Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids alleviate renal fibrosis in chronic kidney disease by reducing macrophage activation and infiltration through the JAG1-NOTCH1/2 pathwayLi, Liu, Yang
et alInt Immunopharmacol (2025) 152, 114454
Abstract: In recent years, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) has been rising. As CKD progresses, it frequently involves inflammatory cell infiltration, contributing to renal fibrosis. Current research indicates that abnormalities in lipid metabolism play a role in this fibrotic process. However, the specific effects of various dietary fatty acids on renal inflammation and fibrosis remains largely unexplored. Our study demonstrates that dietary intake of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids can inhibit macrophage activation and infiltration in a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO), thus reducing the severity of renal fibrosis. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly α-linolenic acid (α-LA), mitigate damage to HK-2 cells and macrophages by targeting the JAG1-NOTCH1/2 pathway and by downregulating the expression of the chemokine MCP-1 and its receptor CCR2. This modulation attenuates macrophage activation and infiltration, reducing the inflammatory response. Furthermore, these fatty acids inhibit fibroblast chemotaxis, reduce fibroblast activation, and mitigate the deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM), thus slowing the progression of renal fibrosis. Our findings underscore the protective effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as α-LA, in preventing injury, inhibiting macrophage activation, and alleviating fibrosis. These results suggests that adjusting the dietary balance of fatty acids may offer a promising strategy to enhance the efficacy of CKD treatment.Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
SARM1 deletion inhibits astrogliosis and BBB damage through Jagged-1/Notch-1/NF-κB signaling to improve neurological function after ischemic strokeFu, Zheng, Li
et alNeurobiol Dis (2025)
Abstract: Reactive astrogliosis is a critical process in the development of ischemic stroke. However, the precise mechanism by which reactive astrogliosis changes the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke remains elusive. Sterile alpha and TIR motif-containing 1 protein (SARM1) plays a key role in axonal degeneration and is involved in different cell death programs that regulate neuronal survival. The present study investigated the role of SARM1 in regulating reactive astrogliosis and neurological function after stroke in whole-body SARM1 knockout (SARM1-/-) mice. SARM1-/- mice showed significantly smaller infarction, slighter apoptosis, and fewer neurological function deficits 1-7 days after ischemic injury. Immunohistochemistry, western blot, and real-time PCR analyses revealed that compared with the wild-type (WT) mice, SARM1-/- mice exhibited reduced astrocytic proliferation, increased anti-inflammatory astrocytes, decreased glial scar formation in the infarct zone on day 7 after ischemic injury. SARM1 deletion also suppressed cerebral microvascular damage and blood-brain barrier (BBB) injury in ischemic brains. Mechanistically, SARM1 deletion inhibited the stroke-triggered activation of NF-κB signaling and decreased the expression of Jagged-1 and NICD in astrocytes. Overall, these findings provide the first line of evidence for a causative role of SARM1 protein in ischemia-induced reactive astrogliosis and ischemic neurovascular damage.Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Hesperetin induces apoptosis in lung squamous carcinoma cells via G2/M cycle arrest, inhibition of the Notch1 pathway and activation of endoplasmic reticulum stressXie, He, Tan
et alInt J Mol Med (2025) 55 (5)
Abstract: Hesperetin (HST), a natural flavonoid, has potent antitumor effects on lung adenocarcinoma; however, its effects on lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) are currently unknown. The present study aimed to investigate the anticancer effects of HST on LUSC cells. The influence of 37.5, 75 and 150 µM HST on the H1703 cell line, and of 75, 150 and 300 µM HST on the H226 cell line was determined using the Cell Counting Kit‑8 method, cell cycle assay, JC‑1 mitochondrial membrane potential assay and Annexin V‑FITC/PI staining. DMSO‑treated cells were used as the control group. Western blotting was performed to detect the protein expression levels of cyclin B1, CDK1, Bcl‑2, Bax, caspase‑3, cleaved caspase‑3, phosphorylated‑eIF2α, eIF2α, glucose‑regulated protein 78, CHOP, Notch1 and Hes‑1. The relationship between endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), Notch1 signaling and apoptosis was examined using the ERS‑inhibitor 4‑phenylbutyric acid (4‑PBA; 500 µM) and the Notch1 signaling activator Jagged‑1 (4 µM). In vivo, mice were divided into control, HST (30, 60 and 90 mg/kg/q2d) and cisplatin (2 mg/kg/q2d) groups to evaluate the anti‑LUSC effects of HST. The results revealed that HST inhibited the viability of H226 and H1703 cells, leading to cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and the induction of cell apoptosis. In addition, HST downregulated the Notch1 signaling pathway and increased ERS. In H1703 cells, 4‑PBA and Jagged‑1 reduced the expression of apoptosis‑related proteins, and Jagged‑1 also reduced the expression of ERS‑related proteins. In vivo, HST reduced tumor growth without any apparent toxic side effects. In conclusion, HST may exert its antitumor effects by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and inhibiting the Notch1 signaling pathway to activate ERS‑induced apoptosis, making it a promising agent for treating LUSC.
