Sensitivity to Neutralizing Antibodies and Resistance to Type I Interferons in SARS-CoV-2 R.1 Lineage Variants, CanadaJacob, Zhang, Ajoge
et alEmerg Infect Dis (2023) 29 (7), 1386-1396
Abstract: Isolating and characterizing emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants is key to understanding virus pathogenesis. In this study, we isolated samples of the SARS-CoV-2 R.1 lineage, categorized as a variant under monitoring by the World Health Organization, and evaluated their sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies and type I interferons. We used convalescent serum samples from persons in Canada infected either with ancestral virus (wave 1) or the B.1.1.7 (Alpha) variant of concern (wave 3) for testing neutralization sensitivity. The R.1 isolates were potently neutralized by both the wave 1 and wave 3 convalescent serum samples, unlike the B.1.351 (Beta) variant of concern. Of note, the R.1 variant was significantly more resistant to type I interferons (IFN-α/β) than was the ancestral isolate. Our study demonstrates that the R.1 variant retained sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies but evolved resistance to type I interferons. This critical driving force will influence the trajectory of the pandemic.
Downregulation of SOCS gene expression can inhibit the formation of acute and persistent BDV infectionsLi, Xia, Meng
et alScand J Immunol (2021) 93 (1), e12974
Abstract: High expression of suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) has been detected during various viral infections. As a negative feedback regulator, SOCS participates in the regulation of multiple signalling pathways. In this study, to study the related mechanism between SOCS and BDV and to explore the effect of SOCS on IFN pathways in nerve cells, downregulated of SOCS1/3 in oligodendroglial (OL) cells and OL cells persistently infected with BDV (OL/BDV) were constructed with RNA interference technology. An interferon inducer (poly I:C, PIC) and an IFN-α/β R1 antibody were used as stimulation in the SOCS1/3 low-expression cell models, qRT-PCR was used to detect type I IFN and BDV nucleic acid expression, Western blot was used to detect the expression of BDV P40 protein. After BDV acute infection with OL cells which with downregulated SOCS expression, the virus accounting was not detected, and the viral protein expression was lower than that of OL/BDV cells; the OL/BDV cells with downregulated SOCS expression had lower virus nucleic acid and protein expression than OL/BDV cells. Stimulated by IFN-α/β R1 antibody, the expression of type I interferon in OL/BDV cells decreased, and the content of BDV nucleic acid and protein increased, which was higher than that of OL/BDV cells. From the results, it was concluded that downregulating SOCS1/3 can inhibit the formation of acute BDV infection and virus replication in persistent BDV infection by promoting the expression of IFN-α/β and that SOCS can be used as a new target for antiviral therapy.© 2020 The Scandinavian Foundation for Immunology.
Glucocorticoid regulation of 24-hour oscillation in interferon receptor gene expression in mouse liverKoyanagi, Suyama, Kuramoto
et alEndocrinology (2006) 147 (11), 5034-40
Abstract: Although the antiviral effect of interferon (IFN) varies depending on 24-h oscillation in the expression of its specific receptor, the mechanism of oscillation remains to be clarified. Here we report that oscillation in the expression of the IFN receptor gene (IFN-alpha/beta R1) in mouse liver is caused by the endogenous rhythm of glucocorticoid secretion. Brief exposure of mouse hepatic cells (Hepa 1-6) to corticosterone (CORT) resulted in a significant decrease in mRNA levels of IFN-alpha/beta R1. The CORT-induced decrease in IFN-alpha/beta R1 mRNA levels was reversed by pretreating the cells with RU486, a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist. The mRNA levels of IFN-alpha/beta R1 gene in the liver of adrenalectomized mice were consistently increased throughout the day. However, a single administration of CORT to adrenalectomized mice significantly decreased the mRNA levels of IFN-alpha/beta R1 in the liver. Furthermore, the rhythmic phase of IFN-alpha/beta R1 expression was modulated after the alteration of rhythmicity in glucocorticoid secretion, which was induced by restricted daily feeding. As a consequence, under manipulation of the feeding schedule, 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthase activities, as an index of antiviral effect, in plasma and liver at 24 h after IFN-alpha injection also varied depending on the alteration of glucocorticoid secretion rhythm. These results suggest that the endogenous rhythm of glucocorticoid secretion is involved in the circadian regulation of IFN-alpha/beta R1 expression in mouse liver. Our findings also support the notion that monitoring the 24-h variation in IFN receptor function is useful for selecting the most appropriate time of day to administer IFN.
