Erythroblastic Sarcoma in Adults and Children: Different Pathways to the Same DestinationFitzpatrick, Yuan, Capa
et alMod Pathol (2025)
Abstract: Erythroblastic sarcoma (ES), the mass-forming presentation of acute erythroid leukemia, is a rare and challenging diagnosis. Given the limited number of published cases, the diagnostic criteria, immunophenotype, and molecular characteristics are not well defined. We describe 56 cases of ES (36 adult and 11 pediatric cases from our cohort, and 9 pediatric cases from the literature). The median age was 60 years among adults and 1.8 years among children. An association with prior cytotoxic therapy or myeloid neoplasm was documented in 10/36 (28%) and 25/36 (69%) adults, respectively, but was not reported in children. Bones were the most common site of involvement among adults (16/36, 44%), whereas soft tissue or central nervous system involvement was most common among children (each 9/20, 45%). Adult and pediatric ES shared similar morphologic features with all cases showing mass formation of erythroblasts and/or involvement of body fluids. Immunophenotypic analysis showed that blasts were positive for CD71 (49/49, 100%), GLUT1 (12/12, 100%), CD43 (37/39, 95%), E-cadherin (38/44, 86%), and CD117 (39/51, 76%) but were mostly negative for CD45 (15/48, 31% positive). Strong and diffuse P53 expression was common among adults (21/24, 88%) and absent among children (3/10, 30% with dim/subset positivity). Although a complex karyotype was common in adult (15/17, 88%) and pediatric ES (8/12, 68%), TP53 mutations were exclusively seen in adult ES (17/19, 89%), at least 11 of which (65%) were biallelic. Instead, pediatric ES was enriched for gene fusions; specific fusions were identified in 10 cases, 7 of which involved NFIA rearrangement. The prognosis was poor among both age groups; 29/37 (78%) patients died from disease with a median overall survival of 3 months. Overall, these results show that adult and pediatric ES have overlapping morphologic and immunophenotypic features but distinct molecular profiles suggesting diverging pathogenesis.Published by Elsevier Inc.
Causal Effects of Inflammatory Cytokines and Immune Cell Phenotypes on Spontaneous Abortion: Evidence From Mendelian RandomizationLin, Tian, Kong
et alInt J Womens Health (2025) 17, 793-806
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the causal relationship between inflammatory cytokines, immune cells and spontaneous abortion (SA).A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses was conducted based on the genetic data of 91 inflammatory cytokines (n=14,824), 731 immune traits (n=3757) and SA (18,680 cases and 162,987 controls) cohorts. Five different MR analysis methods and Bayesian-weighted Mendelian randomization (BWMR) analysis were employed to assess the genetic causal connection. In addition, the robustness of this study results was ensured through comprehensive sensitivity analyses assessing heterogeneity, and potential horizontal pleiotropy and reverse causality.These MR results suggest that higher levels of two inflammatory cytokines and ten immune cells are associated with a lower risk of SA (OR < 1.00). In contrast, fifteen immune cell traits exhibit a positive relationship with SA risk (OR > 1.00). Notably, mediation analysis revealed that the causal effect of programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1) on SA was partially mediated by CD45 expression on Granulocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (GR-MDSCs), and Terminally Differentiated CD4⁻CD8⁻ T cells also acted as mediators in the causal effect of tumor necrosis factor-beta (TNF-β) on SA.This study comprehensively assessed the causal relationship between immune-related exposures and SA, identifying several immune factors associated with SA risk. These finding have implications for clinical guidance in pregnancy preparation.© 2025 Lin et al.
