The Causal Relationships and Therapeutic Targets of Plasma Proteins in Ankylosing SpondylitisWen, Yang, Wang
et alBiomedicines (2025) 13 (2)
Abstract: Objective: The purpose of this study was to assess the causal effects of circulating plasma proteins on ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and to explore potential therapeutic targets. Methods: The study used protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs) for thousands of plasma proteins from nine genome-wide association studies (GWAS) as instrumental variables. The relationship between genetically predicted plasma proteins and AS was assessed through Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis. Further analyses, including colocalization analysis, Steiger filtering analysis, protein-altering variant assessment, protein-protein interaction (PPI), and pathway enrichment analysis, were conducted to validate the robustness and causal direction of the results, as well as to investigate the protein functions and potential drug targets. Results: Nine unique proteins were found to have strong causal associations with AS. Steiger filtering analysis confirmed that all associations identified by MR analysis have a direct causal link from the proteins to AS. Colocalization analysis identified four unique proteins-Interleukin-6 receptor alpha (IL-6Rα), Interleukin-23 receptor (IL-23R), Thrombospondin-2 (THBS2), and Interleukin-1 receptor type 2 (IL-1R2)-that share the same causal variants with AS. PPI and pathway enrichment analysis revealed the potential roles of these proteins in inflammatory responses and immune regulation. Moreover, these proteins were valuable drug targets or considered druggable. Conclusions: This study has identified multiple plasma proteins associated with AS, revealing the important roles of these proteins in the pathogenesis of AS and providing potential therapeutic targets for AS.
Pharmacogenomic insights: IL-23R and ATG-10 polymorphisms in Sorafenib response for hepatocellular carcinomaEl-Sheshtawy, Werida, Bahgat
et alClin Exp Med (2025) 25 (1), 51
Abstract: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer. Sorafenib is the first FDA-approved systemic therapy for advanced HCC. This study investigates the influence of IL-23R (rs7517847) and ATG-10 (rs10514231) genetic polymorphisms on Sorafenib response, survival outcomes, average tolerable dose, and adverse events. This prospective open-label cohort study included 100 HCC patients, assessing IL-23R and ATG-10 genotypes via real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Patient's responses were evaluated using modified RECIST criteria. Statistical analyses evaluated the association of genetic variants with response, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), average tolerable Sorafenib dose, and adverse events. IL-23R TT carriers had the highest Sorafenib response rate (80%) compared to GT (13.3%) and GG (6.7%) (P = 0.021), while ATG-10 TT carriers had a 13.9-fold increased response likelihood (P = 0.001). The T allele in ATG-10 significantly predicted longer PFS (P = 0.025) and OS (P = 0.011), suggesting a potential prognostic role. IL-23R GG carriers received significantly higher Sorafenib doses than TT (P = 0.0174) and GT (P = 0.0227), whereas ATG-10 had no effect on dosage. However, its CT genotype was significantly associated with a higher risk of Hand-Foot Syndrome (P = 0.012), and independent of dose (P = 0.0018). IL-23R and ATG-10 polymorphisms influence Sorafenib response, survival, and tolerability in HCC patients. Genetic screening may improve personalized treatment strategies by optimizing Sorafenib efficacy and minimizing toxicity.This trial was registered on clinicaltrials.gov with registration number NCT06030895, registered on "September 11th, 2023," retrospectively.© 2025. The Author(s).
