Early Notch signals from fibroblastic reticular cells program effector CD8+ T cell differentiationMaurice De Sousa, Perkey, Le Corre
et alJ Exp Med (2025) 222 (5)
Abstract: A better understanding of the mechanisms regulating CD8+ T cell differentiation is essential to develop new strategies to fight infections and cancer. Using genetic mouse models and blocking antibodies, we uncovered cellular and molecular mechanisms by which Notch signaling favors the efficient generation of effector CD8+ T cells. Fibroblastic reticular cells from secondary lymphoid organs, but not dendritic cells, were the dominant source of Notch signals in T cells via Delta-like1/4 ligands within the first 3 days of immune responses to vaccination or infection. Using transcriptional and epigenetic studies, we identified a unique Notch-driven T cell-specific signature. Early Notch signals were associated with chromatin opening in regions occupied by bZIP transcription factors, specifically BATF, known to be important for CD8+ T cell differentiation. Overall, we show that fibroblastic reticular cell niches control the ultimate molecular and functional fate of CD8+ T cells after vaccination or infection through the delivery of early Notch signals.© 2025 Maurice De Sousa et al.
Electroacupuncture Combined with Press Needles Alleviates Simple Obesity via VEGF-C/VEGFR-3/PI3K/AKT Signaling PathwayXia, Yu, Wang
et alObes Facts (2025)
Abstract: Simple obesity is an increasingly prevalent chronic condition. While electroacupuncture (EA) has demonstrated potential in addressing this issue, its effectiveness may be hindered by insufficient continuous stimulation and challenges related to patient adherence. This study aimed to compare the efficacy of EA alone versus EA combined with press needles in the treatment of simple obesity and to explore the underlying mechanisms contributing to weight loss.Eighty simple obese patients with a body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25.0 kg/m2 were divided into two groups: the observation group (treated with EA combined with press needles) and the control group (treated with EA alone). The efficacy of the treatments was evaluated by monitoring obesity indicators. Additionally, obesity rat models were established through a high-fat diet (HFD), and rats were randomly assigned to three groups: obesity control group (no treatment), EA group, and EA combined with press needles group. Treatment outcomes were assessed by monitoring obesity indicators, examining adipose and liver cell morphology using staining techniques, and evaluating intestinal lymphatic vessel function through qRT-PCR, western blot, and immunofluorescence analyses.The patients in the observation group exhibited significantly lower body weight (BW), BMI, body fat percentage (F%), abdominal circumference (A), waist circumference (WC), as well as serum levels of intestinal lymphatic function-related factors such as VEGF-C, delta-like ligand 4 (DLL4), and adrenomedullin (ADM) compared to the control group. Similarly, compared to EA group, EA combined with press needles significantly decreased obesity indexes, serum intestinal lymphatic function-related factors, and improved lymphatic vessel function in obese rats. Mechanistically, the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was inhibited by EA combined with press needles intervention.The combined therapy of EA with press needles had shown significantly superior efficacy in treating simple obesity compared to EA treatment alone. It achieved this by modulating the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, improving lymphatic vessel structure and function, and ultimately inhibiting obesity.The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Targeted siRNA Delivery Against RUNX1 Via tFNA: Inhibiting Retinal Neovascularization and Restoring Vessels Through Dll4/Notch1 SignalingZhou, Xu, Wang
et alInvest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (2025) 66 (3), 39
Abstract: To assess the efficacy of tetrahedral framework nucleic acids (tFNAs) as a delivery system for small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting RUNX1 (siRUNX1) in inhibiting retinal neovascularization (RNV) and restoring vascular integrity via the Dll4/Notch1 signaling pathway.tFNAs and tFNAs-siRUNX1 were synthesized using annealing of single-stranded DNAs and characterized by PAGE and high-performance capillary electrophoresis. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were treated under hypoxic conditions with tFNAs-siRUNX1, and cellular uptake was evaluated using fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. Angiogenesis was assessed through EdU proliferation, tube formation, and wound-healing assays. In vivo experiments used oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) and laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) models in mice, with subsequent imaging by optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus fluorescence angiography. Gene and protein expression were analyzed by RT-PCR and Western blotting, focusing on the Dll4/Notch1 pathway and apoptosis markers.tFNAs-siRUNX1 effectively inhibited endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation in vitro. In OIR and CNV models, it reduced neovascularization, nonperfusion areas, and vascular leakage. The mechanism involved modulation of the Dll4/Notch1 pathway, with decreased Dll4, Notch1, and Hes1 and increased Nts expression. tFNAs-siRUNX1 also reduced endothelial cell apoptosis via the Bcl-2/Bax pathway.tFNAs-siRUNX1 is a promising delivery system for targeting RNV, inhibiting neovascularization, and restoring retinal vascular integrity, providing a potential therapeutic alternative to anti-VEGF treatments.
