilization pathway was found to consume acetate at a 15% faster rate (0.78 ± 0.05 g/g/h) and to produce a 35% higher diol titer (1.16 ± 0.01 g/L) than the baseline diols-producing strain. Moreover, singularly overexpressing the genes encoding alternative acetate uptake pathways as well as alternative isoforms of genes in the malate-to-pyruvate pathway unveiled that leveraging ackA-pta and maeA is more effective in enhancing acetate consumption and diols production, compared to acs and maeB. Finally, the increased substrate consumption rate and diol production obtained in flask-based experiments were confirmed in bench-scale bioreactors operated in fed-batch mode. Consequently, the highest titer of 1.56 g/L achieved in this configuration increased by over 30% compared to the only other similar effort carried out so far.
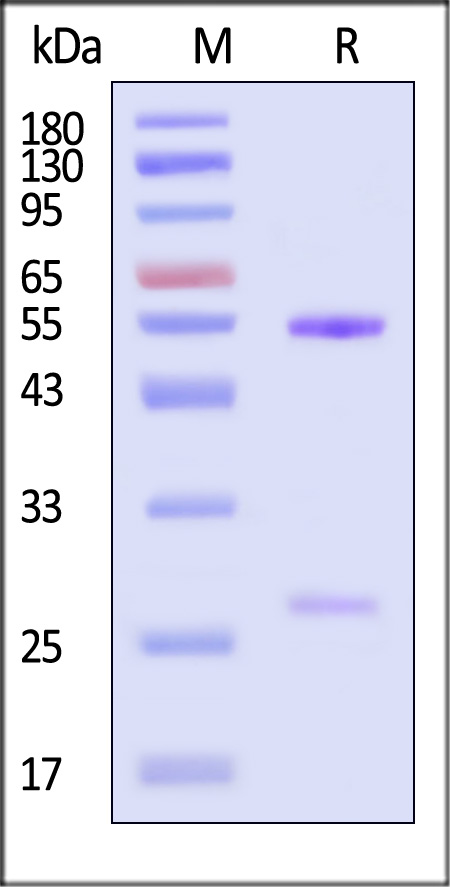
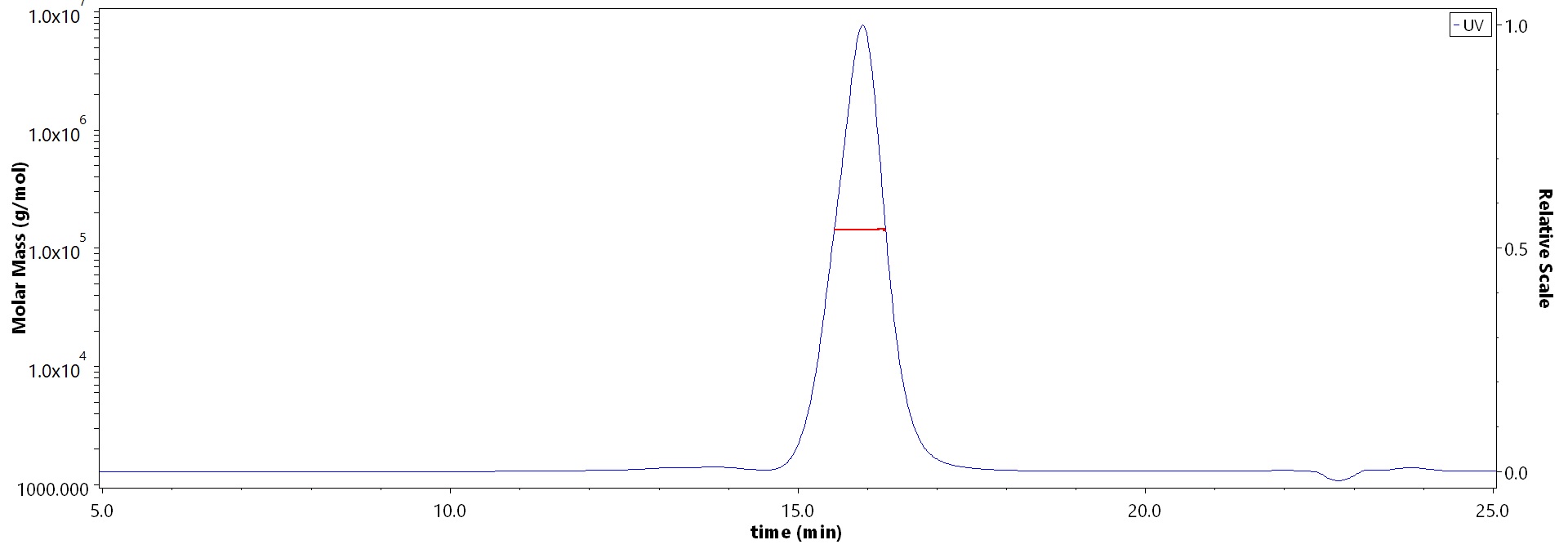
























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















