分子别名(Synonym)
PDGF-BB,PDGF-B,FLJ12858,PDGF2,SIS,SSV,c-sis
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Unconjugated Human PDGF-BB, His,Avitag (PDB-H5127) is expressed from E. coli cells. It contains AA Ser 82 - Thr 190 (Accession # P01127-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Met
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus, followed by an Avi tag (Avitag™)
The protein has a calculated MW of 15.1 kDa. The protein migrates as 17 kDa under reducing (R) condition, and 35 kDa under non-reducing (NR) condition (SDS-PAGE).
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 0.085% TFA in 30% ACN with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
电泳(SDS-PAGE)

Unconjugated Human PDGF-BB, His,Avitag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
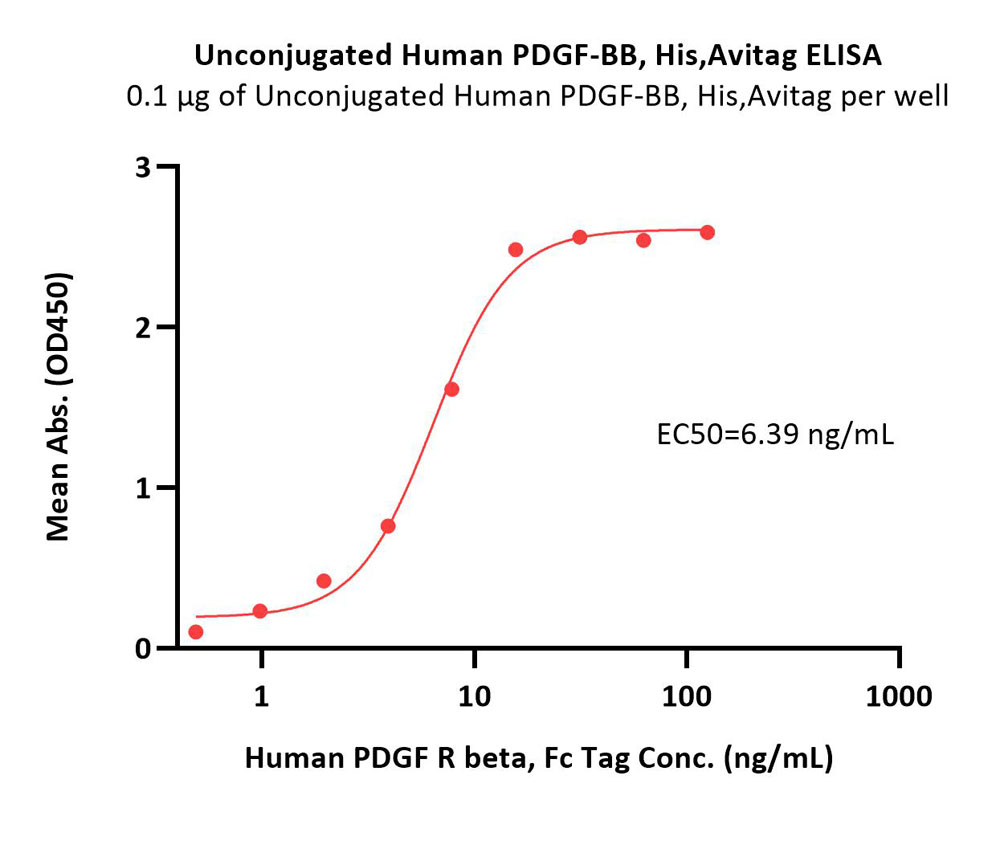
Immobilized Unconjugated Human PDGF-BB, His,Avitag (Cat. No. PDB-H5127) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human PDGF R beta, Fc Tag (Cat. No. PDB-H5259) with a linear range of 0.5-16 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
PDGFs are mitogenic during early developmental stages, driving the proliferation of undifferentiated mesenchyme and some progenitor populations. During later maturation stages, PDGF signalling has been implicated in tissue remodelling and cellular differentiation, and in inductive events involved in patterning and morphogenesis. In addition to driving mesenchymal proliferation, PDGFs have been shown to direct the migration, differentiation and function of a variety of specialised mesenchymal and migratory cell types, both during development and in the adult animal. Other growth factors in this family include vascular endothelial growth factors B and C (VEGF-B, VEGF-C)which are active in angiogenesis and endothelial cell growth, and placenta growth factor (PlGF) which is also active in angiogenesis. PDGF plays a role in embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis. PDGF is a required element in cellular division for fibroblast, a type of connective tissue cell. PDGF is also known to maintain proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Platelet-derived growth factor subunit B is also known as PDGFB, FLJ12858, PDGF2, SIS, SSV, c-sis, is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. PDGFB can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (PDGF-AB), where the dimers are connected by disulfide bonds. Mutations in this gene are associated with meningioma.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining











