FGF-8b分子别名
FGF8,Fibroblast growth factor 8,FGF-8,Androgen-induced growth factor,Heparin-binding growth factor 8 ,AIGF
FGF-8b分子背景
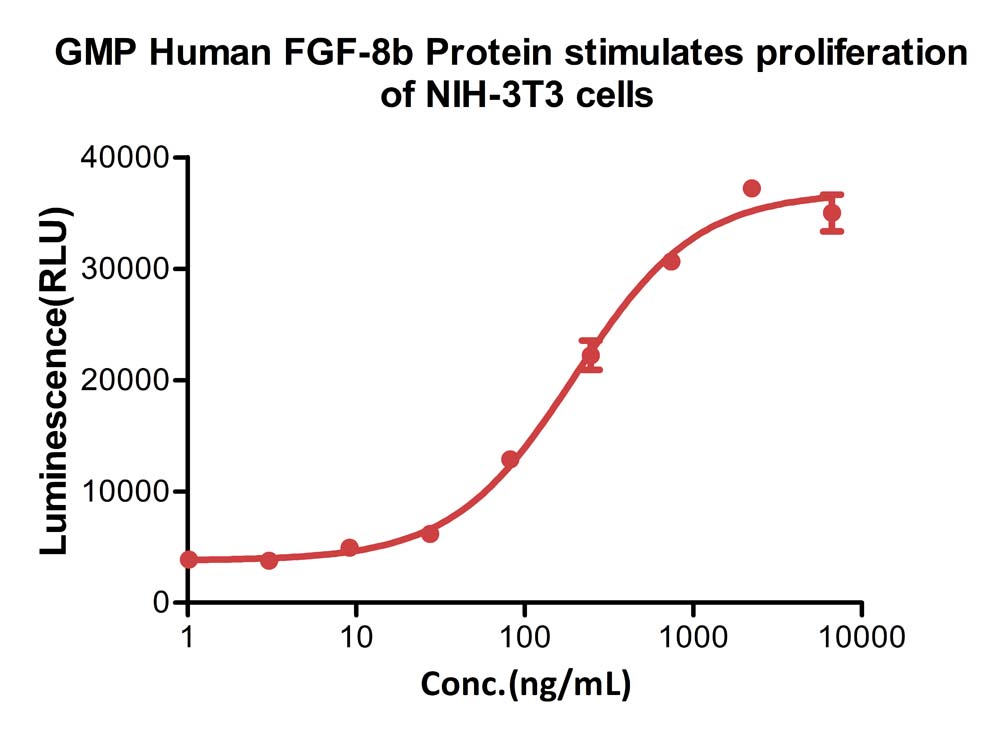
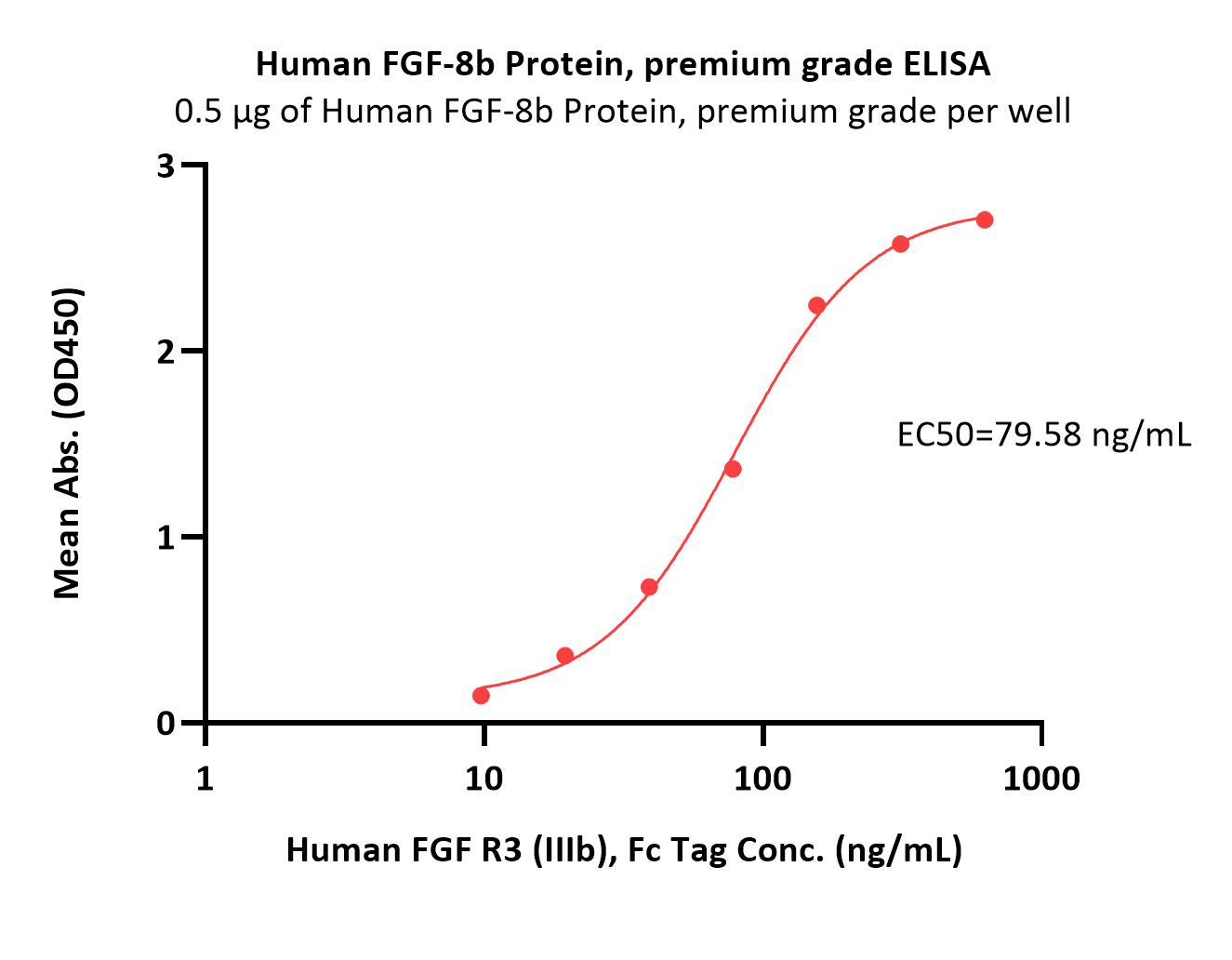
FGF-8 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family that was originally discovered as a growth factor essential for the androgen-dependent growth of mouse mammary carcinoma cells (1-3). Alternate splicing of mouse FGF-8 mRNA generates eight secreted isoforms, designated a-h, but only FGF-8a, b, e and f exist in humans (4). FGF-8 contains a 22 amino acid (aa) signal sequence, an N‑terminal domain that varies according to the isoform (30 aa for FGF-8b; 20 aa for the shortest, FGF-8a), a 125 aa FGF domain and a 37 aa proline‑rich C‑terminal sequence. The FGF domain of FGF-8 shares the most aa identity with FGF17 (75%) and FGF-18 (67%), and the three form an FGF subfamily (2). Mouse FGF-8b shares 100% aa identity with human FGF-8b. FGF-8 is widely expressed during embryogenesis, and mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. It plays an organizing and inducing role during gastrulation, and regulates patterning of the midbrain/hindbrain, eye, ear, limbs and heart in the embryo (2, 5 - 8). The isoforms may play different roles in development. FGF-8b shows the strongest receptor affinity and oncogenic transforming capacity although FGF-8a and FGF-8e are also transforming and have been found in human prostate, breast or ovarian tumors (1, 5, 9-12). FGF-8 shows limited expression in the normal adult, but low levels are found in the reproductive and genitourinary tract, peripheral leukocytes and bone marrow hematopoietic cells (3, 9, 13).






