miR-34a-5p modulation of polycystic ovary syndrome via targeting the NOTCH signaling pathwayZhang, Wang, Liu
et alJ Ovarian Res (2025) 18 (1), 55
Abstract: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is currently recognized as a condition that affects several systems in the body, including the reproductive, endocrine, and cardiovascular systems. Prevalent among teenagers and women of reproductive age. Prior research has demonstrated an elevation of miR-34a-5p within the follicular fluid (FF) of women of PCOS. Despite this, the precise mechanisms through which miR-34a-5p influences granulosa cells (GC) development and function remain poorly characterized.Therefore, this study investigates the involvement and pathogenic mechanisms of miR-34a-5p within GCs in the context of PCOS. The human granulosa-like tumor cell line (KGN) got transfected at a control, as well as a miR-34a-5p mimic and inhibitor, respectively. Monitor cellular proliferation in each experimental group. The experimental methods included RT-qPCR, CCK8, flow cytometry and western blotting. Also, the interaction between miR-34a-5p and the particular sequence of JAG1 has been verified using the dual luciferase assay. Further investigation of the connection involving miR-34a-5p and the Notch signaling pathway was conducted using bioinformatics analysis and experimental methods.The results demonstrated that miR-34a-5p expression was significantly elevated in the serum(p<0. 0001)and FF (p = 0. 0402) of PCOS, whereas its expression in GCs (p = 0. 5522) showed no significant variation. Overexpressing miR-34a-5p caused a decrease in the rate at which KGN cells multiplied and an increase in programmed cell death. Conversely, inhibiting miR-34a-5p resulted in an increase in cell growth and a decrease in programmed cell death. Bioinformatics analysis and experimental results further demonstrated thatmiR-34a-5p interacts with the 3'UTR region of JAG1, leading to a negative regulation of the Jagged1-Notch signaling pathway.In summary, the miR-34a-5p molecule inhibits the growth of GCs as well as triggers programmed cell death by regulating the Jagged1-Notch signaling pathway. Silencing miR-34a-5p prevents dysfunction in GCs. Our analysis implies that miR-34a-5p is a new molecular site to treat PCOS.© 2025. The Author(s).

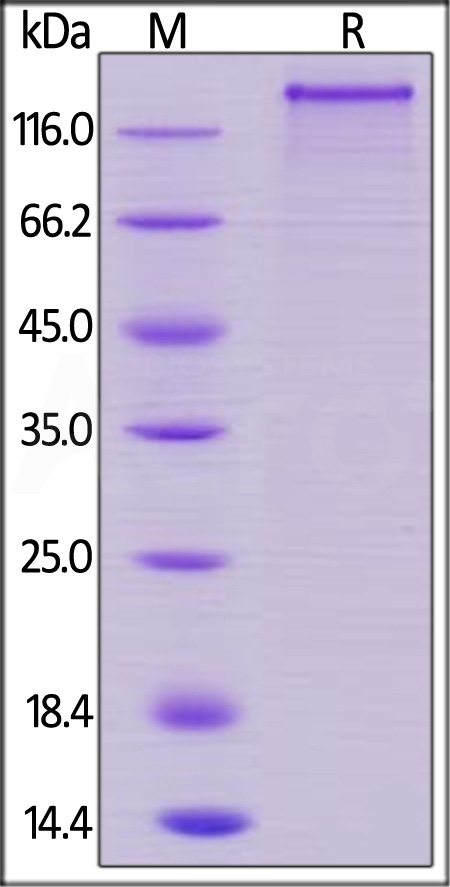
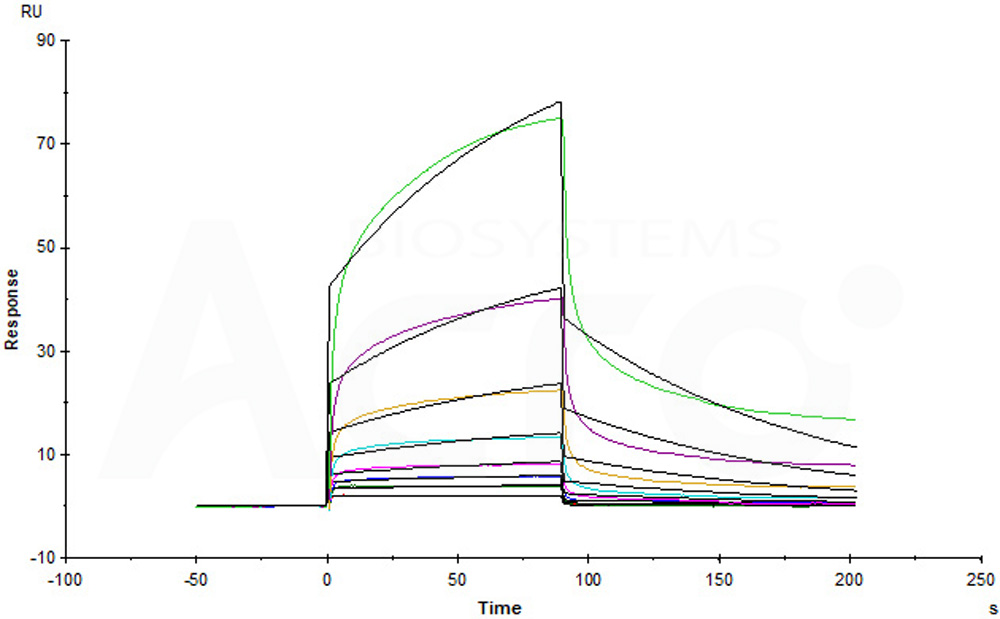
 +添加评论
+添加评论























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining

















