分子别名(Synonym)
SHPS1,SIRPA,CD172A,BIT,MFR,MYD1,P84,PTPNS1
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag (SIA-H52A8) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Glu 31 - Arg 370 (Accession # NP_001035111).
Predicted N-terminus: Glu 31
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a mouse IgG1 Fc tag at the C-terminus
The protein has a calculated MW of 63.0 kDa. The protein migrates as 70-105 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 50 mM Tris, 100 mM Glycine, pH7.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
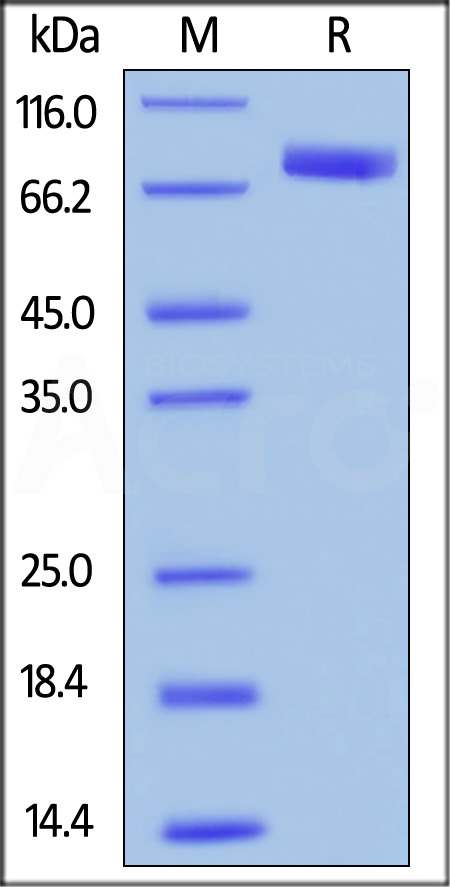
Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
SEC-MALS
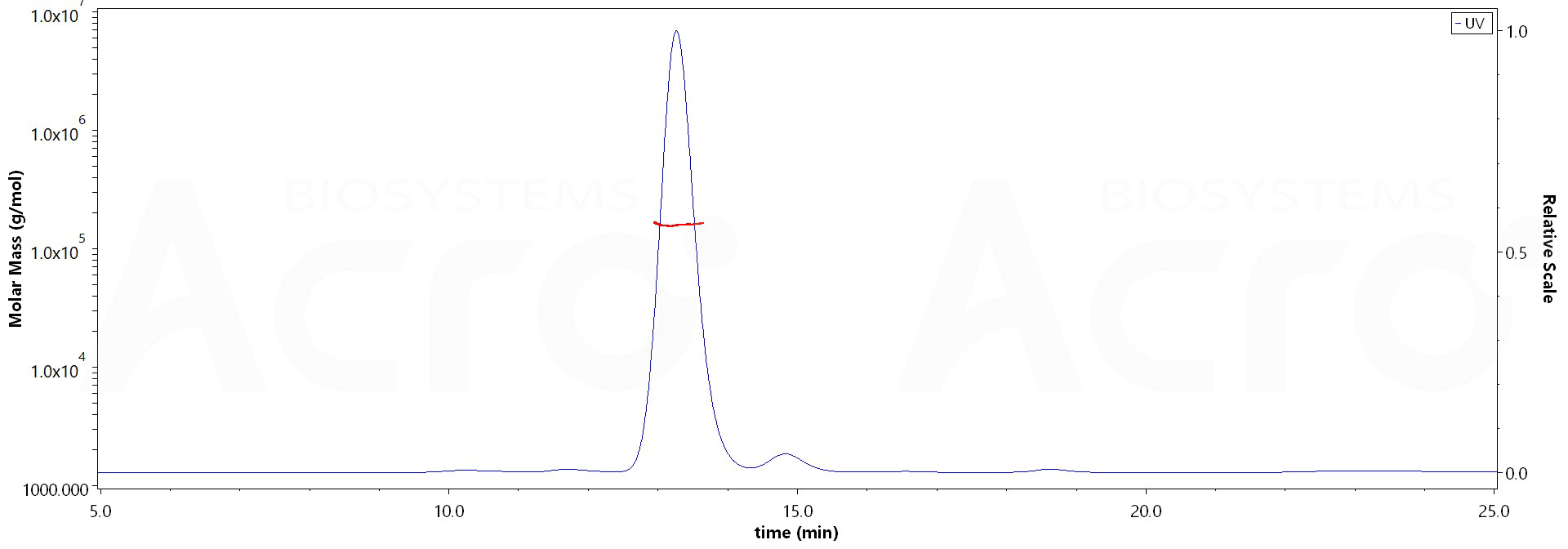
The purity of Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag (Cat. No. SIA-H52A8) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 140-165 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
