分子别名(Synonym)
CTLA4,CD152
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (CT4-H5255) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Ala 37 - Ser 160 (Accession # P16410-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Ala 37
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a human IgG1 Fc tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 39.9 kDa. The protein migrates as 45-55 kDa under reducing (R) condition, and 90 kDa under non-reducing (NR) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>98% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in Tris with Glycine, Arginine and NaCl, pH7.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
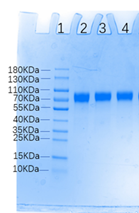
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
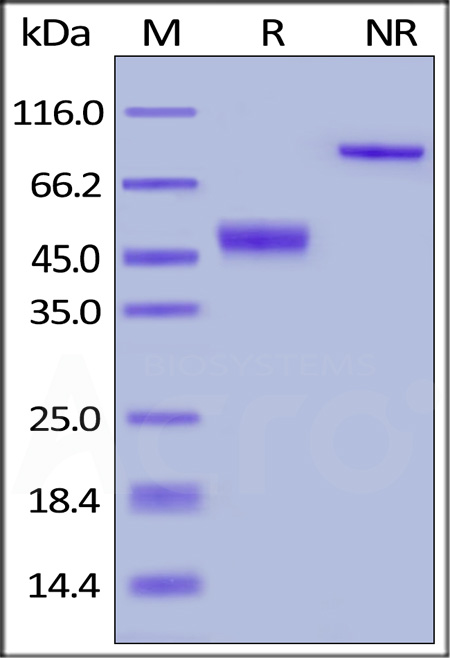
Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 98%.
SEC-MALS
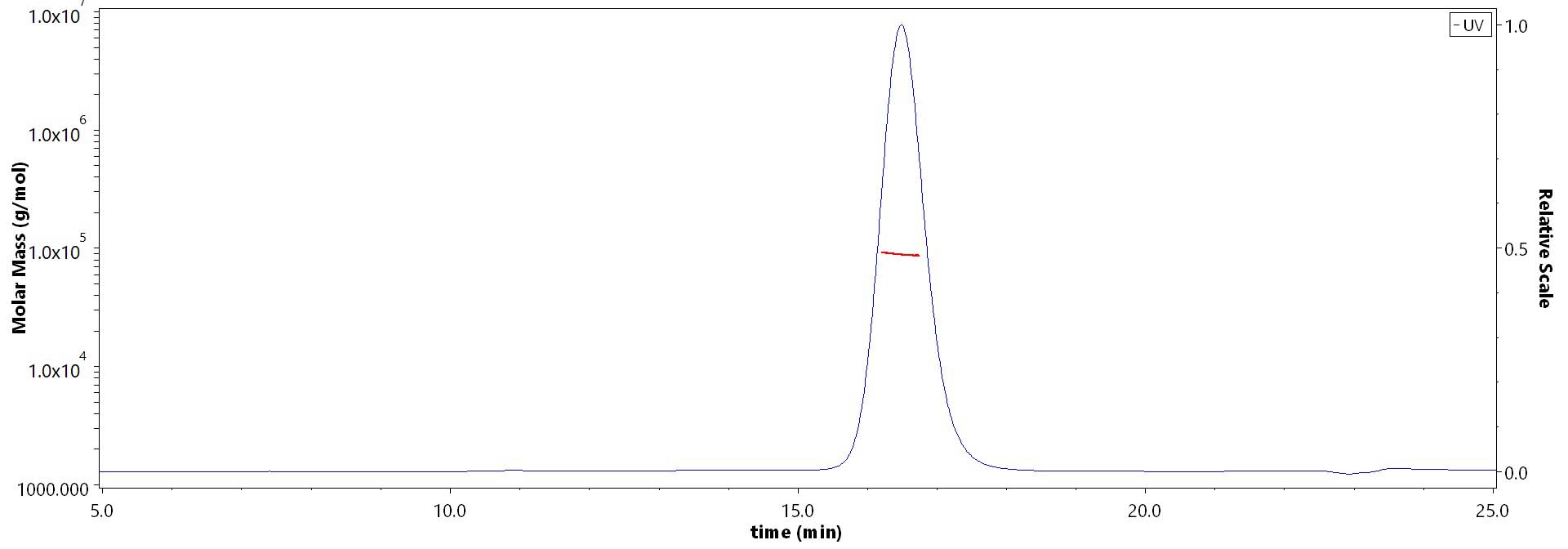
The purity of Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 82-100 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
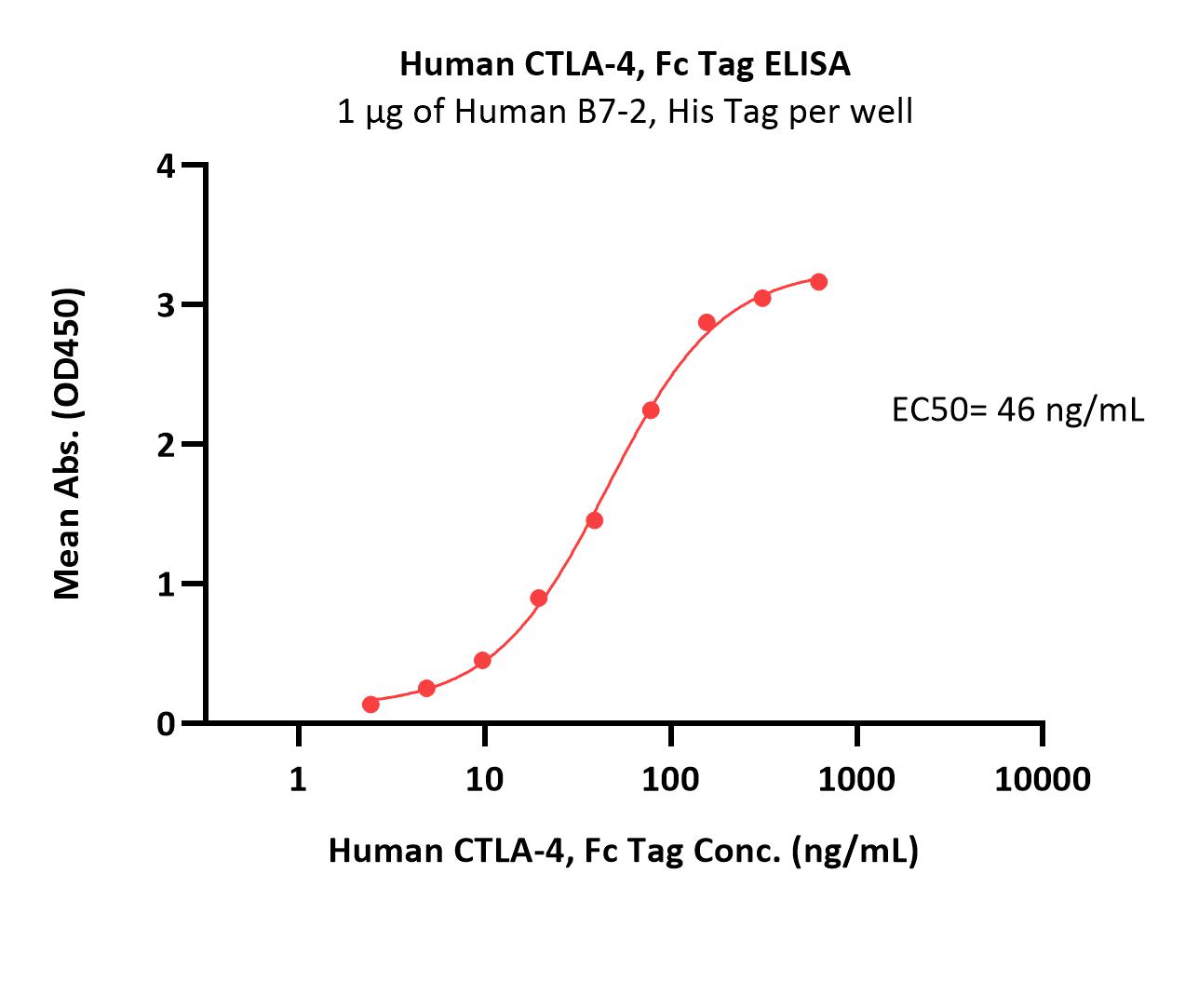
Immobilized Human B7-2, His Tag (Cat. No. CD6-H5223) at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255) with a linear range of 2-78 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
