分子别名(Synonym)
SIGLEC6,CD327,CD33L,CD33L1,OBBP1,OB-BP1,CDw327
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human Siglec-6, Fc Tag (SI6-H5256) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Gln 16 - Val 320 (Accession # AAH35359).
Predicted N-terminus: Gln 16
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a human IgG1 Fc tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 60.3 kDa. The protein migrates as 80-100 kDa under reducing (R) condition, and 130-150 kDa and 250-300 kDa under non-reducing (NR) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 50 mM Tris, 100 mM Glycine, 150 mM NaCl, pH7.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
质量管理控制体系(QMS)
电泳(SDS-PAGE)

Human Siglec-6, Fc Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
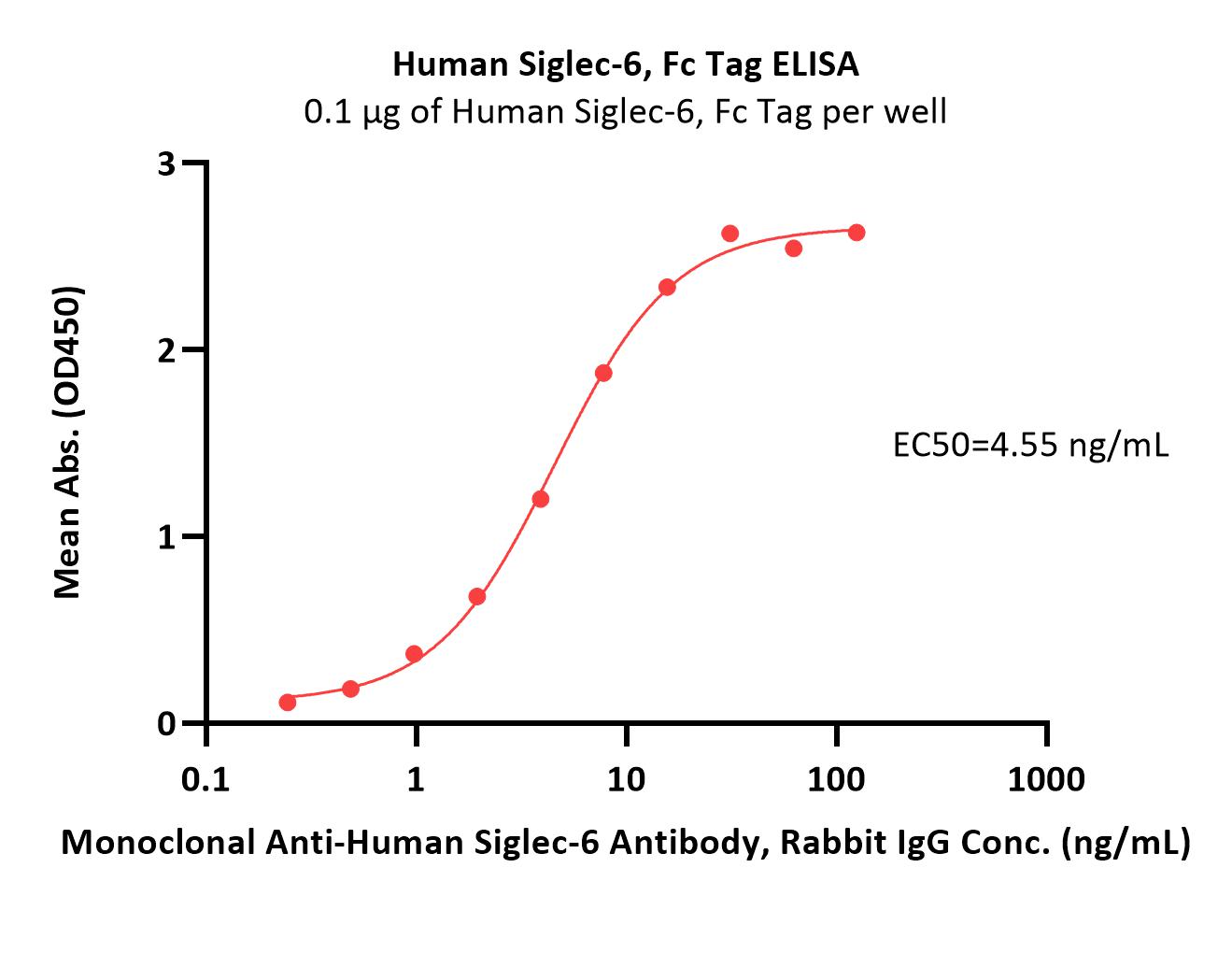
Immobilized Human Siglec-6, Fc Tag (Cat. No. SI6-H5256) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-Human Siglec-6 Antibody, Rabbit IgG with a linear range of 0.2-16 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
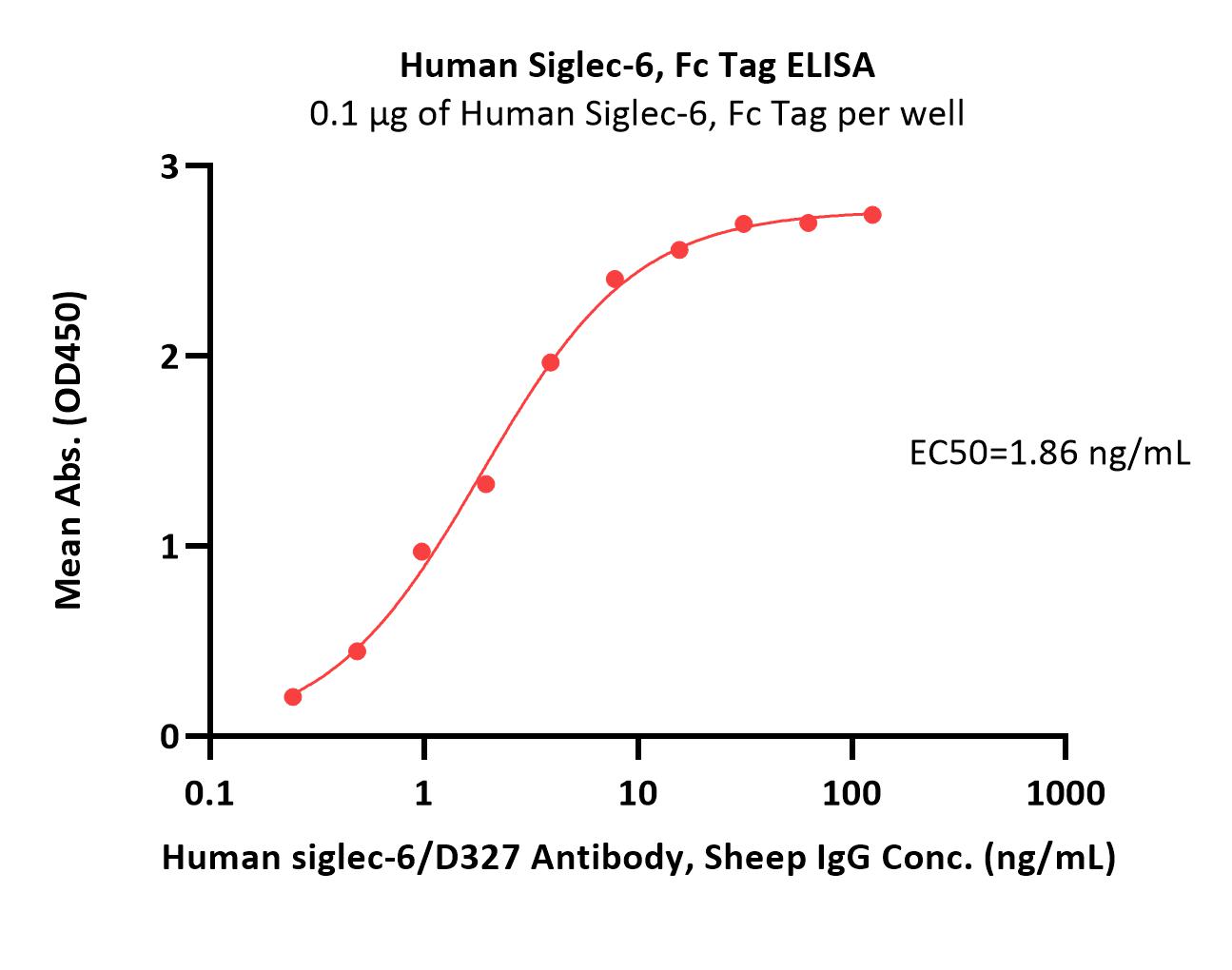
Immobilized Human Siglec-6, Fc Tag (Cat. No. SI6-H5256) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Human siglec-6/D327 Antibody, Sheep IgG with a linear range of 0.2-8 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
Protocol
 +添加评论
+添加评论
- 619XXXXXXX
- The item was expedited very quickly which worked out with our timeline. We are in the process of using the Siglec-6 protein in one of our in-vivo study for immunization. The material itself did not dissolve in complete freund's adjuvant but it was easily made into a fine suspension with the help of some PBS. Overall, I would say the material is easy to work with and the Acro is quick at responding if we have any issues.
- 2022-7-12
背景(Background)
Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 6 (SIGLEC6) is also known as CD antigen CD327, CD33 antigen-like 1 (CD33L or CD33L1), Obesity-binding protein 1 (OB-BP1). SIGLEC6 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and SIGLEC (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin) family, which contains two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains and one Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. SIGLEC6 mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. SIGLEC6 binds to alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining

