Role of interferon alpha/beta receptor chain 1 in the structure and transmembrane signaling of the interferon alpha/beta receptor complexConstantinescu, Croze, Wang
et alProc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1994) 91 (20), 9602-6
Abstract: A previously cloned cDNA encodes one subunit of the human interferon alpha/beta receptor (IFN alpha R), denoted IFN alpha R1. To study the expression and signaling of IFN alpha R1, we used monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated against the baculovirus-expressed ectodomain of IFN alpha R1. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting of lysates from a variety of human cell lines showed that IFN alpha R1 has an apparent molecular mass of 135 kDa. Binding analysis with 125I-labeled mAb demonstrated high levels of cell surface expression of IFN alpha R1 in human cells and in mouse cells transfected with IFN alpha R1 cDNA, whereas no cross-reactivity was observed in control mouse L929 cells expressing only the endogenous mouse receptor. The subunit was rapidly down-regulated by IFN alpha (80% decrease within 2 hr) and degraded upon internalization. The IFN alpha R1 chain appeared to be constitutively associated with the 115-kDa subunit of the IFN alpha/beta receptor, since the mAbs coprecipitated this protein. IFN alpha/beta treatment induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IFN alpha R1 within 1 min, with kinetics paralleling that of the IFN-activated protein-tyrosine kinases Jak1 and Tyk2. Ligand-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IFN alpha R1 was blocked by the kinase inhibitors genistein or staurosporine. Although IFN alpha R1 cDNA-transfected mouse cells expressed high levels of this subunit when compared with empty vector-transfected cells the number of binding sites for human IFN alpha (50-75 sites per cell) was not increased. Human IFN alpha induced the expression of a mouse IFN alpha/beta-responsive gene (the 204 gene) in mouse L929 cells transfected with the IFN alpha R1 cDNA, but not in mock-transfected cells. These results suggest that the IFN alpha R1 subunit acts as a species-specific signal transduction component of the IFN alpha/beta receptor complex.

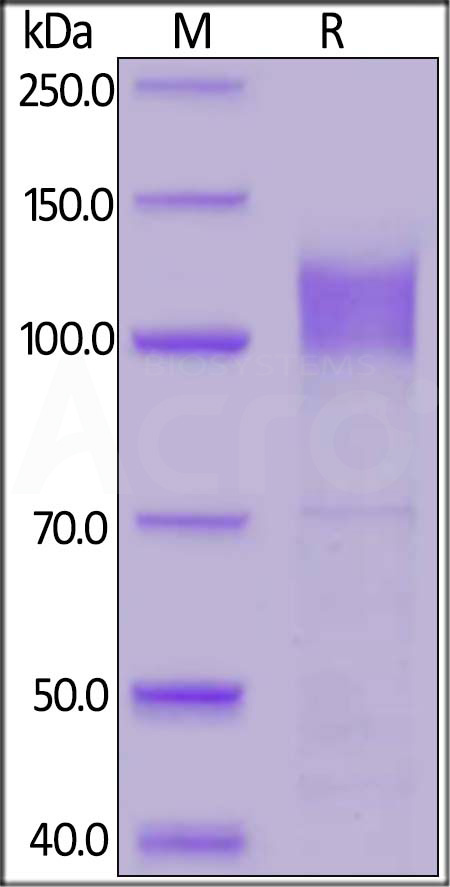
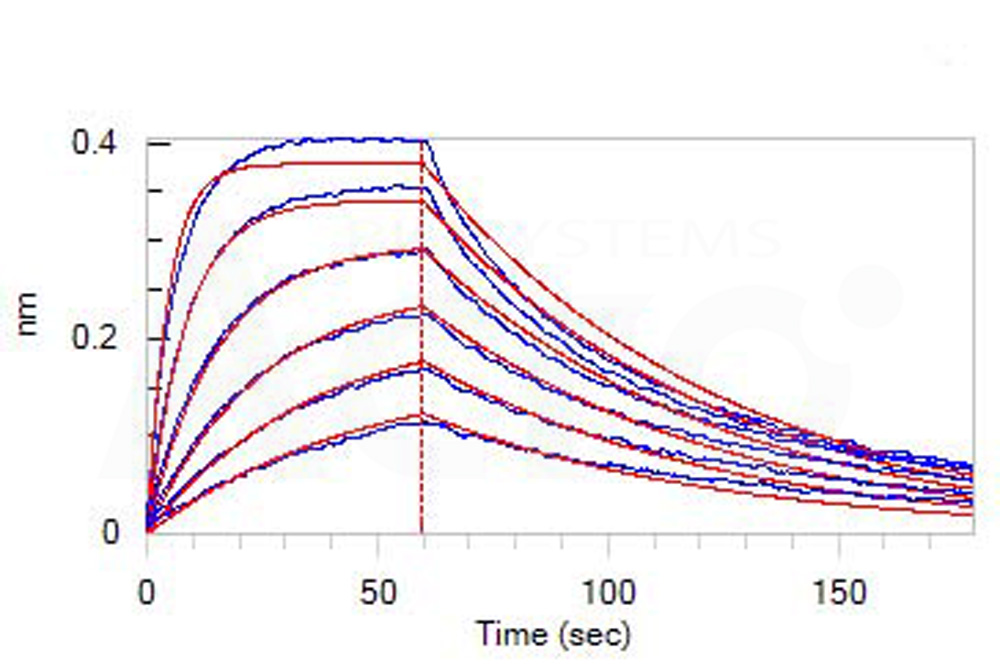























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















