分子别名(Synonym)
CXCR4,CD184,Fusin,D2S201E,FB22,HM89,HSY3RR,LAP3,LCR1,LESTR,NPY3R,NPYR,NPYRL,NPYY3R,WHIM
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human CXCR4 Full Length Protein, Flag,His Tag (CX4-H52D3) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Met 1 - Ser 352 (Accession # P61073-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Asp
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries flag tag at the N-terminus and polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 58.4 kDa.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
This product is not suitable for cell based experiments due to cytotoxicity of detergent.
Detergent buffer is INDISPENSABLE to keep membrane protein soluble and active, under no circumastance should you remove detergent.
Detergent buffer is sold separately and not included in protein, and please contact us if you need the buffer.
If glycerol is not compatible to your application, remove glycerol just before immediate experiment, and NEVER store glycerol-free protein solution.
Supplied as 0.2 μm filtered solution in 50 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, Buffer B, pH7.5 with glycerol as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
运输(Shipping)
This product is supplied and shipped with dry ice, please inquire the shipping cost.
存储(Storage)
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- The product MUST be stored at -70°C or lower upon receipt;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
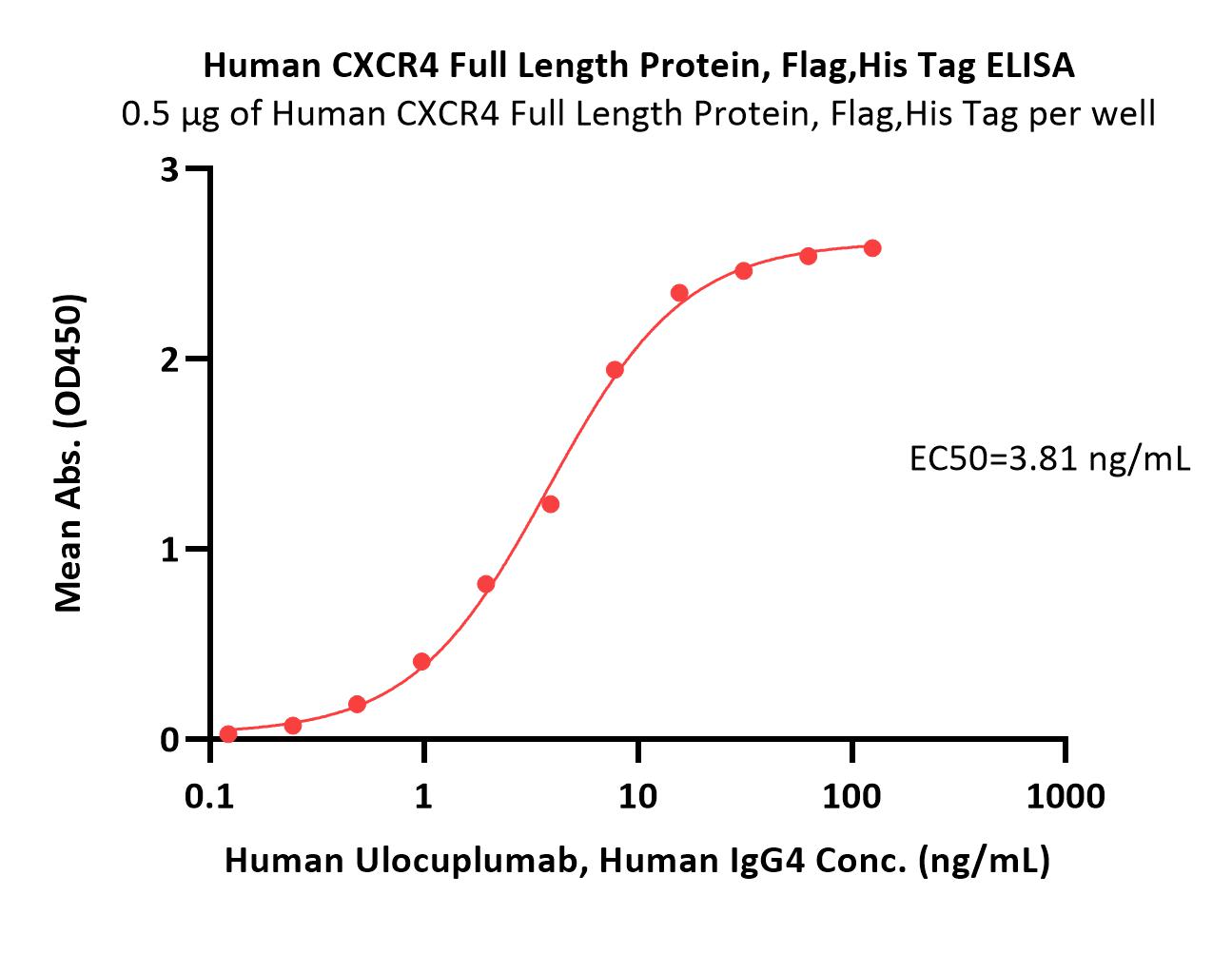
Immobilized Human CXCR4 Full Length Protein, Flag,His Tag (Cat. No. CX4-H52D3) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human Ulocuplumab, Human IgG4 with a linear range of 0.1-16 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol

- 176XXXXXXX0
- 从技术服务知道了这家公司,我们在多项目上委托了BLI服务,服务体验很好,数据及报告做的很漂亮。后续就从百普赛斯直接购买了蛋白,实验数据稳定,蛋白纯度及实验响应比较出色,供货稳定。成为了我们的关键试剂。
- 2022-9-5

- 156XXXXXXX8
- 我们采购该蛋白用于检测自主开发的抗TROP-2抗体的亲和力,通过OCTET检测其亲和动力学,我们用已经获批的IMMU132进行了测试,其亲和动力学常数为nM级别(1.05nM)。
- 2022-4-6
背景(Background)
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 is also known as fusin or CD184 (cluster of differentiation 184), CXCR4, CD184, D2S201E, FB22, HM89, HSY3RR, LAP3, LCR1, LESTR, NPY3R, NPYR, NPYRL, NPYY3R or WHIM. CXCR-4 is an alpha-chemokine receptor specific for stromal-derived-factor-1 (SDF-1 also called CXCL12), a molecule endowed with potent chemotactic activity for lymphocytes. This receptor is one of several chemokine receptors that HIV isolates can use to infect CD4+ T cells. HIV isolates that use CXCR4 are traditionally known as T-cell tropic isolates. Typically, these viruses are found late in infection. It is unclear as to whether the emergence of CXCR4 using HIV is a consequence or a cause of immunodeficiency.CXCR4 is upregulated during the implantation window in natural and hormone replacement therapy cycles in the endometrium, producing, in presence of a human blastocyst, a surface polarization of the CXCR4 receptors suggesting that this receptor is implicated in the adhesion phase of human implantation. SDF-1 and CXCR4 were believed to be a relatively “monogamous“ ligand-receptor pair (other chemokines tend to use several different chemokine receptors in a fairly “promiscuous“ manner). Recent evidence demonstrates ubiquitin is also a natural ligand of CXCR4. Chronic exposure to THC increased T lymphocyte CXCR4 expression on both CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. Drugs that block the CXCR4 receptor appear to be capable of “mobilizing“ hematopoietic stem cells into the bloodstream as peripheral blood stem cells.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining

