Conversion of T Effector Cells Into T Regulatory Cells in Type 1 Diabetes/Latent Autoimmune Diabetes of Adults by Inhibiting eIF5A and Notch PathwaysRafiqi, Aldasouqi, Paparodis
et alImmunotargets Ther (2025) 14, 205-226
Abstract: The generation of functionally active, stable T regulatory cells (Tregs) is a crucial target of type 1 diabetes (T1D) immunotherapy. This study investigated therapeutic intervention for T1D/Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), wherein the diabetogenic proinflammatory Treg (intermediate) cell subset was characterized and driven to a Treg phenotype (CD4+CD25+FOXP3+). This involved simultaneous inhibition of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5a (eIF5a) and Notch pathways using GC7 (N1-Guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane) and Anti-DLL4 (Delta-like-ligand-4).Peripheral blood from patients with T1D/LADA and healthy adults (n=7 each) was used to isolate the CD4+CD25- T cell population and CD4 deficient peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Cells were subjected to GAD65+GC7+anti-DLL4 treatment for seven days and compared with conventional anti-CD3/CD28/CD137 stimulation for conversion into the Tregs. Newly plasticized Tregs were assessed for their suppressive potential against freshly isolated autologous T responder cells. In addition, live, dead, and apoptotic cell counts were performed to evaluate the adverse effects of immunomodulatory treatment on immune cells. The data was analyzed with GraphPad Prism using 1- or 2-way ANOVA and a Student's t-test.A unique population of proinflammatory cytokines expressing intermediate Tregs (CD4+CD25-IFNg+IL17+FOXP3+) was characterized in T1D/LADA patients and found significantly increased compared to age-matched healthy adults. Simultaneous inhibition of eIF5a and Notch pathways could induce Treg phenotype in Treg-deficient CD4+ T cells and CD4 deficient PBMCs from T1D/LADA patients. GAD65+GC7+anti-DLL4 treatment plasticized Tregs withstanding a proinflammatory milieu mimicking T1D/LADA, and the plasticized Tregs exhibited a stable and suppressive functional phenotype. Furthermore, GAD65+GC7+anti-DLL4 treatment had no adverse effects on immune cells.The present approach is a multipronged approach involving the inhibition of eIF5a and Notch pathways that addresses the upregulation of immune tolerance, differentiation, and proliferation of cytotoxic T cells and alleviates β-cell dysfunction. Additionally, this treatment strategy could also be leveraged to boost Treg generation following islet transplantation or as a combinational therapy along with adoptive cell transfer.© 2025 Rafiqi et al.