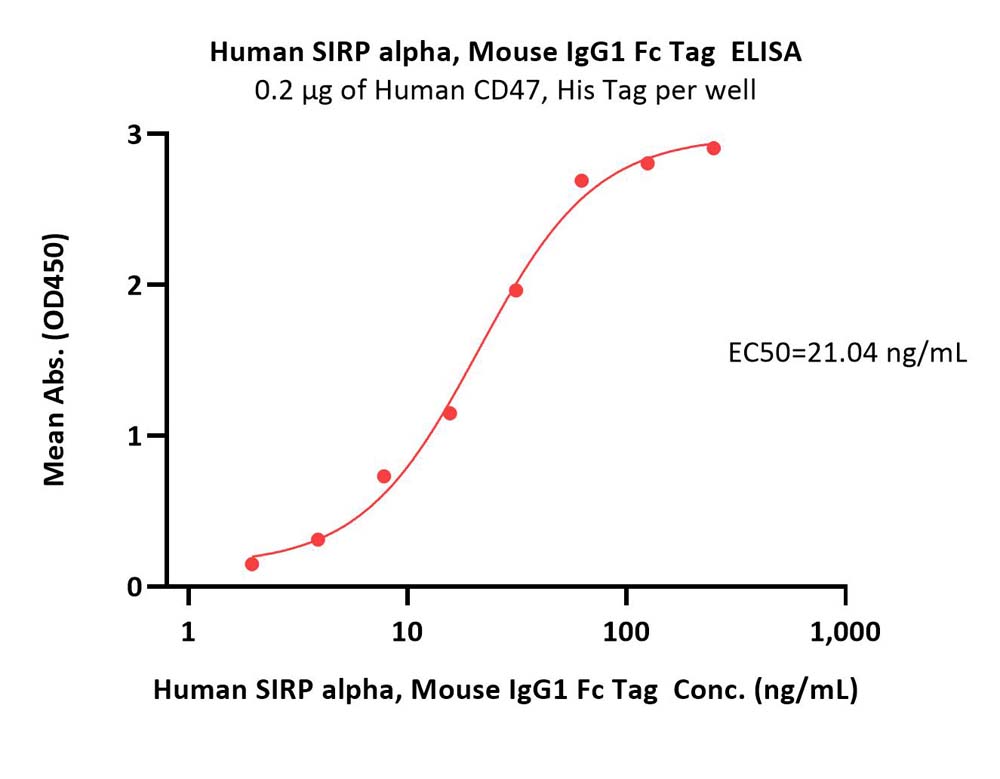
Immobilized Human CD47, His Tag (Cat. No. CD7-H5227) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag (Cat. No. SIA-H52A8) with a linear range of 4-31 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
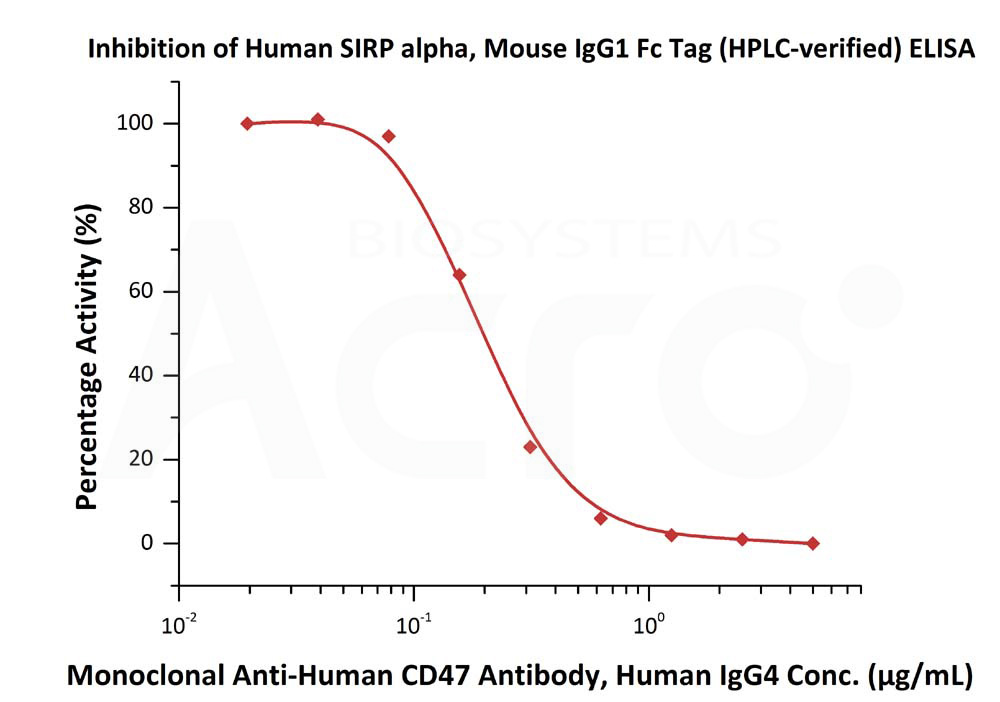
Serial dilutions of Anti-Human CD47 Neutralizing Antibody were added into Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag (Cat. No. SIA-H52A8): Biotinylated Human CD47, Fc,Avitag (Cat. No. CD7-H82F6) binding reactions. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 0.2006 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-FACS
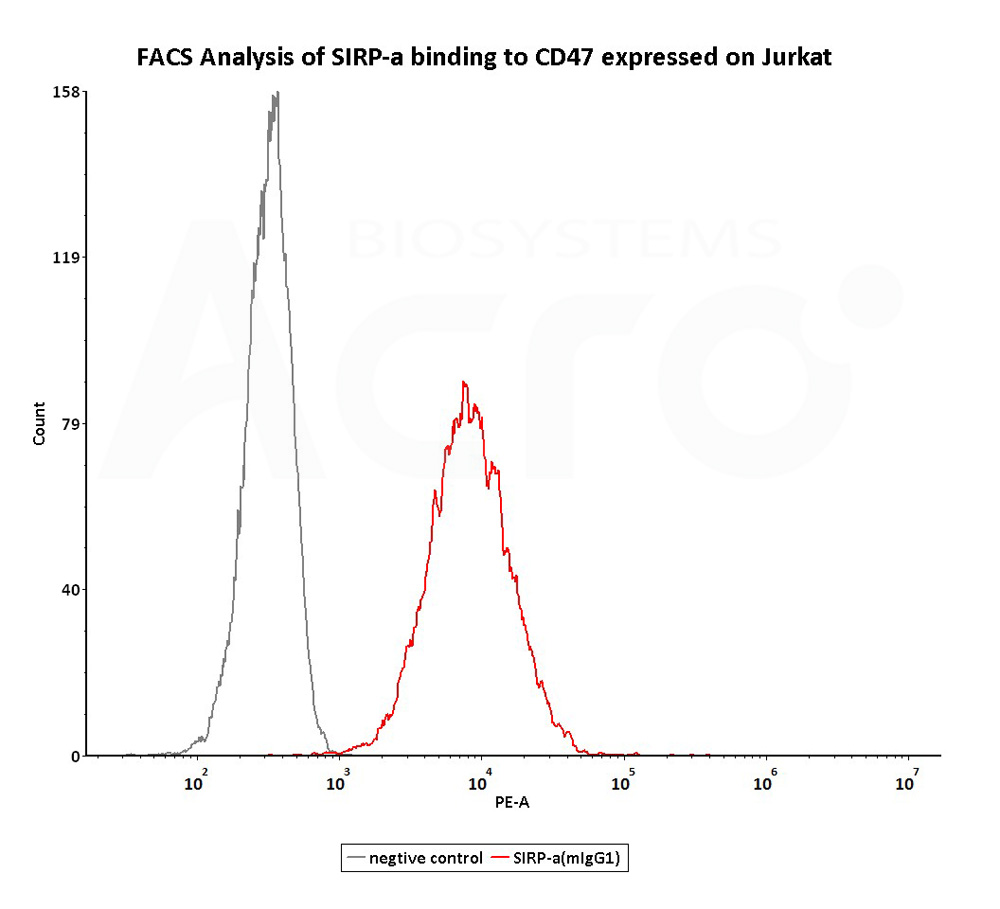
FACS assay shows that Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag (Cat. No. SIA-H52A8) can bind to Jurkat cell expressing CD47. The concentration of SIRP alpha used is 0.3 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