IL-17A, IL-23R, FCGR3A are associated with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in pediatric patients with lupus nephritisYe, Chen, Zhang
et alCytokine (2025) 188, 156874
Abstract: To comprehensively investigate the impact of candidate loci on the susceptibility to neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) in a cohort of Chinese children with lupus nephritis (LN).This case-control study included sixty-two patients. And the case group consisted of 12 LN patients appearing NPSLE, while the control group consisted of 50 LN patients. A total of fifty-four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across twenty genes were genotyped using the Agena Bioscience MassArray iPLEX platform. The associations between susceptibility to NPSLE and candidate SNPs were assessed using SNPStats online software. We evaluated the influence of candidate SNPs on the risk of NPSLE through odds ratios (OR) and 95 % confidence intervals (CI). Additionally, linkage disequilibrium (LD) and coefficient (D' and r2) for haplotypes and their frequencies were performed using the genetic statistical online software SHEsis.Three significant SNPs were identified: IL17RA rs2895332, IL23R rs10889677, and FCGR3A rs396991. AA genotype of FCGR3A rs396991, GG genotype of IL17RA rs2895332 and AA genotype of IL23R rs10889677 exhibited a decreased risk of NPSLE compared to CA and CC genotypes, GA and AA genotypes, and CA and CC genotypes (rs396991 AA vs. CA-CC, OR 5.00, 95 %CI 0.99-25.17, P = 0.029; rs2895332 GG vs. GA-AA, OR 7.83, 95 %CI 1.47-41.79, P = 0.017; rs10889677 AA vs. CA-CC, OR 4.50, 95 %CI 1.08-18.69, P = 0.027). Furthermore, the haplotype A-T-G (STAT4 rs13426947, rs1551443 and rs3024866) appeared to confer protection against the development of NPSLE. The multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that two specific SNPs were significantly associated with an increased risk of NPSLE: [FCGR3A rs396991 (OR = 6.444, 95 %CI = 1.1-37.736, P = 0.039), IL17RA rs2895332 (OR = 0.128, 95 %CI = 0.017-0.963, P = 0.046)]. Notably, the RegulomeDB score of them reached 1 f. Using HaploReg, these loci were in strong LD (r2>0.8) with several SNPs.Our findings indicate that the polymorphisms IL17RA rs2895332, IL23R rs10889677, and FCGR3A rs396991 are significantly associated with the risk of NPSLE in childhood-onset LN.Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
IL-23 Promotes γδT Cell Activity in Dry Eye Disease ProgressionLi, Luo, Liu
et alInvest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (2025) 66 (2), 10
Abstract: Conjunctival-resident γδT cells, the predominant ocular source of interleukin-17A (IL-17A), play crucial roles in dry eye disease (DED) pathogenesis. The upstream regulators of these cells are unknown. This study evaluated the role of conjunctival IL-23 expression in mediating γδT cell generation and elucidated its contribution to dry eye inflammatory responses.Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was used to identify and quantify conjunctival mRNA molecules in γδT cells in mice. The IL-23 level increased in wild-type (WT) and decreased in γδT-deficient (TCRδ-/-) mice after dry eye was induced via an intelligently controlled environmental system (ICES). Flow cytometry and transcriptome sequencing were used to investigate the impact of the changes in IL-23 expression on human γδT cells.The expression of the IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) was greater in γδT cells than in other conjunctival cell types, such as CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and epithelial cells. An increase in IL-23 led to an increase in γδT cell density, which was proportional to dry eye severity. However, in the TCRδ-/- mice, the upregulation of IL-23 failed to increase the expression level of IL-17A and the severity of dry eye. Furthermore, increases in the expression of IL-23 and the number of γδT cells were evident in the ocular surface cells of patients who developed visual display terminal syndrome.An increase in conjunctival IL-23 expression contributes to the induction of the DED inflammatory response through interactions with its cognate receptor on γδT cells and the promotion of their proliferation. The findings of this study suggest that the suppression of IL-17A through the blockade of IL-23R activation may be a viable target for improving the management of inflammation in DED patients.
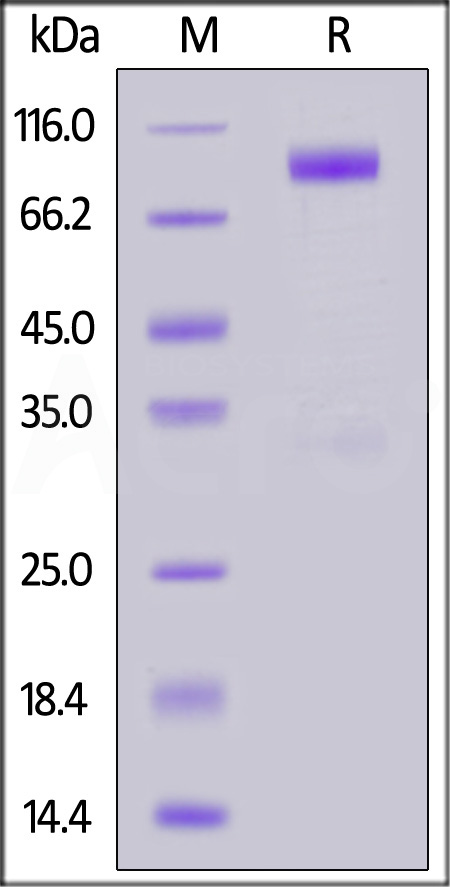


 +添加评论
+添加评论
























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