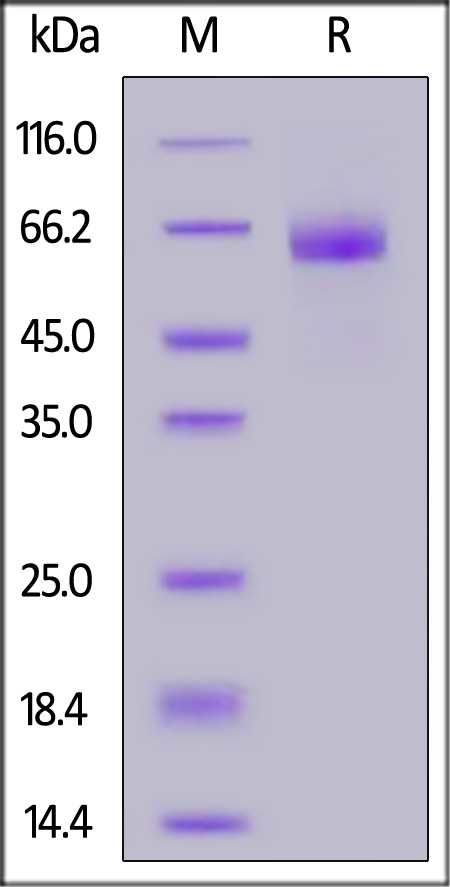
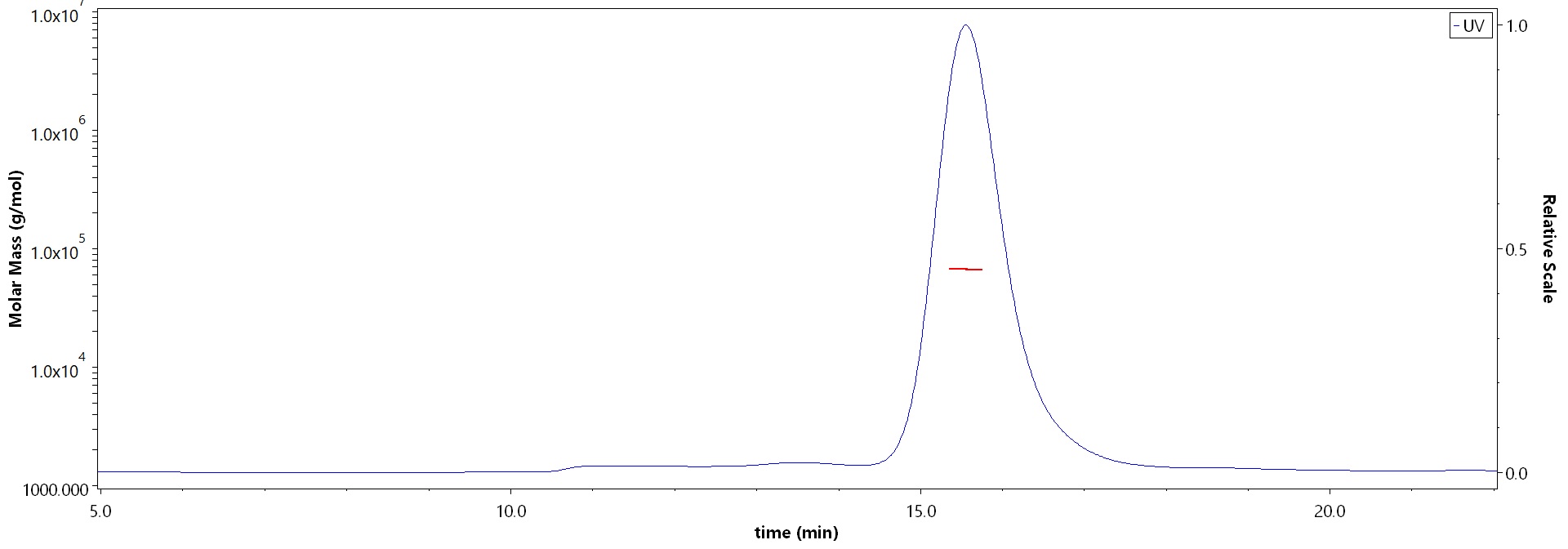
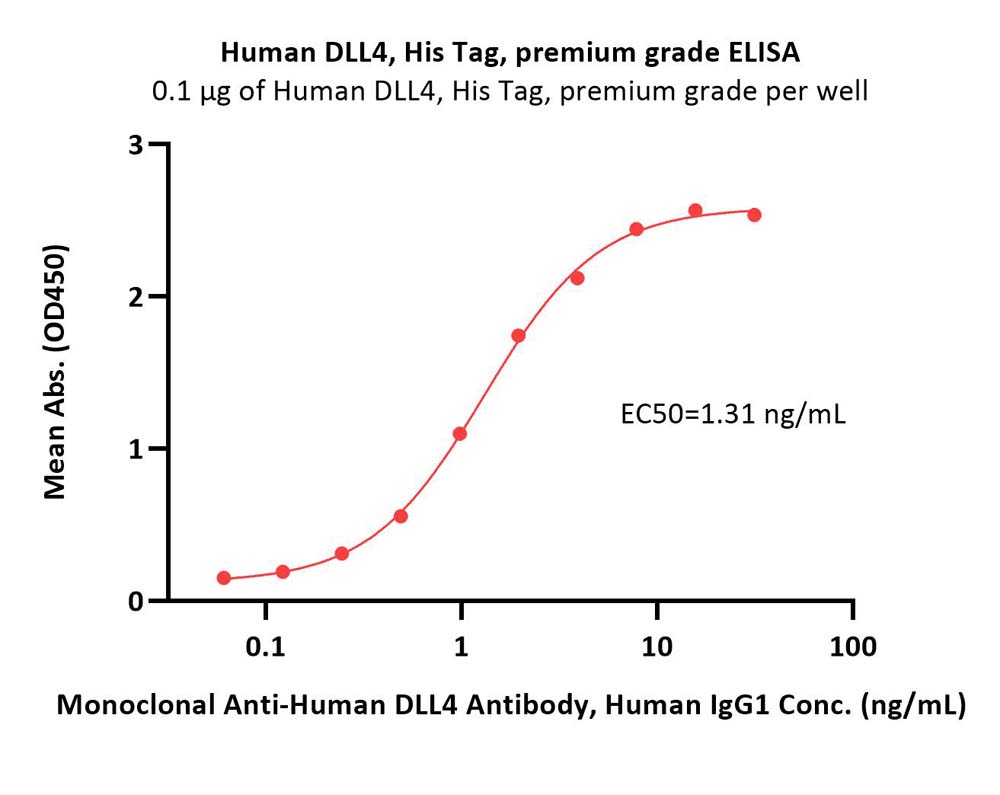