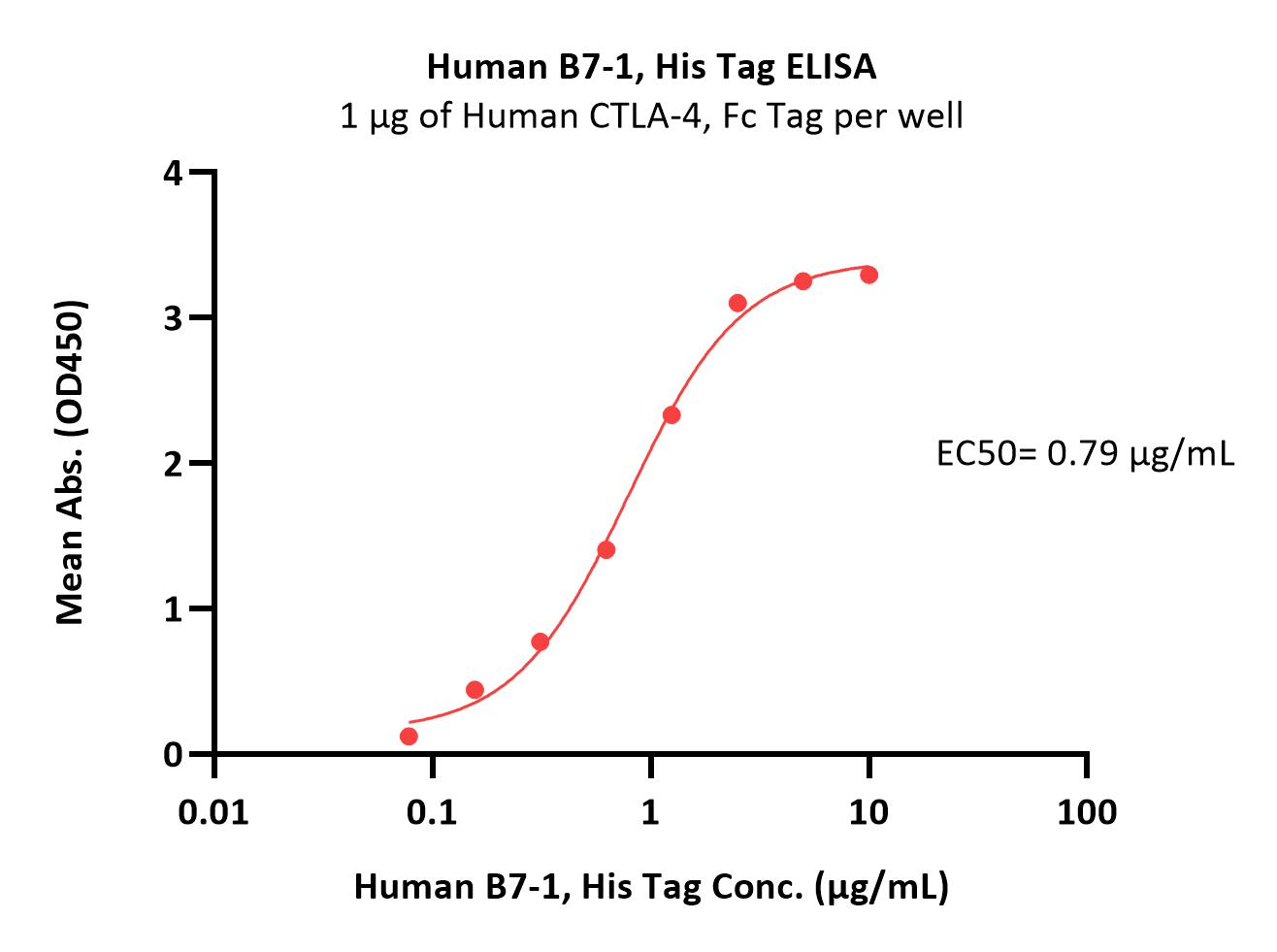
Immobilized Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255) at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human B7-1, His Tag (Cat. No. B71-H5228) with a linear range of 0.156-1.25 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
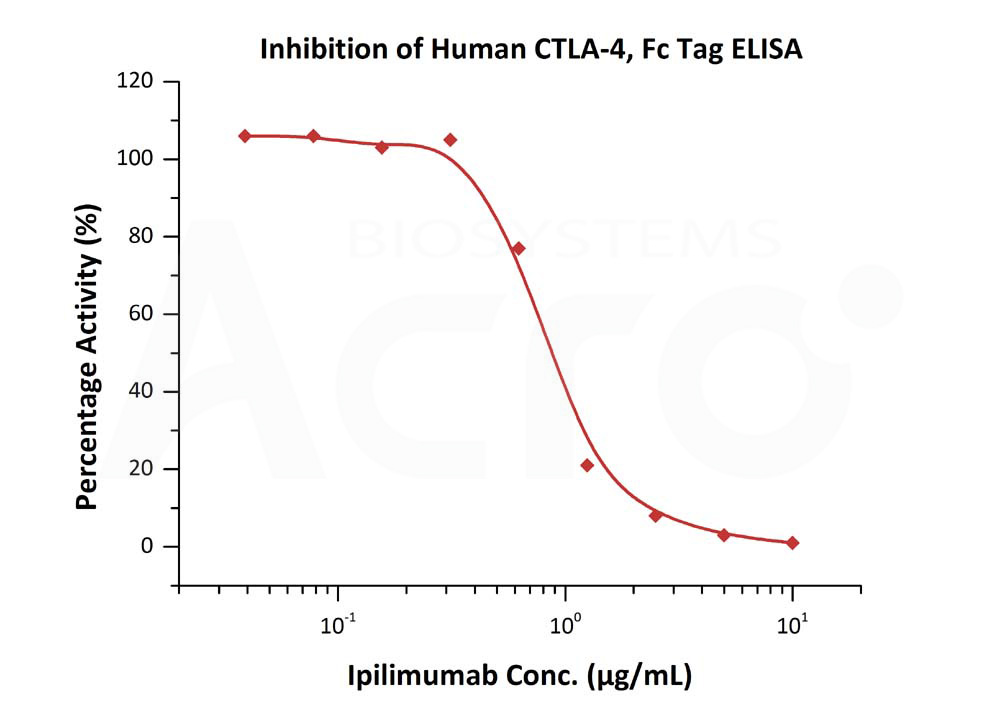
Serial dilutions of Ipilimumab were added into Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255): Biotinylated Human B7-1, Fc,Avitag (Cat. No. B71-H82F2) binding reactions. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.8260 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
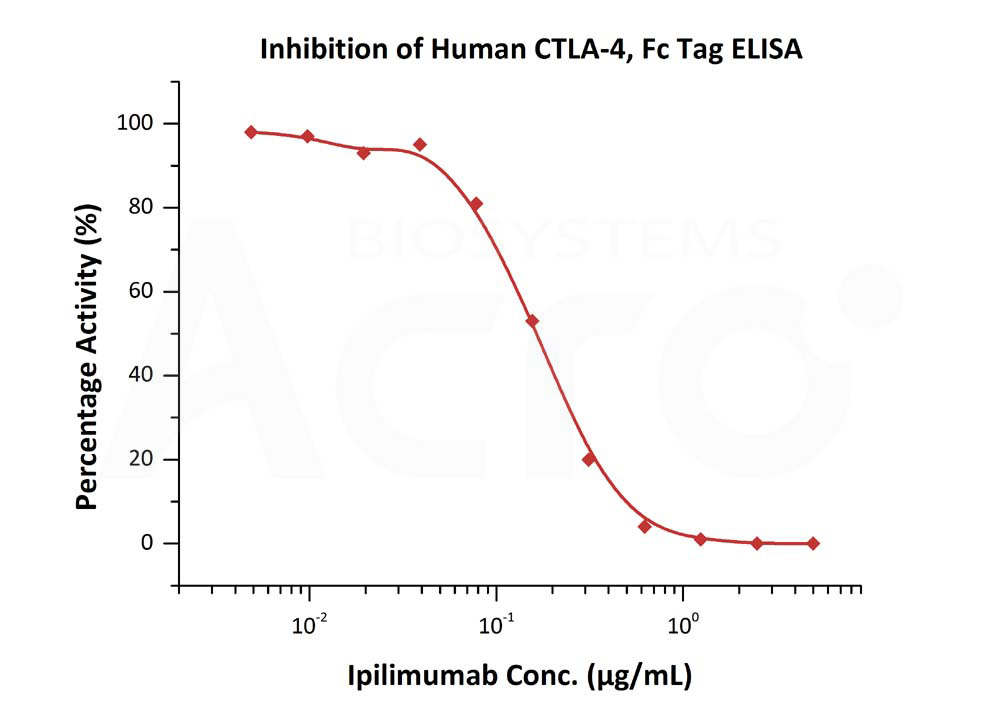
Serial dilutions of Ipilimumab were added into Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255): Biotinylated Human B7-2, Fc,Avitag, premium grade (Cat. No. CD6-H82F5) binding reactions. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.1701 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-BLI
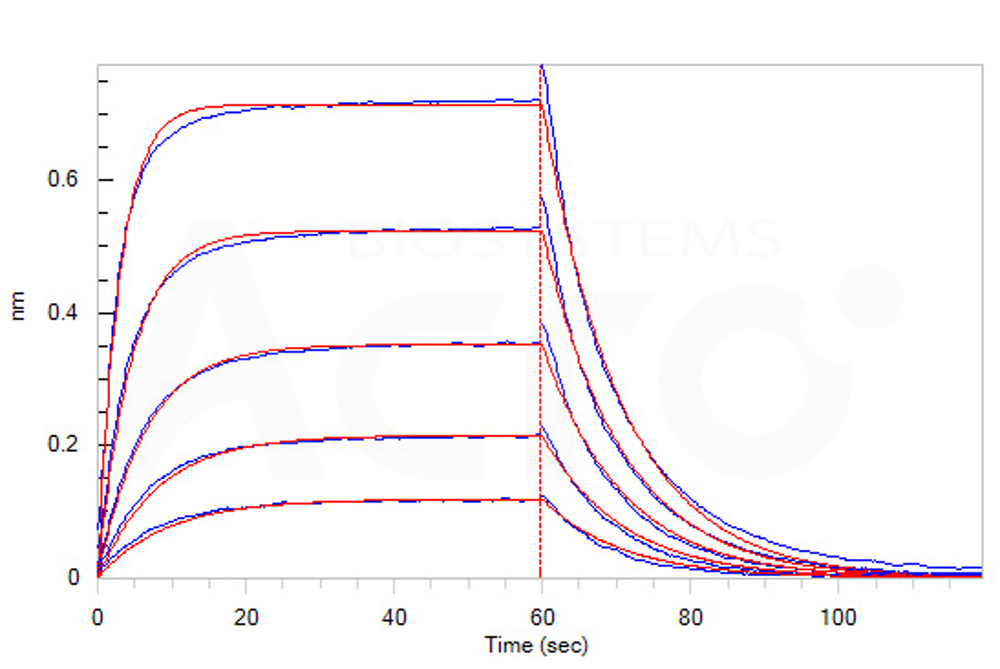
Loaded Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind Human B7-1, His Tag (Cat. No. B71-H5228) with an affinity constant of 0.52 μM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
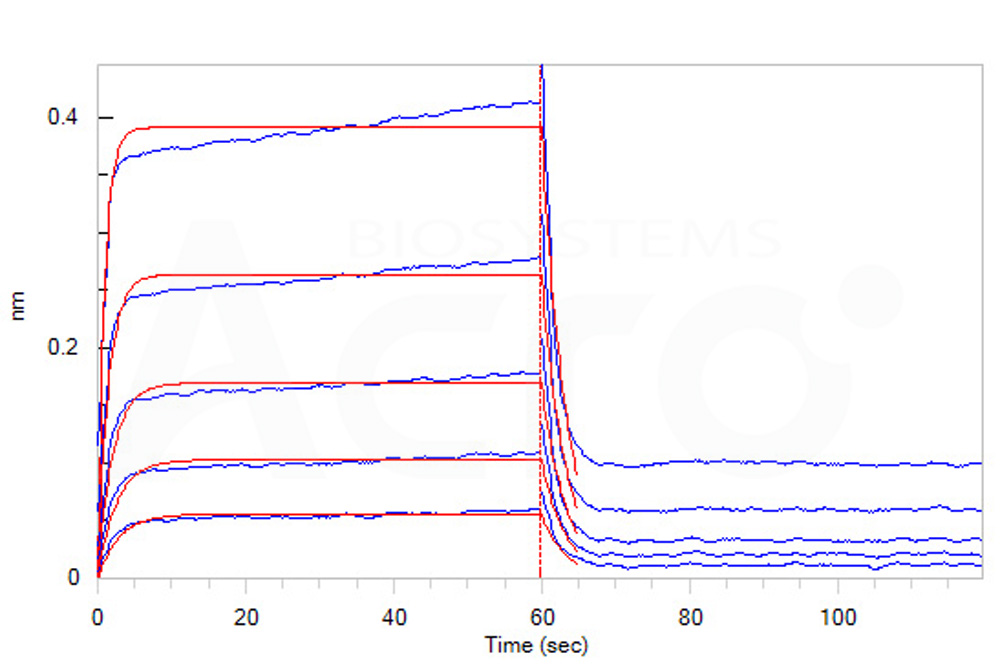