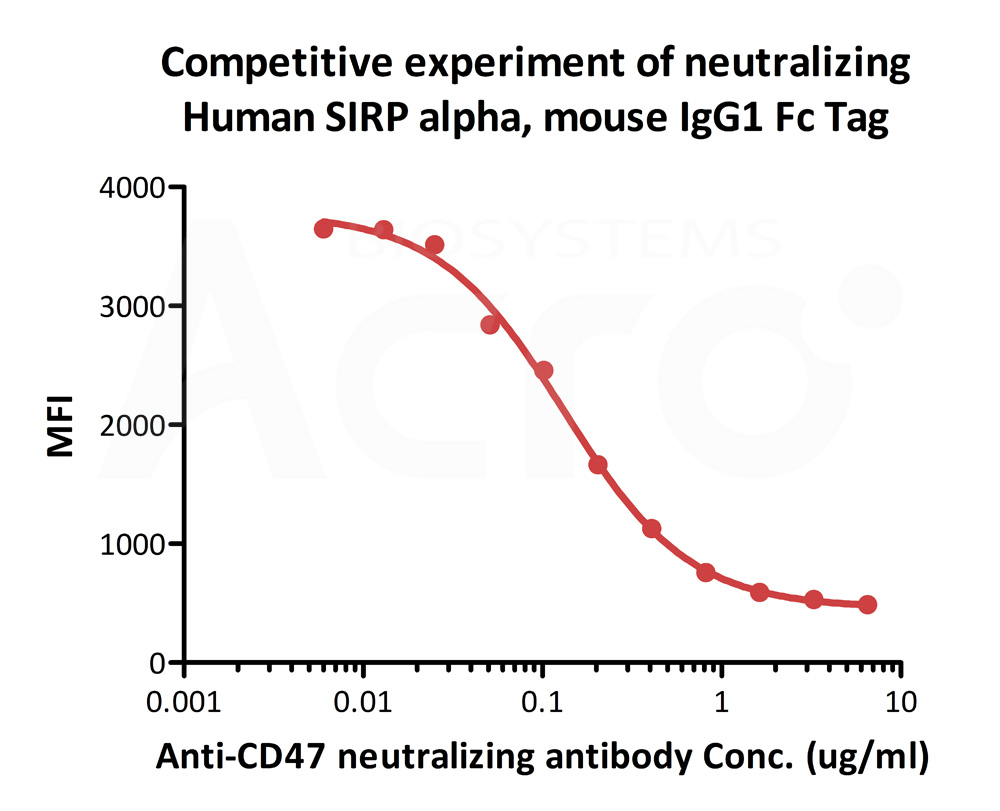
FACS analysis shows that the binding of Human SIRP alpha, Mouse IgG1 Fc Tag (Cat. No. SIA-H52A8) to Jurkat expressing CD47 was inhibited by increasing concentration of neutralizing anti-CD47 antibody. The concentration of SIRP alpha used is 0.3 μg/mL. IC50=0.1318 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论
- 173XXXXXXX3
- 该产品用于药物功能筛选实验, 与阳性对照抗体、CD47+细胞以及ACRO的CD47-biotin具有很好的亲和力,用该蛋白对成功建立稳定的结合测试体系与RBA测试体系。
- 2021-10-13
背景(Background)
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate 1 (SHPS1) is also known as CD172 antigen-like family member A (CD172a), Macrophage fusion receptor, MyD-1 antigen, Signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPA or SIRP alpha) or p84, is a member of the SIRP family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP alpha is Ubiquitous and highly expressed in brain. SIRPA / CD172a is immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor for CD47 and acts as docking protein and induces translocation of PTPN6, PTPN11 and other binding partners from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. SIRPA / SHPS-1 supports adhesion of cerebellar neurons, neurite outgrowth and glial cell attachment and may play a key role in intracellular signaling during synaptogenesis and in synaptic function By similarity. SIRPA / MyD1 involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled cellular responses induced by cell adhesion, growth factors or insulin and mediates negative regulation of phagocytosis, mast cell activation and dendritic cell activation. CD47 binding prevents maturation of immature dendritic cells and inhibits cytokine production by mature dendritic cells.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