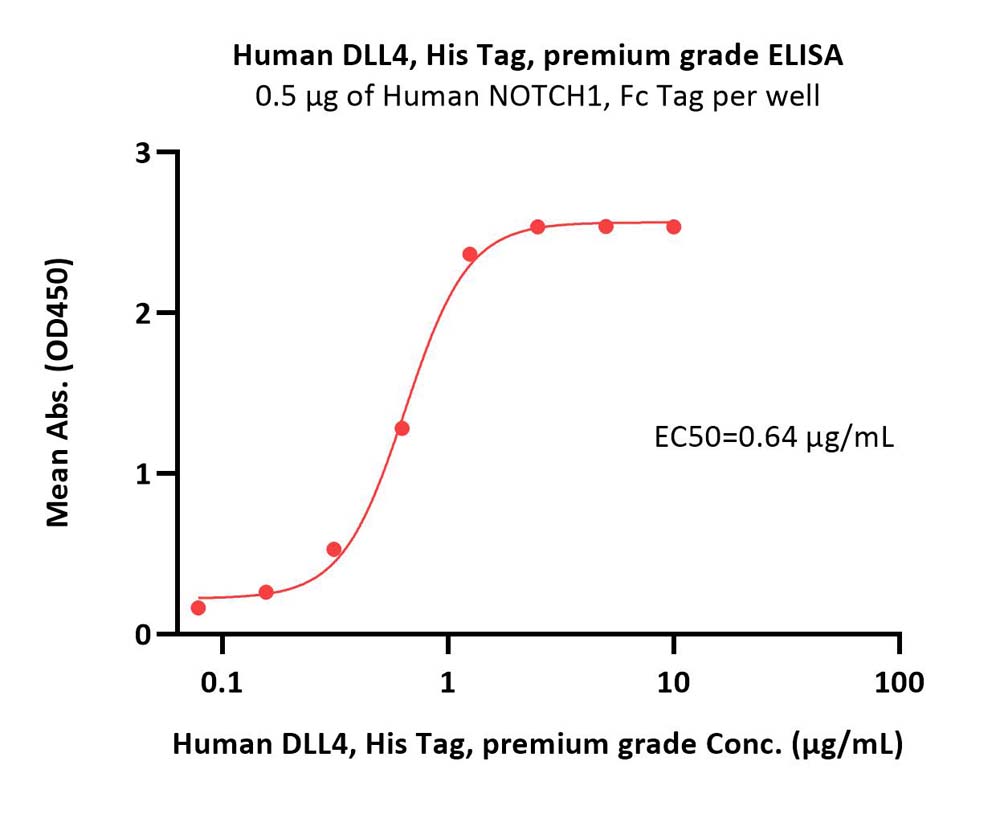























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