Loaded Human CTLA-4, Fc Tag (Cat. No. CT4-H5255) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind Human B7-2, His Tag (Cat. No. CD6-H5223) with an affinity constant of 1.9 μM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论
- 132XXXXXXX7
- 买的这个带Fc标签的蛋白用来做动物免疫,因为免疫动物对蛋白的质量要求还挺高的,就跑了个电泳,做了个液相,质检结果看上去纯度还可以,希望能筛选到合适的抗体
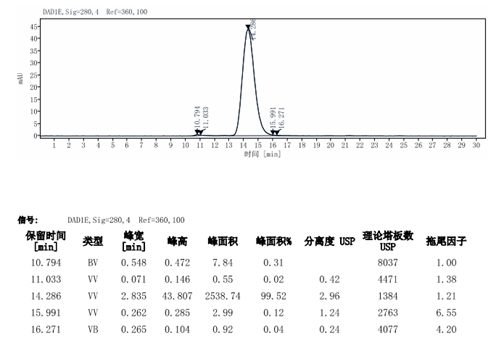
 >
>- 2021-9-1
背景(Background)
CTLA-4 (Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4) is also known as CD152 (Cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system. CTLA4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, which is expressed on the surface of Helper T cells and transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. The protein contains an extracellular V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. Alternate splice variants, encoding different isoforms. CTLA4 is similar to the T-cell co-stimulatory protein, CD28, and both molecules bind to CD80 and CD86, also called B7-1 and B7-2 respectively, on antigen-presenting cells. CTLA4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. Intracellular CTLA4 is also found in regulatory T cells and may be important to their function. Fusion proteins of CTLA4 and antibodies (CTLA4-Ig) have been used in clinical trials for rheumatoid arthritis.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