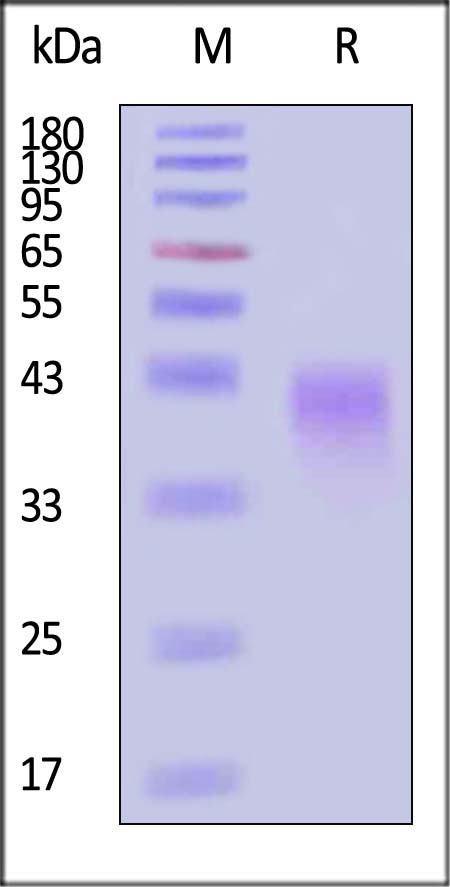
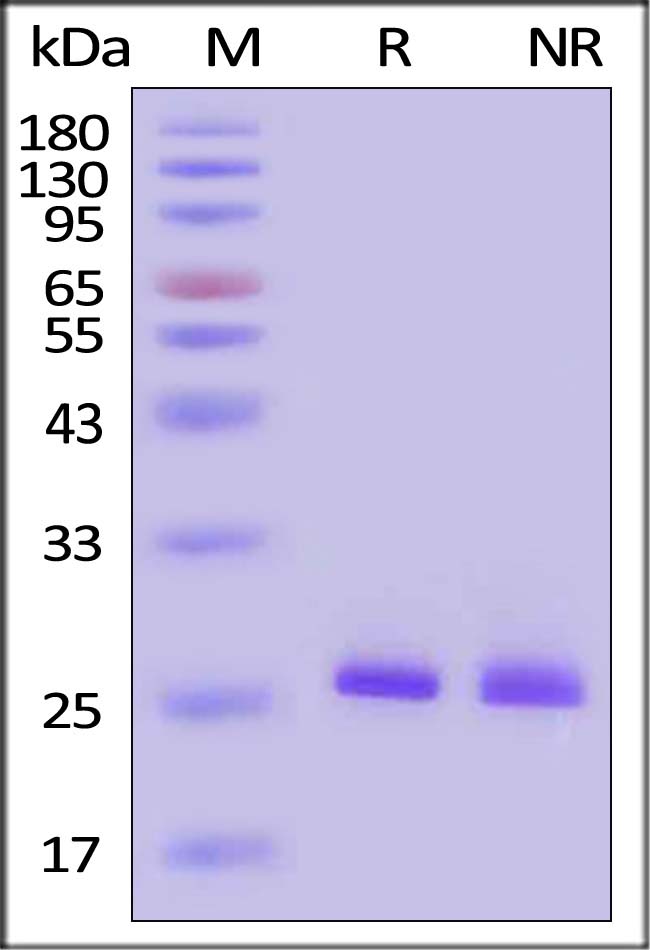
 Star Ribbon预染蛋白Marker蛋白质标记物是生物研究和药物开发的重要组成部分。无论是用于蛋白质电泳还是western blot,我们的预染色蛋白质标记物帮助您快速确定目标蛋白质的分子量或评估转移效率。Fc受体蛋白治疗性抗体的功效取决于Fab片段及其对目标抗原的结合活性,还取决于Fc片段及其与关键Fc受体的相互作用。因此,在抗体工程中候选物必须针对一系列受体进行测试。探索我们的重组Fc受体蛋白质的全面收藏!
Star Ribbon预染蛋白Marker蛋白质标记物是生物研究和药物开发的重要组成部分。无论是用于蛋白质电泳还是western blot,我们的预染色蛋白质标记物帮助您快速确定目标蛋白质的分子量或评估转移效率。Fc受体蛋白治疗性抗体的功效取决于Fab片段及其对目标抗原的结合活性,还取决于Fc片段及其与关键Fc受体的相互作用。因此,在抗体工程中候选物必须针对一系列受体进行测试。探索我们的重组Fc受体蛋白质的全面收藏!































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining