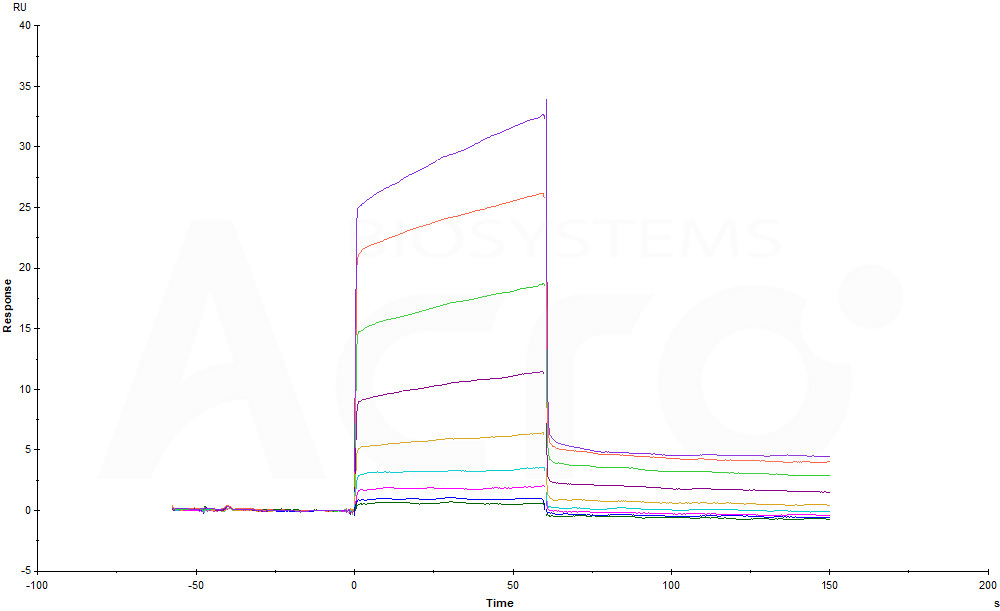
Circulating white blood cell traits, chemokines and small cell lung cancer risk: a Mendelian randomization studyZhu, Wang, Ma
Transl Cancer Res (2025) 14 (2), 1205-1213
Abstract: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) commonly originates in the context of persistent inflammation. The impact of white blood cell (WBC) counts and the presence of infiltrating inflammatory cytokines in relation to tumor initiation, progression, and treatment response in SCLC remains uncertain. To elucidate the potential relationships of circulating WBCs and chemokines with SCLC, we conducted a univariable (UVMR) and multivariable Mendelian randomization (MVMR) study.We conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) investigation to evaluate the causal impact of circulating WBCs and chemokines on the risk of SCLC. The genetic data for SCLC were derived from a genome-wide association study (GWAS) involving 24,108 participants, including 2,664 cases and 21,444 controls of European ancestry. The genetic variances of circulating WBCs and chemokines were also from GWAS. In the analysis of UVMR, the primary method employed was the inverse variance weighted (IVW) method. To infer causality, robust adjusted profile scores, weighted median (WM), and MR Egger were employed as supplementary methods. To ensure the robustness of the MR results, sensitivity analyses, including the Cochran Q test, Egger intercept test, and leave-one-out analysis, were conducted. Furthermore, MVMR was carried out to assess the direct causal effects of WBCs and chemokines on the risk of SCLC.Using two-sample MR, we found that genetic predisposition to CD45RA+ CD8+ T cell, CD39+ CD4+ T cell, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 (CXCL16) was associated with an increased risk of SCLC. There were suggestive inverse associations of genetically predicted dendritic cell, CD14- CD16+ monocyte, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) and C-C motif chemokine ligand 3 (CCL3) with SCLC risk. MVMR further confirmed that CXCL16 exerted a direct effect on SCLC, while CD14- CD16+ monocyte and PSGL-1 indicated that they are protective in SCLC.Using two-sample MR, we found that genetic predisposition to CD45RA+ CD8+ T cell, CD39+ CD4+ T cell, CXCL16 was associated with an increased risk of SCLC. There were suggestive inverse associations of genetically predicted dendritic cell, CD14- CD16+ monocyte, PSGL-1 and CCL3 with SCLC risk. MVMR further confirmed that CXCL16 exerted a direct effect on SCLC, while CD14- CD16+ monocyte and PSGL-1 indicated that they are protective in SCLC.Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Enhancing sickle cell leg ulcer healing with combined photodynamic and photobiomodulation therapies: A pilot experienceFortuna, Oliveira, Xavier
et alJ Tissue Viability (2025) 34 (2), 100879
Abstract: This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of combined photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photobiomodulation (PBM) in treating sickle cell leg ulcers (SCLUs), with a focus on pain reduction and enhanced healing.In this prospective, open-label, uncontrolled pilot study, ten SCD patients with 17 chronic leg ulcers received PDT and PBM treatments. Ulcer severity, pain levels, and microbiome changes were monitored, and clinical data were analyzed using appropriate statistical methods.Among