Treatment strategies for advanced synovial sarcoma: from chemotherapy to TCR-engineered T-cell therapyNakamura, Hasegawa
Int J Clin Oncol (2025)
Abstract: Synovial sarcoma (SS) is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in children and adolescents. Despite the availability of new agents such as pazopanib and trabectedin, the prognosis after recurrence remains poor. Adoptive cell therapy is an emerging therapeutic strategy based on the modulation, manipulation, and selection of autologous T-cells in vitro to overcome immune system tolerance to tumor cells. Cancer-testis antigens are particularly attractive targets for immune therapy because male germ cells lack human leukocyte antigen class I molecules, limiting T-cell responses triggered by antigen presentation. T-cell receptor (TCR) engineered T-cell therapy targeting NY-ESO-1 and MAGE-A4 holds significant promise because of the high positive expression of these antigens in tumors. This approach facilitates the reprogramming of T lymphocytes by a transgenic TCR through gene transfer of TCR α and β chains specific to tumor antigens, offering potential therapeutic advances for patients with advanced SS. Clinical trials of TCR-engineered T-cell therapy targeting NY-ESO-1 and MAGE-A4 have been conducted, with an objective response rate reported to be 40-60% across several trials. This promising efficacy suggests that TCR-engineered T-cell therapy could become an attractive novel therapeutic option for advanced SS, which has limited treatment options in later stages. However, if TCR-engineered T-cell therapy is to be used in clinical practice, the standard approach following the failure of doxorubicin-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced SS must be defined. Future studies will be critical for establishing treatment strategies in this field.© 2025. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Japan Society of Clinical Oncology.
Diffusion and contrast-enhancement MRI phenotypes associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor exposure and with immune cell infiltration in brain metastasesSanvito, Nocera, Wang
et alNeuro Oncol (2025)
Abstract: MRI-derived apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and contrast-enhancement (CE) may represent non-invasive biomarkers to evaluate microstructural tissue changes and histopathological immune cell infiltration induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI).125 lesions across 93 patients were analyzed. ADC (reflecting water diffusivity) and CE T1-subtraction maps (reflecting blood-brain barrier permeability) tumor values were used for bivariate histograms of ADC and CE, and to quantify voxel fractions belonging to highADC-highCE and lowADC-lowCE quadrants. The association between ICI exposure and voxel frequency in ADC-CE quadrants was evaluated with multivariate mixed-effects models accounting for corticosteroid exposure and other variables. In a subset of patients (n=23), the association between immune cell counts (CD45+ cell density) from tissue samples and ADC-CE phenotypes was tested.ICI and corticosteroid exposure were associated with distinct ADC-CE phenotypes on bivariate histograms. ICI-exposed lesions showed significantly higher voxel frequency in the highADC-highCE quadrant (p<0.001) and lower voxel frequency in the lowADC-lowCE quadrant (p<0.01), compared to ICI-naïve lesions. Multivariate analyses confirmed that ICI exposure was an independent determinant of higher voxel frequency in the highADC-highCE quadrant (p=0.001) and lower voxel frequency in the lowADC-lowCE quadrant (p=0.01) in absence of corticosteroid treatment. Corticosteroid usage significantly influenced the relationship between ADC-CE phenotypes and ICI exposure. Voxel frequency in ADC-CE quadrants was correlated with CD45+ cell density in histopathology (partial ρ=0.56 p=0.01 for highADC-highCE, partial ρ=-0.64 p<0.01 for lowADC-lowCE).ADC-CE phenotypes are associated with ICI exposure and immune cell infiltration in BM, representing potential non-invasive markers to monitor ICI-induced pathophysiological changes.© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.
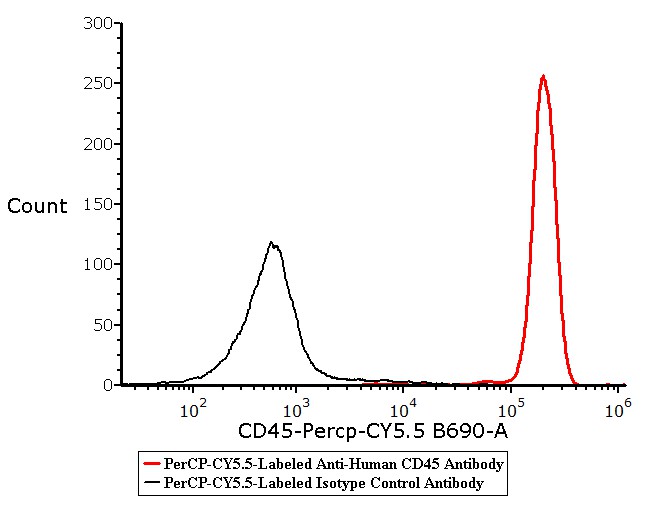























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining
















