分子别名(Synonym)
HGF,HPTA,SF
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human HGF Protein, His Tag (HGF-H52H3) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Gln 32 - Ser 728 (Accession # P14210-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Gln 32
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The mature form of HGF is a disulfide-linked heterodimer composed of proteolytically cleaved α and β chain. The protein has a calculated MW of 81.6 kDa (α chain 53.7 kDa and β chain 27.9 kDa). The protein migrates as 80-90 kDa (alpha & Beta chain), 58-63 kDa (alpha chain), 33 kDa (Beta chain) when calibrated against Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 0.1 EU per μg by the LAL method.
无菌(Sterility)
Negative
支原体(Mycoplasma)
Negative.
纯度(Purity)
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
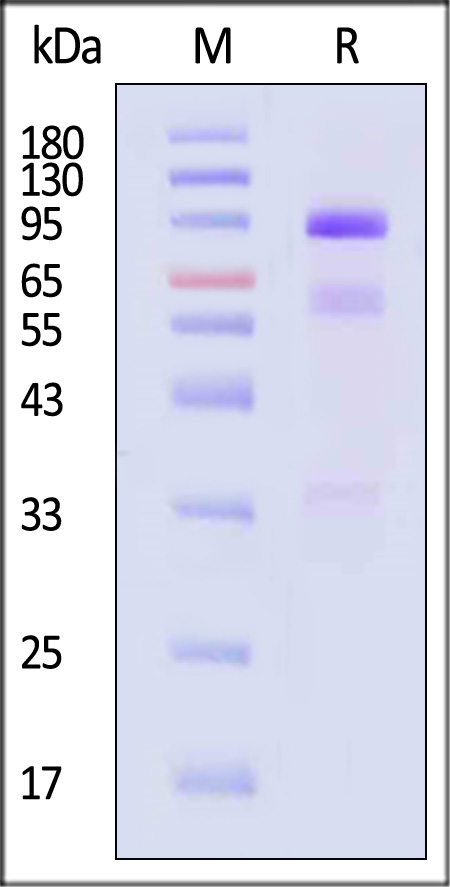
Human HGF Protein, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90% (With Star Ribbon Pre-stained Protein Marker).
SEC-MALS

The purity of Human HGF Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. HGF-H52H3) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 90-105 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-Organoid Culture

Human EGF (Cat. No. EGF-H52H3), Noggin (Cat. No. NON-H5257), R-spondin1 (Cat. No. RS6-H4220), FGF7 (Cat. No. FG7-H52H5), FGF10, HGF (Cat. No. HGF-H52H3) actively support liver ductal organoid growth.
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA

Immobilized Human HGF Protein, His Tag (Cat. No.HGF-H52H3 ) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human HGF R, Fc Tag (Cat. No. MET-H5256) with a linear range of 1-39 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-SPR
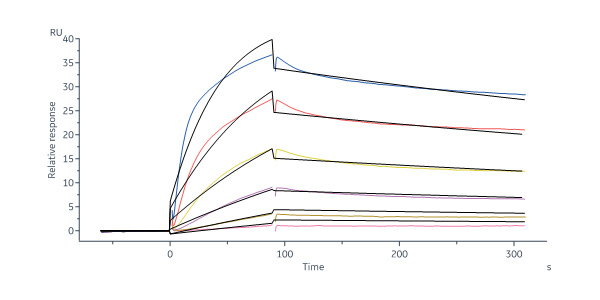
Human HGF R, Fc Tag (Cat. No. MET-H5256) captured on CM5 chip via Anti-human IgG Fc antibodies surface can bind Human HGF Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. HGF-H52H3) with an affinity constant of 0.486 nM as determined in a SPR assay (Biacore 8K) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-BLI

Loaded Human HGF R, Fc Tag (Cat. No. MET-H5256) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind Human HGF Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. HGF-H52H3) with an affinity constant of 3.29 nM as determined in BLI assay (ForteBio Octet Red96e) (Routinely tested).
Protocol
活性(Bioactivity)-Bioactivity CELL BASE

Human HGF Protein, His Tag (Cat. No. HGF-H52H3) stimulates the secrection IL-11 by Saos-2 cells. The specific activity of Human HGF Protein, His Tag is >6.00 x 10^5 IU/mg, which is calibrated against WHO Hepatocyte Growth Factor (precursor) (Human rDNA derived) (NIBSC code: 96/556) (QC tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论
- 188XXXXXXX9
- As a stimulating factor to activate the downstream signaling pathway, ACRO's products have great advantages in speed, and the delivery time is much shorter than that of foreign products, and the effect is good. I hope to continue to make high-quality products
- 2023-4-14

- 182XXXXXXX4
- This product has good specificity in PK experiments, and almost does not produce non-specific binding with plasma or serum, which guarantees the reliability and accuracy of experimental data
- 2023-5-9
背景(Background)
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a paracrine cellular growth, motility and morphogenic factor. Activating ligand for the receptor tyrosine kinase MET by binding to it and promoting its dimerization. Hepatocyte growth factor is secreted by mesenchymal cells and acts as a multi-functional cytokine on cells of mainly epithelial origin. Its ability to stimulate mitogenesis, cell motility, and matrix invasion gives it a central role in angiogenesis, tumorogenesis, and tissue regeneration. In addition, HGF has been implicated in a variety of cancers, including of the lungs, pancreas, thyroid, colon, and breast.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