the treated ulcers, 64.7 % (11 out of 17) showed significant healing, with 9 ulcers achieving complete closure. The average reduction in ulcer size was significant, with a median healing time of 123 days. Pain levels decreased significantly in 82.3 % of treated ulcers (p < 0.001), and a 75.4 % reduction in bacterial load was observed, alongside increased microbiome diversity (p < 0.05). Elevated levels of IL-6 and PSGL-1 were associated with non-healing ulcers, indicating their potential as prognostic biomarkers.The combined PDT and PBM therapy proved to be effective and safe for SCLUs, offering significant improvements in healing and pain reduction. These findings suggest that integrating PDT and PBM into standard care protocols could enhance the management of SCLUs.Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Charge matters: how flanking substrate charge modulates O-glycan Core elongationBallard, Smutny, Chau
et alGlycobiology (2025) 35 (5)
Abstract: Mucin type O-glycan core elongation is typically performed by the C1GALT1, B3GNT6, and ST6GalNAc-I/-II O-glycosyltransferases. These enzymes target the Tn antigen (GalNAc-O-Thr/Ser) dictating the fate of O-glycan elongation, playing important roles in health and disease. Changes in transferase expression and glycan structure are commonly associated with diseases such as cancer, Tn-syndrome, and ulcerative colitis. Despite their significance, their substrate specificities and their biological roles remain elusive. Here, we examine the roles of flanking glycopeptide substrate charge using a library of differently charged glycopeptides and a small library of PSGL-1 Thr57 based charged glycopeptides. We found that C1GALT1 was most influenced by flanking charge preferring negatively charged substrates, while B3GNT6 and ST6GalNAc-II were less influenced, showing unique N- and C-terminal charge preferences. Interestingly, ST6GalNAc-I was not influenced by flanking charge. These charge specificities were further maintained against the charged PSGL-1 glycopeptides, although ST6GalNAc-I showed an increased preference towards a remote N-terminal positive charge. The observed charge preferences were to a large part driven by substrate interactions with the electrostatic surface of the transferase. We propose that negative flanking charge may assist C1GALT1 in targeting key glycosites such as in PSGL-1 and podoplanin. Our findings are consistent with a Golgi hierarchy, where the cis-Golgi localized GalNAc-Ts and C1GALT1 determine the site and thus fate of glycosylation, while the trans-Golgi less-specific ST6GalNAc-I provides a final capping function. This characterization of substrate charge preference furthers our understanding of how these enzymes select their substrates and may contribute to our understanding of their biological roles.© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.



























 Star Ribbon预染蛋白Marker蛋白质标记物是生物研究和药物开发的重要组成部分。无论是用于蛋白质电泳还是western blot,我们的预染色蛋白质标记物帮助您快速确定目标蛋白质的分子量或评估转移效率。Fc受体蛋白治疗性抗体的功效取决于Fab片段及其对目标抗原的结合活性,还取决于Fc片段及其与关键Fc受体的相互作用。因此,在抗体工程中候选物必须针对一系列受体进行测试。探索我们的重组Fc受体蛋白质的全面收藏!
Star Ribbon预染蛋白Marker蛋白质标记物是生物研究和药物开发的重要组成部分。无论是用于蛋白质电泳还是western blot,我们的预染色蛋白质标记物帮助您快速确定目标蛋白质的分子量或评估转移效率。Fc受体蛋白治疗性抗体的功效取决于Fab片段及其对目标抗原的结合活性,还取决于Fc片段及其与关键Fc受体的相互作用。因此,在抗体工程中候选物必须针对一系列受体进行测试。探索我们的重组Fc受体蛋白质的全面收藏!


























 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining